Option time value represents the portion of an option's price attributed to the remaining time until expiration, reflecting the potential for favorable price movement. This value decreases as the expiration date approaches, a process known as time decay, impacting your trading strategy and risk management. Explore the rest of the article to understand how time value influences option pricing and how you can leverage it effectively.
Table of Comparison
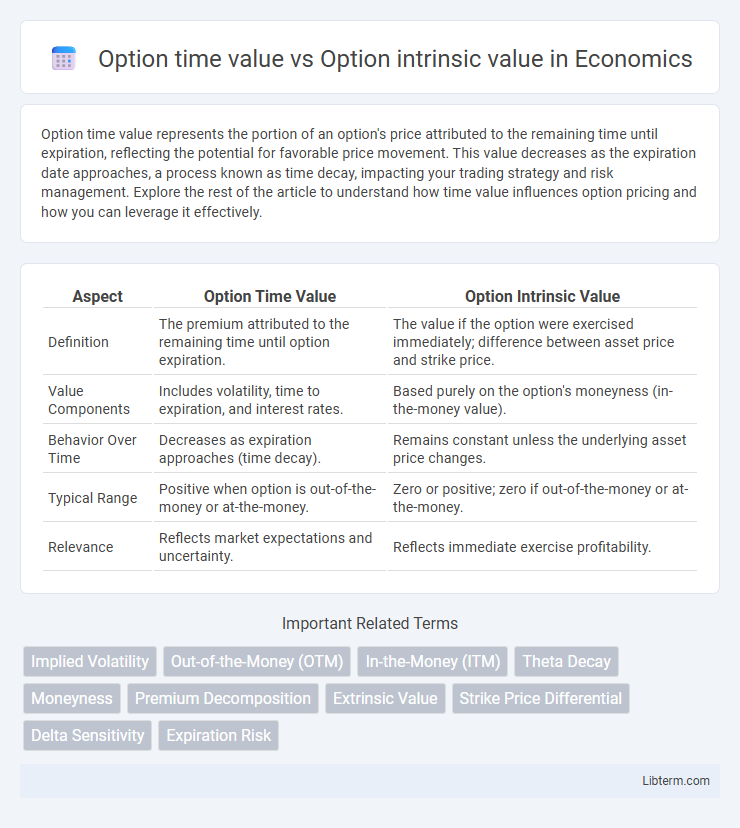
| Aspect | Option Time Value | Option Intrinsic Value |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The premium attributed to the remaining time until option expiration. | The value if the option were exercised immediately; difference between asset price and strike price. |
| Value Components | Includes volatility, time to expiration, and interest rates. | Based purely on the option's moneyness (in-the-money value). |
| Behavior Over Time | Decreases as expiration approaches (time decay). | Remains constant unless the underlying asset price changes. |
| Typical Range | Positive when option is out-of-the-money or at-the-money. | Zero or positive; zero if out-of-the-money or at-the-money. |
| Relevance | Reflects market expectations and uncertainty. | Reflects immediate exercise profitability. |
Understanding Options: Time Value vs Intrinsic Value
Option intrinsic value represents the immediate profit potential of an option, calculated as the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the option's strike price, reflecting how much an option is "in-the-money." Time value accounts for the additional premium traders are willing to pay based on the remaining time until expiration and the possibility of favorable price movement, decreasing as the option approaches expiration in a process called time decay. Understanding the balance between intrinsic value and time value is essential for option traders to assess an option's total premium and make informed trading decisions.
Defining Intrinsic Value in Options
Intrinsic value in options represents the immediate profit potential if the option were exercised at the current market price of the underlying asset. For a call option, intrinsic value is calculated as the difference between the underlying asset's price and the strike price, only if this difference is positive; otherwise, it is zero. In contrast, a put option's intrinsic value is determined by subtracting the underlying asset's price from the strike price, with a minimum of zero, reflecting the option's built-in, real value excluding any time value.
What is Option Time Value?
Option time value represents the portion of an option's premium attributable to the remaining time until expiration, reflecting the potential for the underlying asset's price to move favorably. It decreases as the option approaches its expiration date, a phenomenon known as time decay or theta erosion. Unlike intrinsic value, which measures the immediate profitable difference between the underlying asset's price and the option's strike price, time value captures the speculative premium based on volatility, time, and market expectations.
Mathematical Calculation of Intrinsic Value
Option intrinsic value is mathematically calculated as the difference between the underlying asset's current market price and the option's strike price, but only if this difference is positive; otherwise, the intrinsic value is zero. For a call option, intrinsic value = max(0, Spot Price - Strike Price), and for a put option, intrinsic value = max(0, Strike Price - Spot Price). Time value equals the option premium minus the intrinsic value, reflecting the additional value attributed to the time remaining until expiration and the potential for further favorable price movement.
Factors Influencing Option Time Value
Option time value is influenced by factors such as the underlying asset's volatility, time remaining until expiration, and prevailing interest rates. Higher volatility increases the probability of favorable price movement, enhancing time value, while longer time until expiration allows more opportunity for the option to gain intrinsic value. Interest rates impact the cost of carrying the underlying asset, subtly affecting the option's time value through changes in the risk-free rate.
Relationship Between Option Price, Intrinsic Value, and Time Value
Option price consists of intrinsic value and time value, where intrinsic value reflects the immediate profitability of exercising the option and time value represents the potential for additional profit before expiration. Intrinsic value is calculated as the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the option's strike price when favorable, while time value depends on factors like volatility, time until expiration, and interest rates. As expiration nears, time value decays, causing the option price to converge toward intrinsic value, emphasizing the critical relationship between these components in pricing models like Black-Scholes.
At-the-Money, In-the-Money, and Out-of-the-Money Options
At-the-Money (ATM) options have zero intrinsic value and their premium consists entirely of time value, reflecting the probability of moving In-the-Money (ITM) before expiration. In-the-Money options possess positive intrinsic value equal to the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the strike price, with remaining premium representing time value. Out-of-the-Money (OTM) options lack intrinsic value and their price is composed solely of time value, which decreases as expiration approaches.
The Role of Expiry in Option Value
Option time value decreases as the expiry date approaches, reflecting the diminishing probability of the option gaining additional intrinsic value. Intrinsic value is the immediate gain if the option is exercised at expiry, determined by the difference between the underlying asset's price and the strike price. The closer the option is to expiry, the lower the time value, making intrinsic value the dominant component of total option value.
How Volatility Affects Time Value
Option time value increases with higher volatility because greater price fluctuations raise the probability of the option finishing in-the-money before expiration. Intrinsic value remains constant regardless of volatility as it depends solely on the difference between the underlying asset's current price and the option's strike price. Elevated implied volatility expands the option's time premium, enhancing its overall market price due to increased uncertainty.
Practical Examples: Intrinsic vs Time Value in Options Trading
An option's intrinsic value represents the immediate profit if exercised, such as a call option with a strike price of $50 when the stock trades at $60, yielding an intrinsic value of $10. The time value reflects the potential for further profit before expiration, for instance, a call option priced at $12 with an intrinsic value of $10 has a time value of $2, indicating premium paid for remaining time and volatility. Traders analyze both values to determine whether to exercise, hold, or sell options, balancing guaranteed gains against speculative benefits.
Option time value Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com