Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country over a specific period, reflecting economic health and growth. Understanding GDP helps you assess a nation's economic performance and compare it with other economies. Explore the rest of the article to learn how GDP impacts your financial decisions and global markets.
Table of Comparison
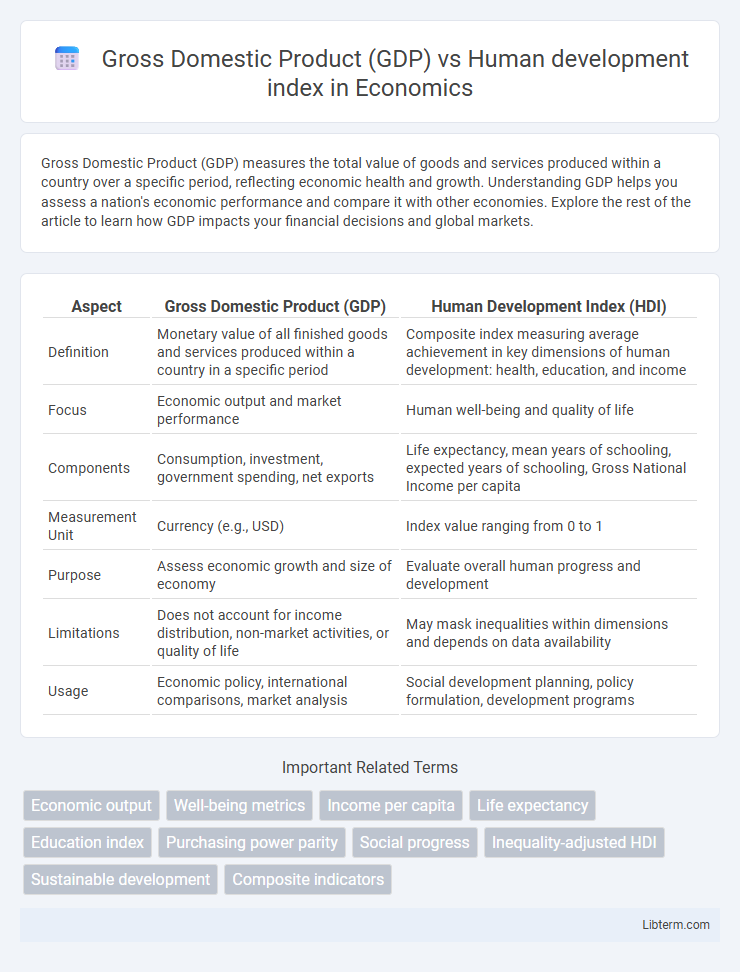
| Aspect | Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | Human Development Index (HDI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within a country in a specific period | Composite index measuring average achievement in key dimensions of human development: health, education, and income |
| Focus | Economic output and market performance | Human well-being and quality of life |
| Components | Consumption, investment, government spending, net exports | Life expectancy, mean years of schooling, expected years of schooling, Gross National Income per capita |
| Measurement Unit | Currency (e.g., USD) | Index value ranging from 0 to 1 |
| Purpose | Assess economic growth and size of economy | Evaluate overall human progress and development |
| Limitations | Does not account for income distribution, non-market activities, or quality of life | May mask inequalities within dimensions and depends on data availability |
| Usage | Economic policy, international comparisons, market analysis | Social development planning, policy formulation, development programs |
Understanding Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within a country's borders over a specific period, serving as a key indicator of economic activity and market performance. Unlike the Human Development Index (HDI), which incorporates health, education, and income dimensions to assess overall societal well-being, GDP focuses solely on economic output without directly addressing quality of life factors. Understanding GDP helps economists and policymakers evaluate economic growth, make fiscal decisions, and compare economies globally based on production and consumption levels.
What is the Human Development Index (HDI)?
The Human Development Index (HDI) is a composite statistic used to measure a country's average achievements in three basic aspects of human development: health, education, and standard of living. Unlike Gross Domestic Product (GDP), which focuses solely on economic output, HDI incorporates life expectancy, mean years of schooling, and gross national income per capita to provide a more comprehensive assessment of well-being. This index enables comparisons of social and economic development levels across countries, highlighting overall quality of life beyond mere economic performance.
Key Components of GDP
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures economic performance through key components: consumption, investment, government spending, and net exports, offering a quantitative snapshot of a country's economic activity. Unlike the Human Development Index (HDI), which incorporates indicators like life expectancy, education, and per capita income to assess overall well-being, GDP strictly quantifies market transactions and economic output. Understanding GDP's components helps analyze production, expenditure patterns, and economic growth, whereas HDI provides a broader view of human progress and quality of life.
Major Indicators in HDI
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the economic output of a country but does not account for social well-being factors, which are core to the Human Development Index (HDI). The HDI incorporates major indicators such as life expectancy at birth, mean years of schooling, expected years of schooling, and Gross National Income (GNI) per capita to provide a composite measure of a country's development. These indicators reflect health, education, and standard of living, offering a more comprehensive assessment of human progress beyond purely economic metrics.
Differences Between GDP and HDI
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the total economic output of a country and reflects its economic performance, while the Human Development Index (HDI) evaluates broader aspects like life expectancy, education, and per capita income to assess overall human well-being. GDP emphasizes quantitative economic activity, whereas HDI incorporates qualitative factors affecting quality of life and social progress. Unlike GDP, HDI provides a more comprehensive perspective on development by integrating health, knowledge, and living standards indicators.
Limitations of GDP as a Measure
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures economic output but fails to account for income inequality, environmental degradation, and overall quality of life. Unlike the Human Development Index (HDI), which incorporates health, education, and living standards, GDP overlooks social and well-being factors. This limitation makes GDP an incomplete indicator for assessing a country's comprehensive development and human welfare.
Limitations of HDI as a Measure
The Human Development Index (HDI) has limitations such as its inability to capture income inequality, cultural factors, and political freedoms, which are critical for comprehensive development assessment. Unlike GDP, which quantifies economic output, HDI combines life expectancy, education, and per capita income but oversimplifies complex human development dimensions. This can lead to misleading conclusions about a country's true progress and well-being.
Real-World Examples: GDP vs HDI Rankings
Singapore ranks highly in GDP per capita due to its robust economy and global trade networks, yet its Human Development Index (HDI) score reflects not only income but also education and healthcare quality, ranking it slightly differently. Norway consistently tops the HDI rankings, demonstrating that high life expectancy, education, and income contribute to human development beyond GDP measures alone. In contrast, countries like Qatar exhibit very high GDP per capita driven by natural resources but have HDI scores that highlight gaps in social factors relative to economic wealth.
The Role of GDP and HDI in Policy Making
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) serves as a key economic indicator measuring a country's total economic output, guiding policymakers in fiscal and monetary decisions to promote growth. The Human Development Index (HDI), encompassing health, education, and income, provides a broader perspective for long-term social policy planning by highlighting disparities in living standards. Integrating GDP with HDI enables governments to design balanced policies that foster economic expansion while improving human welfare and social equity.
Moving Toward Comprehensive Development Metrics
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures economic output, while the Human Development Index (HDI) assesses broader well-being by combining income, education, and health indicators. Moving toward comprehensive development metrics involves integrating economic performance with social and human capital factors to better capture quality of life and equitable progress. This holistic approach enables policymakers to design strategies that foster sustainable development beyond mere economic growth.
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com