Total return measures the complete performance of an investment by combining capital gains, dividends, and interest income over a specific period. It offers a comprehensive view of your investment's growth, going beyond just price appreciation. Explore the rest of the article to understand how total return can impact your financial decisions.
Table of Comparison
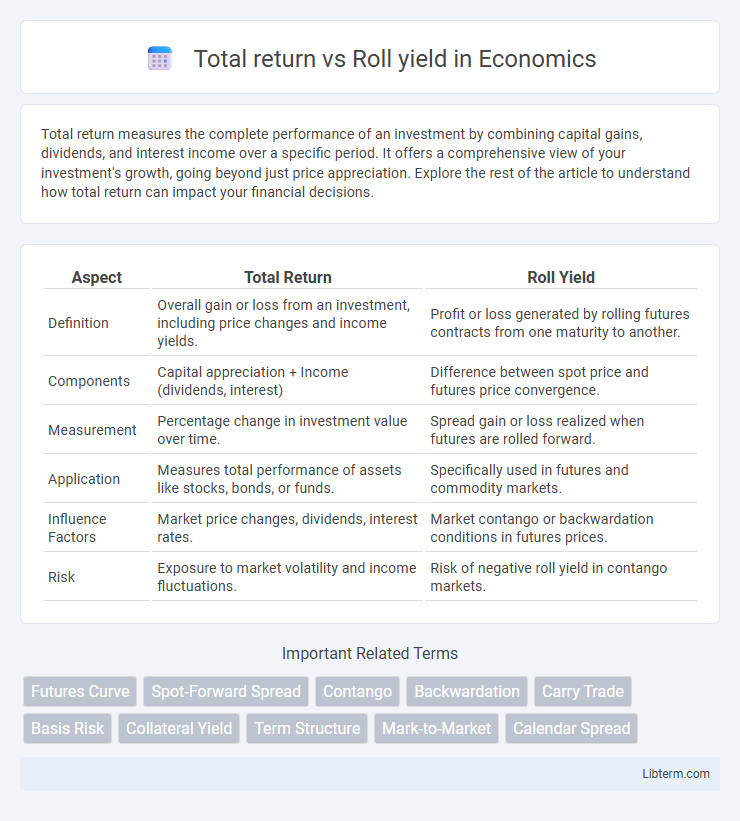
| Aspect | Total Return | Roll Yield |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Overall gain or loss from an investment, including price changes and income yields. | Profit or loss generated by rolling futures contracts from one maturity to another. |
| Components | Capital appreciation + Income (dividends, interest) | Difference between spot price and futures price convergence. |
| Measurement | Percentage change in investment value over time. | Spread gain or loss realized when futures are rolled forward. |
| Application | Measures total performance of assets like stocks, bonds, or funds. | Specifically used in futures and commodity markets. |
| Influence Factors | Market price changes, dividends, interest rates. | Market contango or backwardation conditions in futures prices. |
| Risk | Exposure to market volatility and income fluctuations. | Risk of negative roll yield in contango markets. |
Understanding Total Return: A Comprehensive Overview
Total return measures the overall gain or loss from an investment, including price appreciation, dividends, and interest, providing a complete picture of investment performance. Roll yield specifically refers to gains or losses from futures contracts as they approach expiration and are rolled into new contracts, impacting returns in commodity trading and fixed income strategies. Understanding total return requires integrating price changes with income components, whereas roll yield isolates the effect of contract rollover in futures markets.
What Is Roll Yield? Definition and Key Concepts
Roll yield refers to the gains or losses that result from the convergence of futures contract prices toward the spot price as the contract approaches expiration. It is a key concept in futures trading, representing the impact of rolling over contracts from the front month to the next delivery month. Total return includes both the roll yield and changes in the underlying asset price, providing a comprehensive measure of investment performance in futures markets.
Components of Total Return in Investments
Total return in investments encompasses both capital appreciation and income generated from interest or dividends, reflecting the overall gain or loss over a specific period. Roll yield, a component often seen in futures trading, arises from the price difference when rolling contracts forward, impacting total return especially in commodities and fixed income investments. Understanding the distinct roles of income, price changes, and roll yield enables investors to more accurately evaluate performance and strategy effectiveness.
How Roll Yield Impacts Commodity and Futures Markets
Roll yield significantly influences commodity and futures markets by affecting the total return investors realize when futures contracts approach expiration. Positive roll yield occurs when near-term contracts are cheaper than deferred contracts (contango), boosting returns as contracts are rolled forward, while negative roll yield arises in backwardation, where expiring contracts are more expensive, eroding returns. Understanding roll yield dynamics enables market participants to better assess risks and optimize strategies in commodities investing and futures trading.
Differences Between Total Return and Roll Yield
Total return measures the overall profit or loss from holding an asset, including price appreciation and income components like dividends or interest. Roll yield specifically captures gains or losses from the futures contract price converging to the spot price as it approaches expiration, reflecting the impact of contango or backwardation in the futures market. Unlike total return, roll yield isolates the effect of futures curve dynamics without incorporating underlying asset price changes or income distributions.
Factors Affecting Total Return vs Roll Yield
Factors affecting total return include the underlying asset price changes, interest income, and dividend payouts, which collectively influence the overall profitability of an investment. Roll yield is primarily impacted by the shape of the futures curve, such as contango or backwardation, and the timing of contract rollovers in futures markets. Understanding the interplay between asset price volatility, cost of carry, and market structure is crucial for analyzing the differential returns from total return and roll yield strategies.
Practical Examples: Comparing Total Return and Roll Yield
Total return measures the overall profit from an investment, including price appreciation and any income received, while roll yield captures gains or losses from rolling futures contracts as they approach expiration. For example, a crude oil futures investor might experience positive roll yield during backwardation when near-month contracts trade at a premium, enhancing total returns beyond price changes alone. Conversely, during contango, roll yield can be negative, reducing total returns despite rising spot prices.
The Role of Contango and Backwardation in Roll Yield
Roll yield is the profit or loss generated from rolling futures contracts as they approach expiration, significantly influenced by market conditions like contango and backwardation. In a contango market, where futures prices are higher than spot prices, roll yield tends to be negative due to selling lower-priced expiring contracts and buying higher-priced distant contracts. Conversely, backwardation, characterized by futures prices below spot prices, results in positive roll yield as contracts are rolled into cheaper futures, enhancing total return.
Strategies to Maximize Total Return and Manage Roll Yield
Maximizing total return in commodity investing requires a balanced strategy combining spot price appreciation and effective management of roll yield, which arises from futures contract rollovers. Employing techniques such as calendar spread trading and selective contract maturation helps mitigate negative roll yield and enhances overall portfolio performance. Integrating these approaches with dynamic asset allocation and risk management further optimizes total returns while controlling exposure to adverse roll yield effects.
Choosing Between Total Return and Roll Yield Approaches
Choosing between total return and roll yield approaches depends on investment goals and market conditions. Total return captures overall profitability by combining price appreciation and income from dividends or interest, providing a comprehensive performance metric for diversified portfolios. Roll yield focuses on gains or losses from futures contract price convergence, offering insights for strategies emphasizing timing and contract selection in commodity or fixed-income markets.
Total return Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com