Intra-firm trade involves the exchange of goods and services between different branches or subsidiaries of the same multinational company, often spanning multiple countries. This type of trade plays a crucial role in global supply chains, affecting pricing strategies, tax planning, and regulatory compliance. Discover how intra-firm trade impacts your business operations and the broader economy in the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
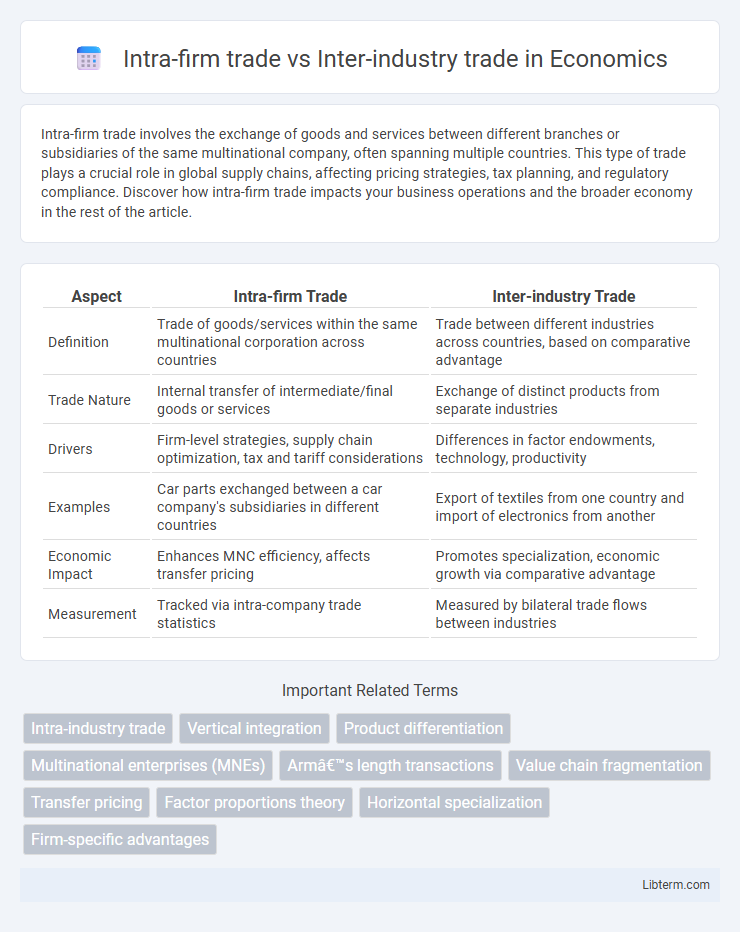
| Aspect | Intra-firm Trade | Inter-industry Trade |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trade of goods/services within the same multinational corporation across countries | Trade between different industries across countries, based on comparative advantage |
| Trade Nature | Internal transfer of intermediate/final goods or services | Exchange of distinct products from separate industries |
| Drivers | Firm-level strategies, supply chain optimization, tax and tariff considerations | Differences in factor endowments, technology, productivity |
| Examples | Car parts exchanged between a car company's subsidiaries in different countries | Export of textiles from one country and import of electronics from another |
| Economic Impact | Enhances MNC efficiency, affects transfer pricing | Promotes specialization, economic growth via comparative advantage |
| Measurement | Tracked via intra-company trade statistics | Measured by bilateral trade flows between industries |
Introduction to Intra-firm and Inter-industry Trade
Intra-firm trade involves the exchange of goods and services within the same multinational corporation, often between different subsidiaries or branches across countries, emphasizing internal supply chain optimization and efficiency. Inter-industry trade occurs between separate firms operating in different industries or sectors, driven by comparative advantage and specialization, where countries export products in which they have a production efficiency and import others. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for analyzing global trade patterns, investment strategies, and the impact of globalization on corporate structures and international markets.
Defining Intra-firm Trade: Concepts and Examples
Intra-firm trade refers to transactions conducted between different branches, subsidiaries, or divisions of the same multinational corporation across national borders, facilitating internal supply chains and resource optimization. Examples include a U.S.-based automotive company exporting car components to its manufacturing plant in Mexico for final assembly or a technology firm transferring software licenses from its European headquarters to its Asian branches. This type of trade contrasts with inter-industry trade, which occurs between different industries or independent firms operating in global markets.
