The public sector plays a crucial role in providing essential services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure that support societal well-being and economic stability. Efficient management and transparent governance within the public sector enhance service delivery and build public trust. Explore the rest of the article to understand how the public sector impacts your daily life and the economy.
Table of Comparison
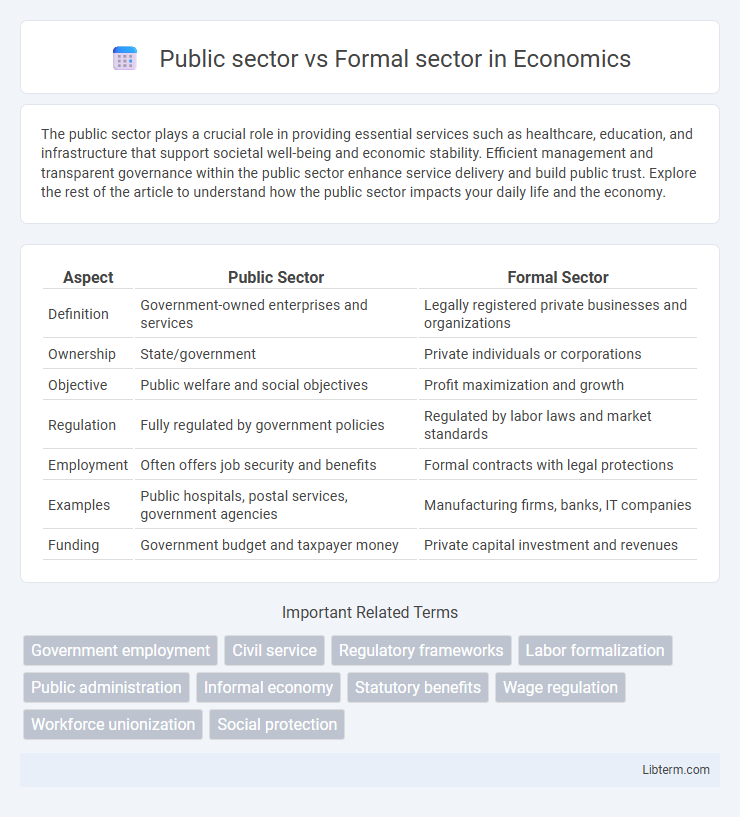
| Aspect | Public Sector | Formal Sector |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Government-owned enterprises and services | Legally registered private businesses and organizations |
| Ownership | State/government | Private individuals or corporations |
| Objective | Public welfare and social objectives | Profit maximization and growth |
| Regulation | Fully regulated by government policies | Regulated by labor laws and market standards |
| Employment | Often offers job security and benefits | Formal contracts with legal protections |
| Examples | Public hospitals, postal services, government agencies | Manufacturing firms, banks, IT companies |
| Funding | Government budget and taxpayer money | Private capital investment and revenues |
Introduction to Public and Formal Sectors
The public sector comprises government-owned organizations and agencies delivering essential services such as healthcare, education, and infrastructure. The formal sector includes legally registered businesses and enterprises operating within established regulatory frameworks, ensuring labor rights and tax compliance. Both sectors play vital roles in economic development, with the public sector focusing on public welfare and the formal sector driving economic growth and job creation.
Defining the Public Sector
The public sector encompasses government-owned organizations and agencies responsible for providing essential services such as education, healthcare, and public safety, funded primarily through taxation. It operates with the primary goal of serving the public interest rather than generating profit, contrasting with the formal sector that includes private businesses engaged in commercial activities. Public sector institutions play a crucial role in regulating the economy, maintaining law and order, and delivering social welfare programs.
Understanding the Formal Sector
The formal sector consists of businesses and organizations officially registered with the government, complying with labor laws, taxation, and social security regulations. It provides legal protection to workers, ensures systematic record-keeping, and facilitates access to credit and government services. Unlike the public sector, which includes government-operated entities, the formal sector primarily comprises private enterprises and industries operating within regulated frameworks.
Key Differences Between Public and Formal Sectors
The public sector consists of government-controlled organizations providing public services, while the formal sector includes private businesses operating within legal and regulatory frameworks. Public sector entities prioritize social welfare and public interest, whereas formal sector companies focus on profit generation and market competition. Employment in the public sector often offers more job security and benefits compared to the formal sector, which typically demands higher efficiency and productivity standards.
Employment Opportunities in Each Sector
The public sector primarily offers employment in government agencies, educational institutions, and healthcare services, providing job stability and benefits often backed by state funding. The formal sector includes all registered enterprises and officially recognized businesses, spanning industries like manufacturing, finance, and retail, where employees typically receive regulated wages and social security. Employment opportunities in the public sector often prioritize policy implementation and public welfare, while the formal sector focuses on economic growth and private enterprise development, resulting in diverse job roles and career progression paths.
Governance and Regulation
The public sector operates under stringent government governance and regulatory frameworks designed to ensure transparency, accountability, and public welfare. Formal sector enterprises adhere to established labor laws, tax regulations, and compliance standards enforced by regulatory bodies, promoting legal business practices and economic stability. Effective regulation in both sectors fosters trust, enhances service delivery, and supports sustainable development within the economy.
Wage Structures and Benefits Comparison
Public sector wage structures typically feature standardized pay scales based on seniority and qualifications, ensuring transparent and equitable compensation across roles. Benefits in the public sector often include comprehensive health insurance, pension plans, job security, and paid leave, which are more robust compared to the formal private sector. Formal sector wages vary more significantly with market conditions, performance, and industry, and benefits packages may be less consistent, often reflecting company policies and financial capacity.
Job Security and Career Growth
Public sector jobs typically offer higher job security due to government backing and stable funding, reducing the risk of layoffs compared to the formal sector. Career growth in the public sector often follows a structured, promotion-based system with clear hierarchies, while the formal sector provides faster advancement opportunities driven by performance and market demand. Employees in the formal sector benefit from dynamic skill development and competitive salary increments, whereas public sector roles emphasize long-term stability and pension benefits.
Challenges Faced by Both Sectors
The public sector faces challenges such as bureaucratic inefficiencies, limited budget allocations, and political interference that hinder optimal service delivery. The formal sector struggles with regulatory compliance costs, labor market rigidity, and difficulties in adapting to rapid technological changes. Both sectors must address issues related to workforce skills gaps and maintaining transparency to improve operational effectiveness.
Conclusion: Choosing Between Public and Formal Sectors
Choosing between the public sector and the formal sector depends largely on individual career goals, job stability, and desired work culture. The public sector often provides greater job security, structured benefits, and opportunities for public service impact. The formal sector typically offers higher salary potential, innovation-driven environments, and faster career progression, making careful evaluation essential for aligning personal priorities with sector characteristics.
Public sector Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com