Profit maximization focuses on increasing your business's earnings by optimizing revenue and minimizing costs. Efficient resource allocation and strategic pricing play critical roles in achieving maximum profitability. Explore the rest of this article to learn essential tactics for boosting your profits.
Table of Comparison
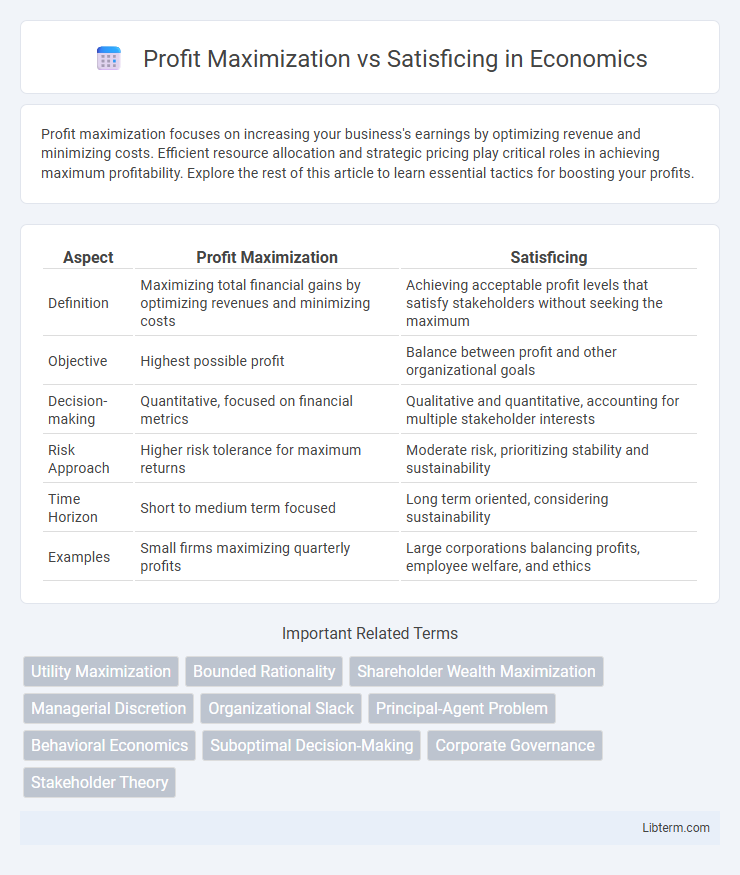
| Aspect | Profit Maximization | Satisficing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maximizing total financial gains by optimizing revenues and minimizing costs | Achieving acceptable profit levels that satisfy stakeholders without seeking the maximum |
| Objective | Highest possible profit | Balance between profit and other organizational goals |
| Decision-making | Quantitative, focused on financial metrics | Qualitative and quantitative, accounting for multiple stakeholder interests |
| Risk Approach | Higher risk tolerance for maximum returns | Moderate risk, prioritizing stability and sustainability |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term focused | Long term oriented, considering sustainability |
| Examples | Small firms maximizing quarterly profits | Large corporations balancing profits, employee welfare, and ethics |
Introduction to Profit Maximization and Satisficing
Profit maximization is a strategic objective where firms aim to achieve the highest possible financial gain within a specific time frame by optimizing revenue and minimizing costs. Satisficing, a concept introduced by Herbert Simon, refers to the decision-making process where firms pursue satisfactory or "good enough" outcomes rather than absolute maximization, often due to bounded rationality and limited information. Understanding the distinction between profit maximization and satisficing is essential in organizational behavior and economic models, as it influences corporate strategies and resource allocation.
Defining Profit Maximization
Profit maximization refers to the business goal of achieving the highest possible financial gain by increasing revenues and reducing costs within a specific period. It involves analyzing marginal costs and marginal revenues to determine the most profitable level of production or service delivery. This strategy prioritizes short-term financial performance, often seeking to optimize shareholder value through quantitative financial metrics.
Understanding Satisficing in Business
Satisficing in business refers to the strategy of aiming for a satisfactory or adequate outcome rather than the absolute maximum profit, balancing resource constraints and risk tolerance. Companies practicing satisficing prioritize steady growth, customer satisfaction, and long-term sustainability over aggressive profit maximization. This approach reduces decision-making complexity and supports adaptive management in dynamic market environments.
Key Differences Between Profit Maximization and Satisficing
Profit maximization focuses on increasing a firm's financial gains to the highest possible level, prioritizing short-term revenue and cost efficiency. Satisficing emphasizes achieving acceptable or sufficient outcomes rather than the absolute maximum profit, often balancing stakeholder interests and long-term sustainability. Key differences include the goal orientation--maximizing shareholder wealth versus meeting multiple objectives--and the decision-making approach, where profit maximization relies on quantitative analysis, and satisficing incorporates qualitative factors and trade-offs.
Theoretical Foundations of Each Approach
Profit maximization is rooted in neoclassical economic theory, assuming firms aim to maximize shareholder wealth by optimizing revenue and minimizing costs under constraints. Satisficing, introduced by Herbert A. Simon, challenges this by emphasizing bounded rationality, where decision-makers seek satisfactory solutions rather than optimal ones due to limited information and cognitive limitations. These contrasting theoretical foundations highlight profit maximization's focus on optimal efficiency versus satisficing's emphasis on practical decision-making within real-world complexities.
Advantages of Profit Maximization
Profit maximization drives firms to allocate resources efficiently, boosting shareholder value and fostering long-term growth through reinvestment opportunities. It incentivizes innovation and productivity improvements by aligning management goals with financial performance metrics. Emphasizing profit maximization enhances competitive positioning by enabling firms to respond swiftly to market changes and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Satisficing
Satisficing prioritizes reaching a satisfactory outcome rather than the absolute maximum profit, reducing decision-making time and lowering cognitive overload. This approach benefits businesses by promoting flexibility and adaptability in uncertain markets, enabling quicker responses to changing conditions. However, satisficing may result in suboptimal financial performance and missed opportunities for higher profitability compared to strict profit maximization strategies.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Profit maximization drives companies like Amazon to prioritize revenue growth and market dominance, often investing heavily in technology and infrastructure to outpace competitors. In contrast, satisficing is evident in family-owned businesses such as local bakeries, which aim for steady profits and customer satisfaction rather than aggressive expansion. Case studies of companies like Patagonia show satisficing by balancing profit with environmental and social goals, demonstrating a strategic choice beyond maximizing financial returns.
Impact on Stakeholders and Decision-Making
Profit maximization often prioritizes shareholder wealth, potentially at the expense of employees, customers, and the environment, leading to short-term gains but long-term stakeholder dissatisfaction. Satisficing balances multiple stakeholder interests by aiming for satisfactory rather than optimal financial outcomes, fostering sustainable decision-making and stronger stakeholder relationships. This approach mitigates risks associated with aggressive profit pursuits while promoting ethical practices and organizational resilience.
Choosing the Right Strategy for Your Business
Profit maximization focuses on increasing a company's earnings to the highest possible level, ideal for businesses aiming for rapid growth and competitive advantage. Satisficing prioritizes achieving acceptable, sustainable outcomes by balancing profit with other factors like employee satisfaction and long-term stability. Selecting the right strategy depends on your business goals, industry dynamics, and resource availability to ensure optimal financial health and operational efficiency.
Profit Maximization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com