The underlying asset price represents the current market value of the financial instrument or commodity on which a derivative is based, such as stocks, bonds, or commodities. This price is crucial for determining the value of options, futures, and other derivative contracts, influencing your investment strategies and risk management. Explore the rest of the article to understand how fluctuations in the underlying asset price impact your trading decisions.
Table of Comparison
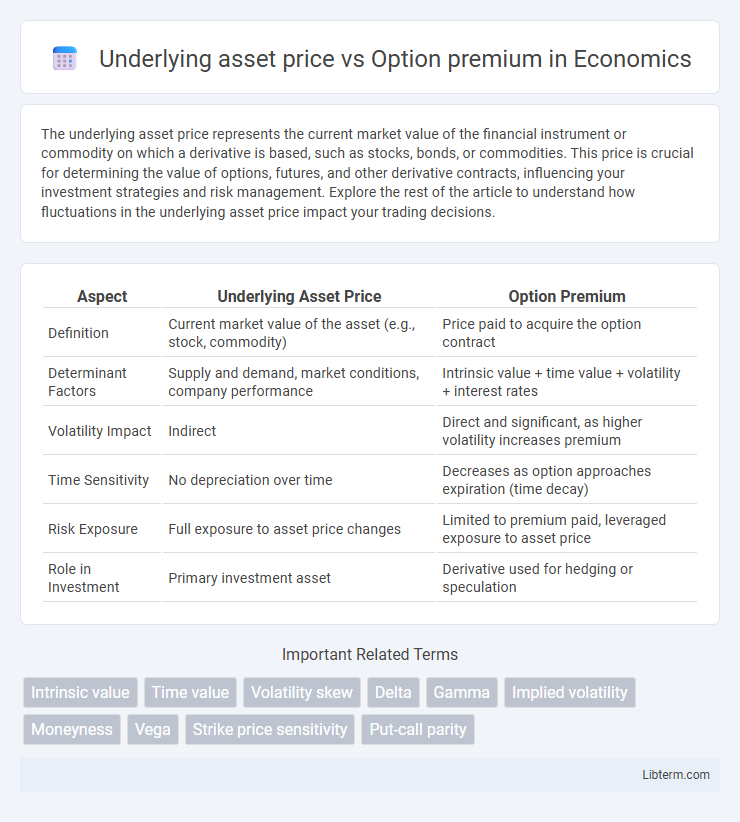
| Aspect | Underlying Asset Price | Option Premium |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Current market value of the asset (e.g., stock, commodity) | Price paid to acquire the option contract |
| Determinant Factors | Supply and demand, market conditions, company performance | Intrinsic value + time value + volatility + interest rates |
| Volatility Impact | Indirect | Direct and significant, as higher volatility increases premium |
| Time Sensitivity | No depreciation over time | Decreases as option approaches expiration (time decay) |
| Risk Exposure | Full exposure to asset price changes | Limited to premium paid, leveraged exposure to asset price |
| Role in Investment | Primary investment asset | Derivative used for hedging or speculation |
Understanding Underlying Asset Price
The underlying asset price is the current market value of the asset on which an option contract is based, such as stocks, commodities, or indices. This price directly influences the option premium, as it determines the intrinsic value and potential profitability of the option at expiration. Understanding the fluctuations of the underlying asset price helps traders assess risk and make informed decisions about buying or selling options.
What Is an Option Premium?
An option premium is the price paid by the buyer to acquire the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell the underlying asset at a predetermined strike price before or on the expiration date. This premium reflects factors such as the underlying asset price, volatility, time until expiration, and market demand, influencing the option's intrinsic and extrinsic values. Fluctuations in the underlying asset price directly impact the option premium, with increases generally raising call option premiums and decreasing put option premiums.
Relationship Between Asset Price and Option Premium
The option premium is directly influenced by the underlying asset price, with call option premiums increasing as the asset price rises and put option premiums increasing as the asset price falls. This relationship reflects the intrinsic value component of the option premium, where higher asset prices boost call option value and depress put option value. Time value and volatility also impact premiums, but the asset price remains the primary determinant in the option pricing model.
Factors Influencing Option Premiums
Option premium is primarily influenced by the underlying asset price, with the premium generally increasing as the asset price approaches or exceeds the option's strike price. Other significant factors affecting option premiums include time to expiration, volatility of the underlying asset, interest rates, and dividends expected during the option's lifetime. Higher volatility and longer time to expiration typically lead to higher premiums due to the increased probability of profitable price movements before expiry.
Intrinsic Value and Its Impact
The option premium is directly influenced by the underlying asset price, where intrinsic value represents the difference between the asset price and the option's strike price when favorable. A higher underlying asset price relative to the strike price increases the intrinsic value, thereby elevating the option premium. This intrinsic value is crucial in determining the option's true worth, separating it from time value and volatility components.
The Role of Time Value
The underlying asset price directly impacts the intrinsic value of an option, while the option premium reflects both intrinsic value and time value. Time value accounts for the potential price movement of the underlying asset before expiration, influencing the premium even when intrinsic value is zero. As expiration approaches, the time value declines, causing the option premium to converge with the intrinsic value.
Volatility Effects on Option Premiums
Option premiums are highly sensitive to the volatility of the underlying asset price, as increased volatility raises the likelihood of the option finishing in-the-money, thus inflating its value. Implied volatility directly influences the time value component of the option premium, often causing premiums to escalate even when the underlying price remains stable. Traders closely monitor volatility indices like the VIX to gauge expected market fluctuations and adjust option pricing models accordingly.
Market Sentiment and Pricing Dynamics
The underlying asset price directly influences the option premium through intrinsic value and market sentiment, where rising prices typically increase call option premiums due to expected profitability. Market sentiment drives supply and demand dynamics, causing premiums to fluctuate beyond theoretical prices based on volatility and investor expectations. Pricing dynamics also incorporate time decay and implied volatility, which modify option premiums independently of changes in the underlying asset price.
Real-World Examples: Price vs Premium
The underlying asset price directly influences the option premium, as seen in Tesla stock options where a rise in Tesla's share price from $600 to $700 causes call option premiums to increase significantly, reflecting higher intrinsic value and market volatility. In real-world scenarios like Apple Inc., when Apple's stock price hovers around $150, the option premium for in-the-money calls is substantially higher than out-of-the-money calls due to the greater likelihood of profitable exercise. Historical data from Amazon options illustrates that even moderate changes in the underlying asset price can lead to disproportionate shifts in option premiums, driven by factors such as time to expiration and implied volatility.
Key Takeaways for Traders
Option premiums are directly influenced by the underlying asset price, as increases in asset value typically raise call option premiums while decreases elevate put option premiums. Implied volatility and time to expiration also significantly affect the premium, often amplifying sensitivity to underlying price movements. Traders must monitor these dynamics closely to optimize entry and exit points, managing risk and maximizing returns effectively.
Underlying asset price Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com