Lean manufacturing focuses on eliminating waste and improving efficiency by streamlining processes and maximizing value for the customer. It emphasizes continuous improvement, just-in-time production, and reducing inventory to enhance productivity and reduce costs. Discover how implementing lean manufacturing principles can transform Your operations by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
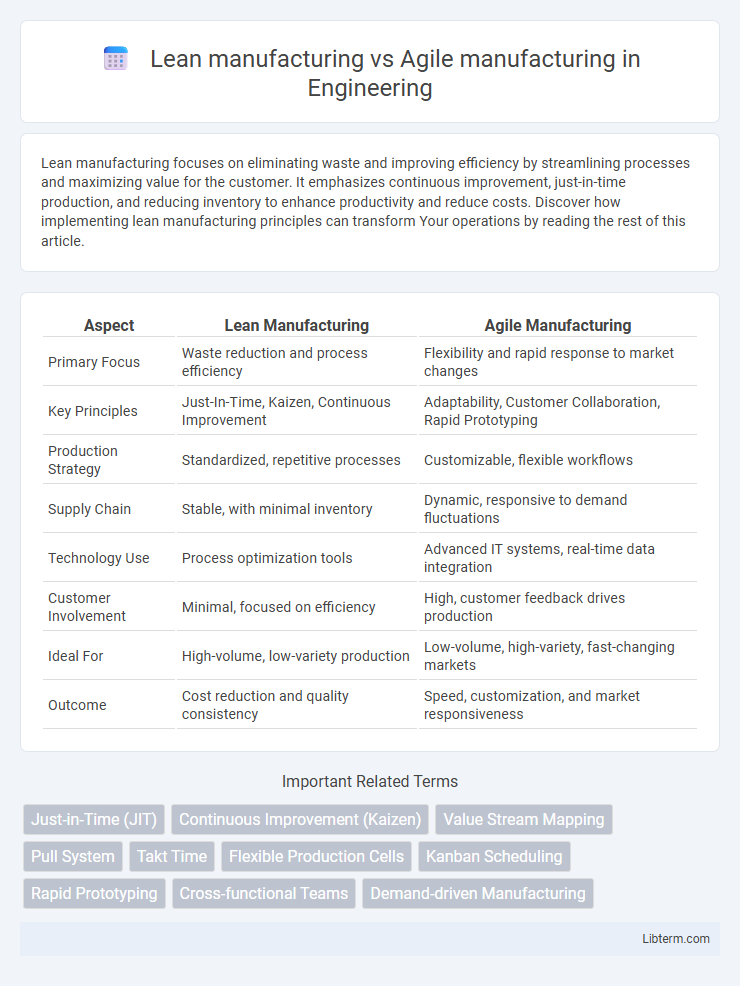
| Aspect | Lean Manufacturing | Agile Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Waste reduction and process efficiency | Flexibility and rapid response to market changes |
| Key Principles | Just-In-Time, Kaizen, Continuous Improvement | Adaptability, Customer Collaboration, Rapid Prototyping |
| Production Strategy | Standardized, repetitive processes | Customizable, flexible workflows |
| Supply Chain | Stable, with minimal inventory | Dynamic, responsive to demand fluctuations |
| Technology Use | Process optimization tools | Advanced IT systems, real-time data integration |
| Customer Involvement | Minimal, focused on efficiency | High, customer feedback drives production |
| Ideal For | High-volume, low-variety production | Low-volume, high-variety, fast-changing markets |
| Outcome | Cost reduction and quality consistency | Speed, customization, and market responsiveness |
Introduction to Lean and Agile Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing emphasizes eliminating waste and improving process efficiency by focusing on value-added activities, employing tools like Just-In-Time (JIT) production and continuous improvement (Kaizen). Agile manufacturing prioritizes flexibility and responsiveness to rapidly changing customer demands, leveraging modular production systems and real-time data analytics to adapt workflows quickly. Both methodologies aim to enhance production effectiveness but differ by Lean's focus on efficiency and Agile's focus on adaptability within dynamic market environments.
