Price level anchors stabilize consumer expectations by setting a consistent reference point for inflation and economic performance. Maintaining a credible price level anchor helps central banks control inflation and reduce uncertainty in financial markets. Explore the full article to understand how a price level anchor impacts your economic decisions and market stability.
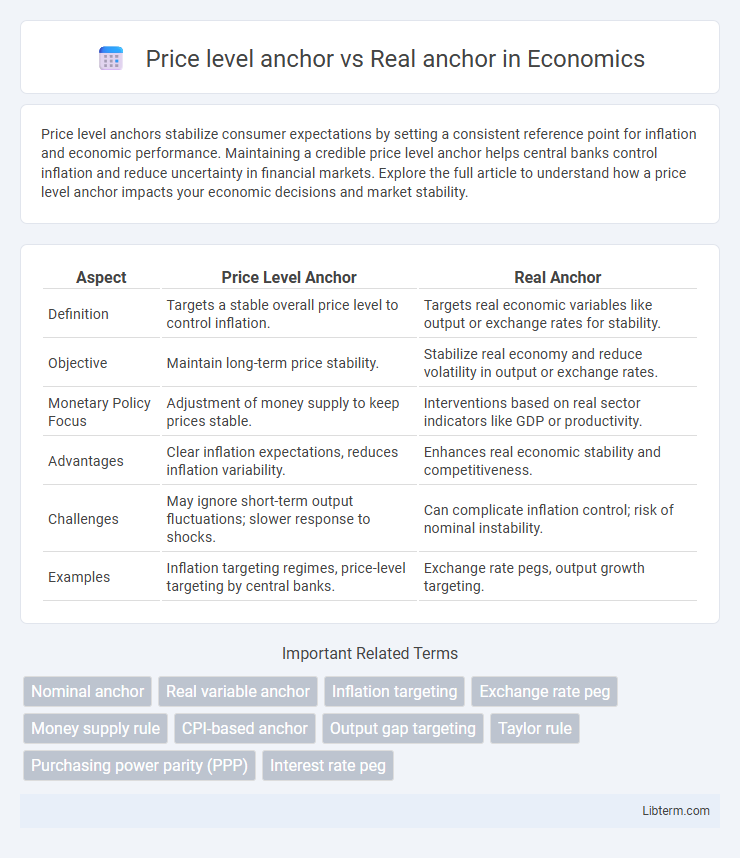
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Price Level Anchor | Real Anchor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Targets a stable overall price level to control inflation. | Targets real economic variables like output or exchange rates for stability. |
| Objective | Maintain long-term price stability. | Stabilize real economy and reduce volatility in output or exchange rates. |
| Monetary Policy Focus | Adjustment of money supply to keep prices stable. | Interventions based on real sector indicators like GDP or productivity. |
| Advantages | Clear inflation expectations, reduces inflation variability. | Enhances real economic stability and competitiveness. |
| Challenges | May ignore short-term output fluctuations; slower response to shocks. | Can complicate inflation control; risk of nominal instability. |
| Examples | Inflation targeting regimes, price-level targeting by central banks. | Exchange rate pegs, output growth targeting. |
Introduction to Price Level Anchors and Real Anchors
Price level anchors stabilize an economy by targeting a specific price index, such as the Consumer Price Index (CPI), to control inflation expectations and maintain price stability. Real anchors focus on fundamental economic variables like the output gap or unemployment rate, aiming to stabilize the economy by influencing real economic activity rather than just nominal prices. Both approaches serve as critical frameworks in monetary policy, guiding central banks in setting policies that ensure long-term economic stability.
Defining Price Level Anchors
Price level anchors are mechanisms used in monetary policy to stabilize inflation by targeting a specific price index or price level over time, ensuring the general price level remains predictable. Unlike real anchors, which focus on real economic variables such as output or employment, price level anchors emphasize controlling nominal price movements to build credibility and guide inflation expectations. Central banks adopting price level targeting commit to adjusting policies to correct deviations from the predetermined price level path, promoting long-term price stability.
Understanding Real Anchors
Real anchors stabilize inflation expectations by linking monetary policy to tangible economic variables such as output or employment, rather than relying solely on nominal measures like price levels. Understanding real anchors involves recognizing their role in promoting long-term economic stability by adjusting policy based on real economic activity, which helps prevent the distortionary effects of inflation on purchasing power. This approach contrasts with price level anchors that focus on maintaining a fixed price level, offering a more flexible framework responsive to changing economic conditions.
Key Differences Between Price Level and Real Anchors
Price level anchors maintain a fixed target for the overall price index, stabilizing inflation expectations by signaling the desired price level path. Real anchors, such as targeting the natural rate of output or employment, focus on long-term economic fundamentals rather than directly controlling inflation or price levels. The key difference lies in price level anchors emphasizing nominal stability, while real anchors prioritize sustainable economic growth and resource utilization.
Theoretical Foundations of Anchoring in Monetary Policy
Price level anchors stabilize inflation expectations by targeting a specific price index over time, guiding long-term price stability through explicit numerical goals. Real anchors, such as output or employment targets, emphasize sustainable economic fundamentals, aligning monetary policy with structural economic conditions to mitigate inflationary or deflationary pressures. Theoretical foundations highlight that credible anchoring mechanisms reduce uncertainty, enhance policy effectiveness, and prevent time-inconsistent monetary behaviors by firmly influencing agents' expectations.
Economic Impacts of Price Level Anchors
Price level anchors stabilize inflation expectations by targeting a specific price index, reducing uncertainty and fostering consistent economic growth. Their use can lower long-term interest rates, encourage investment, and maintain purchasing power, leading to improved consumer confidence and spending. However, strict adherence to price level anchors may limit monetary policy flexibility, potentially exacerbating economic downturns during supply shocks or financial crises.
Real Anchor Mechanisms in Practice
Real anchor mechanisms stabilize inflation by targeting measures linked to the economy's real variables, such as unemployment rates or output gaps, rather than nominal price levels. Central banks implementing real anchors often use indicators like the NAIRU (non-accelerating inflation rate of unemployment) to guide monetary policy and maintain long-term price stability. This approach anchors inflation expectations by aligning policy decisions with sustainable economic performance, reducing reliance on nominal targets that can be distorted by transient price shocks.
Policy Implications: Choosing the Right Anchor
Price level anchors provide policy stability by targeting the overall price index, reducing inflation volatility and guiding long-term expectations effectively. Real anchors, such as output or employment targets, emphasize sustainable economic growth and can enhance credibility by addressing real economic variables. Selecting the appropriate anchor depends on the specific economic context, where price level targeting suits economies prioritizing inflation control, while real anchors benefit those focusing on growth and employment outcomes.
Case Studies: Global Examples of Anchoring Strategies
Multinational corporations employ price level anchors by setting reference prices in major markets such as the U.S. or EU to stabilize expectations, as seen in Apple's consistent pricing strategies across countries. Real anchors focus on tangible metrics like production cost or competitor benchmarks; Toyota utilizes real anchors by aligning vehicle prices with manufacturing costs and local market conditions globally. Case studies from Coca-Cola reveal hybrid anchoring strategies combining global price level references with localized real anchor adjustments to optimize market competitiveness.
Future Trends in Monetary Policy Anchors
Price level anchors maintain long-term price stability by targeting a specific price index, providing clear expectations about inflation trajectories. Real anchors emphasize fundamental economic variables such as output or employment to stabilize monetary policy under supply shocks and structural changes. Future trends indicate a hybrid approach blending price level targets with real economic metrics, leveraging advanced data analytics and machine learning to enhance flexibility and precision in monetary policy frameworks.
Price level anchor Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com