Information economics examines how information asymmetry impacts economic decisions and market outcomes, influencing pricing, contracts, and resource allocation. It explores issues like adverse selection, moral hazard, and signaling within various industries and marketplaces. Discover how understanding these concepts can enhance your decision-making by reading the full article.
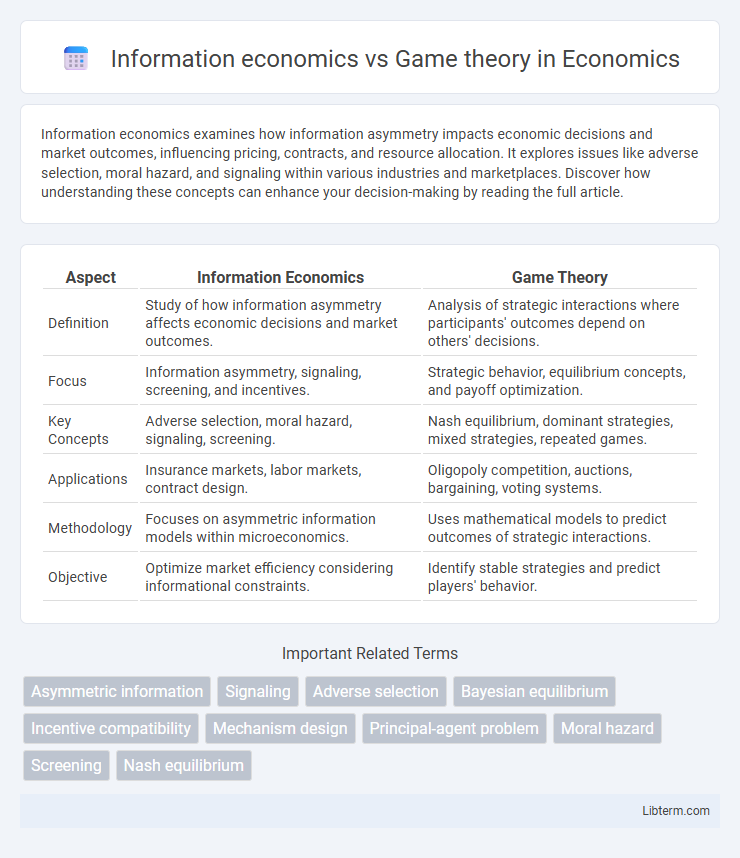
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Information Economics | Game Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of how information asymmetry affects economic decisions and market outcomes. | Analysis of strategic interactions where participants' outcomes depend on others' decisions. |
| Focus | Information asymmetry, signaling, screening, and incentives. | Strategic behavior, equilibrium concepts, and payoff optimization. |
| Key Concepts | Adverse selection, moral hazard, signaling, screening. | Nash equilibrium, dominant strategies, mixed strategies, repeated games. |
| Applications | Insurance markets, labor markets, contract design. | Oligopoly competition, auctions, bargaining, voting systems. |
| Methodology | Focuses on asymmetric information models within microeconomics. | Uses mathematical models to predict outcomes of strategic interactions. |
| Objective | Optimize market efficiency considering informational constraints. | Identify stable strategies and predict players' behavior. |
Introduction to Information Economics and Game Theory
Information economics studies how information asymmetry affects economic decision-making and market outcomes, emphasizing concepts like adverse selection and moral hazard. Game theory analyzes strategic interactions among rational agents, exploring equilibrium concepts such as Nash equilibrium to predict behavior in competitive and cooperative scenarios. Both fields intersect to address how information availability influences strategic decision-making in economics and beyond.
Defining Information Economics: Key Concepts and Applications
Information economics analyzes how information asymmetry impacts decision-making, market behavior, and economic outcomes, emphasizing concepts like adverse selection, moral hazard, and signaling. It applies to insurance markets, contract design, and financial markets where parties possess unequal information, influencing incentives and risk distribution. This discipline differs from game theory by focusing on informational structures rather than strategic interactions, yet often intersects when modeling economic agents' behaviors under uncertainty.
Fundamentals of Game Theory: Strategies and Payoffs
Game theory fundamentally analyzes strategic interactions where players choose actions to maximize their payoffs under conditions of uncertainty and interdependence. Key concepts include strategies, which are defined plans of action, and payoffs, representing the outcomes' values for each player based on the strategy profile. This contrasts with information economics, which emphasizes the role of information asymmetry and incentive structures, but both fields intersect in studying decision-making and strategic behavior.
Similarities Between Information Economics and Game Theory
Information economics and game theory both analyze strategic decision-making under conditions of uncertainty and asymmetric information. Both fields utilize models of players or agents who have private information influencing their choices and the resulting outcomes. These disciplines share common tools such as signaling, screening, and incentive compatibility to understand behavior and optimize resource allocation.
Key Differences: Information Asymmetry vs Strategic Behavior
Information economics centers on information asymmetry, where one party possesses more or better information than another, leading to market inefficiencies and adverse selection problems. Game theory examines strategic behavior among rational agents who anticipate others' actions and adjust their strategies accordingly in competitive or cooperative settings. While information economics highlights the impact of hidden or unequal information, game theory focuses on predicting outcomes based on strategic interactions and decision-making processes.
Role of Information in Economic Decision-Making
Information economics studies how information asymmetry affects market outcomes and influences pricing, contracts, and resource allocation, highlighting the impact of private and public information on economic efficiency. Game theory analyzes strategic interactions where players have different information sets, emphasizing how information availability and credibility shape equilibrium strategies and decision-making under uncertainty. Both fields underscore the critical role of information in optimizing economic decisions and predicting agents' behavior in competitive and cooperative environments.
Game Theory’s Approach to Uncertainty and Information
Game theory addresses uncertainty and information by modeling strategic interactions where players have incomplete or asymmetric knowledge about others' choices, payoffs, or types. It uses concepts like Bayesian games and signaling to analyze how players form beliefs, update information, and make decisions under uncertainty. This approach captures the dynamics of private information, revealing optimal strategies in competitive and cooperative environments.
Real-World Applications: Markets and Strategic Interactions
Information economics examines how information asymmetry impacts market behavior, pricing, and contract design, influencing sectors like insurance, finance, and labor markets. Game theory models strategic interactions among rational agents, providing insights into competitive behavior, negotiation, and regulatory policies in markets such as auctions, oligopolies, and voting systems. Together, these disciplines enhance understanding of decision-making processes and optimize outcomes in real-world economic environments.
Challenges and Limitations in Information Economics and Game Theory
Information economics faces challenges such as asymmetric information, adverse selection, and moral hazard, which complicate market efficiency and lead to suboptimal outcomes. Game theory struggles with limitations including assumptions of rationality, difficulties in predicting equilibrium in complex or dynamic games, and challenges in modeling incomplete information scenarios accurately. Both fields must address the complexity of human behavior and imperfect information to improve predictive power and real-world applicability.
Future Directions in Information Economics and Game Theory
Future directions in information economics emphasize the integration of machine learning algorithms to enhance decision-making under uncertainty and the development of dynamic contract theories addressing real-time data flow. Game theory research focuses on expanding models to incorporate behavioral economics insights and the impact of digital platforms on strategic interactions. Both fields converge on advancing computational tools for predictive analytics and adaptive strategies in complex economic environments.
Information economics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com