Core Principles of Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction, continuous improvement, and delivering value by optimizing workflows and eliminating non-value-added activities in production. Agile manufacturing prioritizes flexibility, rapid response to customer demands, and adaptability in processes to efficiently handle market changes. Core principles of Lean Manufacturing include identifying value from the customer's perspective, mapping the value stream, creating continuous flow, establishing pull systems, and pursuing perfection through constant refinement.
Core Principles of Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing emphasizes flexibility, rapid response to market changes, and customer-centric production, contrasting with Lean manufacturing's focus on waste reduction and process efficiency. Core principles of Agile manufacturing include modular product design, collaborative networks, and adaptive supply chains to swiftly adjust production based on demand variability. This approach leverages real-time data integration and cross-functional teams to accelerate innovation and enhance product customization.
Key Differences Between Lean and Agile Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing emphasizes minimizing waste and improving efficiency through standardized processes, focusing on cost reduction and consistent quality. Agile manufacturing prioritizes flexibility and rapid response to changing customer demands by utilizing adaptable workflows and cross-functional teams. The key difference lies in Lean's focus on efficiency and stability versus Agile's focus on responsiveness and adaptability in dynamic markets.
Advantages of Lean Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing enhances operational efficiency by minimizing waste and streamlining production processes, leading to significant cost savings and improved resource utilization. It fosters a culture of continuous improvement, empowering workers to identify and eliminate inefficiencies, which increases product quality and customer satisfaction. The scalable nature of Lean principles also enables companies to maintain consistent performance and adapt to demand variability without excessive inventory buildup.
Advantages of Agile Manufacturing
Agile manufacturing offers superior flexibility in responding to market changes and customer demands, enabling companies to quickly adapt production processes and customize products. This approach enhances collaboration across supply chains and integrates advanced technologies like IoT and AI for real-time decision-making. Compared to lean manufacturing, agile manufacturing supports innovation and scalability, driving faster time-to-market and increased competitive advantage.
Challenges in Implementing Lean and Agile
Implementing Lean manufacturing faces challenges such as resistance to cultural change, complexity in maintaining continuous waste reduction, and difficulty in aligning supplier processes with Lean principles. Agile manufacturing encounters obstacles including managing rapid product changes, ensuring real-time communication across cross-functional teams, and integrating flexible supply chains without escalating costs. Both methodologies demand significant organizational commitment, robust training programs, and adaptive IT systems to overcome these implementation hurdles effectively.
When to Choose Lean vs. Agile Manufacturing
Lean manufacturing is ideal for environments with stable demand and repetitive production processes focused on minimizing waste and maximizing efficiency through continuous improvement. Agile manufacturing suits industries facing high variability and customization requirements, enabling rapid response to market changes and customer needs with flexible production systems. Choose Lean when consistent quality and cost control are priorities, while Agile is preferred for adaptability and speed in dynamic markets.
Case Studies: Lean vs. Agile in Action
Case studies comparing Lean and Agile manufacturing highlight distinct approaches to efficiency and adaptability, with Lean focusing on waste reduction and streamlining production processes exemplified by Toyota's production system. Agile manufacturing case studies, such as those in the tech industry, emphasize flexibility and rapid response to market changes, demonstrated by companies like Zara in fast fashion. Analysis shows Lean excels in predictable, high-volume environments while Agile thrives in dynamic settings requiring quick product iterations.
Future Trends in Manufacturing Methodologies
Lean manufacturing emphasizes waste reduction and process efficiency, while Agile manufacturing prioritizes flexibility and rapid response to market changes. Future trends point to an integration of Lean's streamlined workflows with Agile's adaptability, driven by advancements in AI, IoT, and real-time data analytics. Smart factories will leverage these hybrid methodologies to enhance productivity, customization, and resilience in complex supply chains.
Lean manufacturing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com