Understanding Inter-industry Trade: Key Characteristics
Inter-industry trade involves the exchange of goods and services between different industries or sectors, often driven by comparative advantage and specialization. Key characteristics include the trade of distinctly different products, such as machinery for agricultural products, reflecting differences in factor endowments and technology levels. This type of trade typically enhances economic efficiency by allowing countries to focus on industries where they have relative strengths, fostering growth and diversification.
Historical Evolution of Global Trade Patterns
Intra-firm trade emerged prominently in the late 20th century with the rise of multinational corporations optimizing production across borders, shifting global trade patterns towards complex supply chains. Historically, inter-industry trade dominated during the early phases of globalization, characterized by exchanges of distinct products between countries with different factor endowments, as explained by classical trade theories like Heckscher-Ohlin. The evolution from inter-industry to intra-firm trade reflects increased economic integration, technological advancements, and the growing importance of global value chains in international commerce.
Economic Drivers of Intra-firm Trade
Intra-firm trade is primarily driven by multinational corporations optimizing production processes across borders, leveraging economies of scale, scope, and technological advantages within the firm to reduce costs and mitigate risks. Transfer pricing strategies and the need for coordination of intermediate inputs enhance efficiency in global supply chains, distinguishing intra-firm transactions from inter-industry trade, which involves exchanges between firms in different sectors. Economic drivers such as market segmentation, product differentiation, and regulatory arbitrage also play critical roles in fostering intra-firm trade dynamics.
Factors Influencing Inter-industry Trade
Inter-industry trade is primarily influenced by differences in factor endowments, technological variations, and comparative advantages between countries, leading to the exchange of distinct goods across industries. Variations in labor skills, capital intensity, and resource availability drive specialization and trade patterns in inter-industry contexts. In contrast, intra-firm trade often depends more on firm-specific advantages and internal production networks than on broad factor differences.
Comparative Analysis: Intra-firm vs Inter-industry Trade
Intra-firm trade involves transactions of goods and services within the same multinational corporation across different countries, emphasizing economies of scale and centralized management, while inter-industry trade occurs between distinct industries and countries specializing in different products based on comparative advantage. Intra-firm trade often features intermediate goods and components with high product differentiation, driven by supply chain integration and cost minimization, whereas inter-industry trade relies on factor endowments and technological differences leading to exchange of final goods. Empirical studies show intra-firm trade accounts for up to 30-40% of total trade in advanced economies, reflecting globalization trends, compared to inter-industry trade's dominance in traditional trade theories focused on distinct sector exchanges.
Impact on Global Value Chains and Supply Networks
Intra-firm trade enhances coordination and efficiency within multinational corporations, allowing seamless integration across global value chains and optimizing supply networks through standardized processes and internal transactions. Inter-industry trade fosters specialization and comparative advantage between different sectors, driving diversification and innovation across global supply networks by exchanging distinct products and inputs. The interplay between these trade types influences the complexity and resilience of global value chains, with intra-firm transactions stabilizing flows and inter-industry trade expanding market reach and technological diffusion.
Policy Implications and Trade Regulation
Intra-firm trade, characterized by transactions within multinational corporations, often requires tailored policy frameworks to address transfer pricing and prevent tax base erosion, influencing international tax regulations and trade agreements. Inter-industry trade, involving exchanges of distinct products across different sectors, demands broad trade policies supporting competitive tariffs and sector-specific regulations to enhance comparative advantage and market access. Effective trade regulation must balance these dynamics by fostering transparency, ensuring fair competition, and mitigating regulatory arbitrage between intra-firm and inter-industry trade flows.
Future Trends and Challenges in International Trade
Intra-firm trade is expected to grow with multinational corporations optimizing supply chains through digital technologies and automation, enhancing efficiency and responsiveness. Inter-industry trade faces challenges from shifting geopolitical landscapes and protectionist policies that disrupt traditional comparative advantages and global value chains. Both trade types must adapt to sustainability demands and fluctuating trade regulations to maintain competitiveness in an evolving international market.
Intra-firm trade Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com