A follower profile reveals key insights about the demographics, interests, and behaviors of an audience, enabling targeted content creation and marketing strategies. Understanding your follower profile helps optimize engagement and tailor messages to resonate effectively. Discover how analyzing your follower profile can transform your social media presence in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
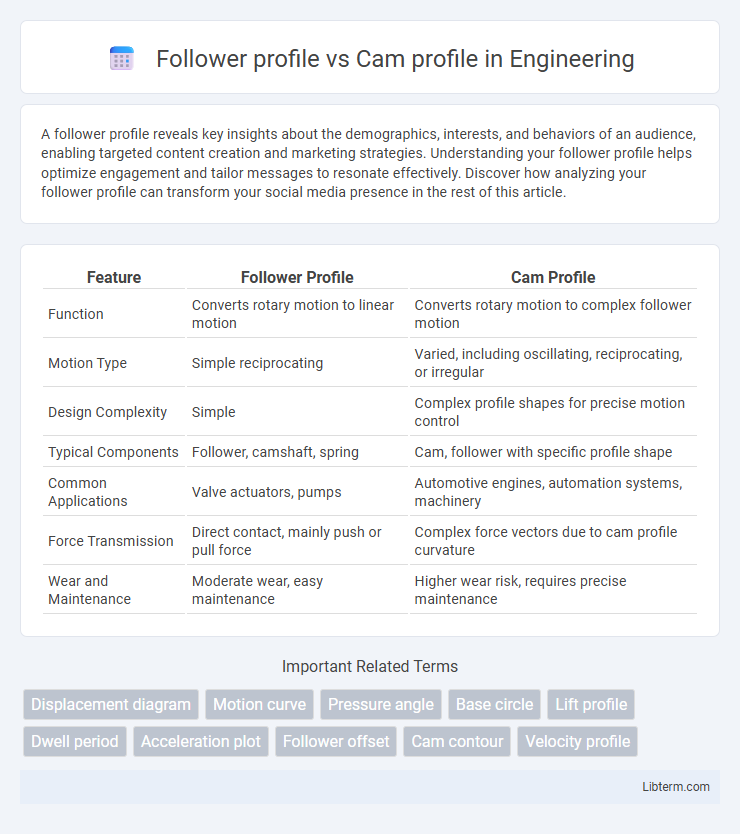
| Feature | Follower Profile | Cam Profile |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts rotary motion to linear motion | Converts rotary motion to complex follower motion |
| Motion Type | Simple reciprocating | Varied, including oscillating, reciprocating, or irregular |
| Design Complexity | Simple | Complex profile shapes for precise motion control |
| Typical Components | Follower, camshaft, spring | Cam, follower with specific profile shape |
| Common Applications | Valve actuators, pumps | Automotive engines, automation systems, machinery |
| Force Transmission | Direct contact, mainly push or pull force | Complex force vectors due to cam profile curvature |
| Wear and Maintenance | Moderate wear, easy maintenance | Higher wear risk, requires precise maintenance |
Introduction to Follower and Cam Profiles
Follower and cam profiles are critical components in gear design, defining the motion transfer between parts. A follower profile traces the cam's surface, determining the follower's displacement, velocity, and acceleration during operation. An optimized cam profile ensures smooth movement and precise timing, while the follower profile adapts to convert the cam's rotary motion into the desired linear or oscillatory motion efficiently.
Understanding Cam Profiles: Definition and Function
Cam profiles are precise geometric specifications that describe the shape of a camshaft lobe, crucial for controlling valve timing in internal combustion engines. Unlike follower profiles, which define the motion path of the follower in contact with the cam, cam profiles determine the lift, duration, and timing of valve operations, impacting engine performance and efficiency. Understanding cam profiles enables engineers to optimize engine dynamics by tailoring valve actuation to specific performance requirements.
Exploring Follower Profiles: Types and Applications
Follower profiles, characterized by their concave shape with a constant velocity ratio, are crucial in applications requiring smooth, gradual motion such as automated production lines and valve actuations. These profiles facilitate precise control over displacement and velocity, enabling the design of cam mechanisms that optimize performance for specific tasks involving repetitive linear or oscillatory follower movements. Selecting the appropriate follower profile enhances system efficiency, reduces wear, and ensures accurate motion transfer in mechanical components across diverse industrial setups.
Key Differences Between Follower and Cam Profiles
Follower profiles and cam profiles differ primarily in their design and application within mechanical systems. Follower profiles are shaped to trace the contour of a cam, converting rotary motion into precise linear or oscillatory motion, impacting follower displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Cam profiles define the cam's contour that governs follower movement, influencing motion smoothness, mechanical efficiency, and wear characteristics in cam-follower mechanisms.
Types of Cam Profiles: Radial, Tangential, and More
Cam profiles, such as radial and tangential, significantly influence follower motion in mechanical systems. Radial cams produce follower displacement perpendicular to the camshaft, ideal for lift applications, while tangential cams control follower motion through contact along the cam's edge, offering smoother transitions. More complex profiles like harmonic or conjugate cams optimize follower accuracy and minimize backlash in high-precision machinery.
Types of Follower Profiles: Knife Edge, Roller, and Flat
Follower profiles in cams include Knife Edge, Roller, and Flat types, each tailored for specific mechanical needs. Knife Edge followers minimize contact area, reducing friction but increasing wear on cam surfaces, ideal for precision movements. Roller followers incorporate a rolling element to reduce friction and wear significantly, enhancing durability and smooth operation in high-speed or heavy-load applications, while Flat followers provide a balance with broader contact surfaces, offering stability and durability in moderate-speed environments.
Design Considerations for Cam and Follower Profiles
Design considerations for cam and follower profiles prioritize precise geometry to ensure smooth motion transfer and reduce wear. Cam profiles require careful analysis of curvature and pressure angles to maintain consistent contact and avoid jamming during rotation. Follower profiles must accommodate varying cam shapes while providing stable support and minimizing friction for accurate and reliable mechanical performance.
Performance Comparison: Follower Profile vs. Cam Profile
The Follower Profile excels in handling variable loads with its ability to respond dynamically to changing requirements, offering smoother motion under fluctuating torque conditions. In contrast, the Cam Profile provides superior precision and repeatability in complex motion patterns due to its rigid, predefined path, resulting in optimized timing and accuracy. Performance comparison reveals the Follower Profile's advantage in adaptability and energy efficiency, while the Cam Profile dominates in high-precision applications demanding consistent positional control.
Common Applications of Cam and Follower Systems
Follower profiles and cam profiles are essential components in cam and follower systems, widely applied in automotive engines and automated machinery. Cam profiles determine the motion type--such as translating or oscillating--and influence follower displacement, velocity, and acceleration critical for valve timing in internal combustion engines and precise actuation in textile machinery. Follower profiles accommodate various shapes like knife-edge or roller types, optimizing contact efficiency and wear resistance in packaging machines and printing presses.
Future Trends in Cam-Follower Mechanisms
Future trends in cam-follower mechanisms emphasize the development of intelligent follower profiles that adapt to dynamic loads and reduce wear through advanced materials and coatings. Innovations in follower profile geometry, such as asymmetric and variable curvature designs, enhance performance by optimizing contact stress distribution and minimizing friction. Integration of sensor technology in cam followers enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, driving increased reliability and efficiency in automotive and industrial applications.
Follower profile Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com