Hydraulic drive systems use fluid power to transmit energy, offering precise control and high force output in various industrial applications. These systems are essential for heavy machinery, enabling efficient movement and operation under demanding conditions. Discover how your operations can benefit from the strengths of hydraulic drives by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
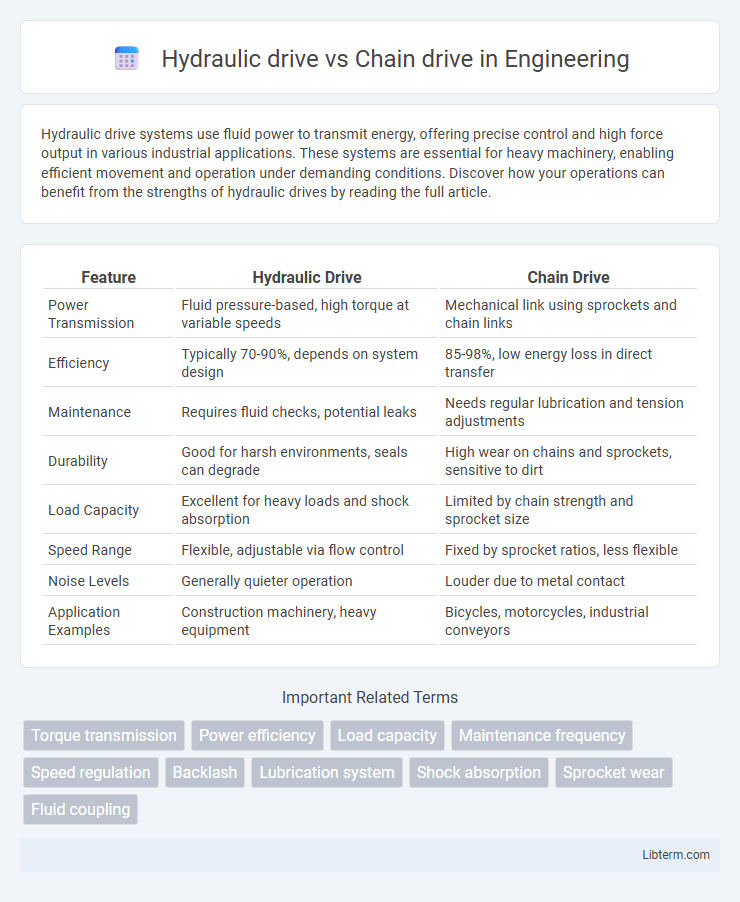
| Feature | Hydraulic Drive | Chain Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Power Transmission | Fluid pressure-based, high torque at variable speeds | Mechanical link using sprockets and chain links |
| Efficiency | Typically 70-90%, depends on system design | 85-98%, low energy loss in direct transfer |
| Maintenance | Requires fluid checks, potential leaks | Needs regular lubrication and tension adjustments |
| Durability | Good for harsh environments, seals can degrade | High wear on chains and sprockets, sensitive to dirt |
| Load Capacity | Excellent for heavy loads and shock absorption | Limited by chain strength and sprocket size |
| Speed Range | Flexible, adjustable via flow control | Fixed by sprocket ratios, less flexible |
| Noise Levels | Generally quieter operation | Louder due to metal contact |
| Application Examples | Construction machinery, heavy equipment | Bicycles, motorcycles, industrial conveyors |
Introduction to Hydraulic and Chain Drives
Hydraulic drives utilize fluid power to transmit energy through pressurized liquids, offering precise control and high torque at low speeds, commonly used in heavy machinery and industrial applications. Chain drives transmit mechanical power through interlocking metal links, providing efficient torque transfer and durability in applications like bicycles and motorcycles. Understanding their fundamental operating principles highlights hydraulic drives' flexibility and smooth operation versus chain drives' simplicity and mechanical robustness.
How Hydraulic Drives Work
Hydraulic drives operate by using pressurized fluid to transmit power through a system of pumps, valves, and cylinders, converting hydraulic energy into mechanical motion. This method offers precise control over speed and torque, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring smooth, variable power output. In contrast to chain drives, hydraulic systems reduce mechanical wear and provide greater flexibility in power transmission over varying distances and directions.
How Chain Drives Operate
Chain drives operate by transmitting mechanical power through a series of linked metal chains, which engage with toothed sprockets attached to rotating shafts. This direct engagement allows for efficient transfer of torque and precise synchronization between driving and driven components, making chain drives suitable for applications requiring reliable, low-slip motion control. Compared to hydraulic drives, chain drives offer lower energy loss and simpler maintenance, particularly in environments where consistent mechanical linkage is critical.
Key Advantages of Hydraulic Drives
Hydraulic drives offer precise control over torque and speed, allowing for smooth and variable motion in industrial machinery. Their sealed systems reduce maintenance needs compared to chain drives, which require regular lubrication and adjustments to prevent wear. High power density and the ability to transmit force over long distances make hydraulic drives ideal for heavy-duty applications where chain drives may struggle.
Key Advantages of Chain Drives
Chain drives offer superior power transmission efficiency with minimal slippage, making them ideal for high-torque applications. They require less maintenance compared to hydraulic drives, as they do not rely on fluid pressure systems that can leak or degrade over time. Chain drives also provide precise speed ratios and robust performance in harsh environments, where hydraulic systems might face contamination or temperature-related issues.
Efficiency Comparison: Hydraulic vs Chain
Hydraulic drives typically exhibit lower mechanical efficiency, averaging around 70-85%, due to energy losses from fluid friction and leakage, whereas chain drives achieve higher efficiency levels, often exceeding 95%, because of direct mechanical power transmission with minimal losses. Chain drives also maintain consistent efficiency under varying loads and speeds, while hydraulic systems experience efficiency drops during partial loads and frequent start-stop operations. The selection between hydraulic and chain drives hinges on balancing the superior efficiency and reliability of chains against the flexibility and smooth torque control offered by hydraulic systems.
Maintenance Requirements
Hydraulic drives require regular fluid checks, filter replacements, and hose inspections to prevent leaks and ensure optimal pressure performance. Chain drives demand frequent lubrication, tension adjustments, and cleaning to avoid wear and elongation that can compromise efficiency. Maintenance intervals for hydraulic systems tend to be longer but more complex, whereas chain drives involve simpler, more frequent routine care.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Lifespan
Hydraulic drives typically require a higher initial investment due to complex components like pumps and fluid reservoirs, whereas chain drives offer a lower upfront cost with simpler mechanical parts. Lifespan analysis shows chain drives may need more frequent maintenance and replacements due to wear and stretching, while hydraulic drives often provide longer service life with proper fluid management. Cost efficiency over time depends on application demands, with hydraulic systems favored for durability despite higher initial expenses and chain drives preferred for budget-conscious projects with moderate usage.
Common Applications in Industry
Hydraulic drives are commonly used in heavy machinery such as excavators, forklifts, and industrial presses due to their high power density and precise control. Chain drives find widespread application in conveyor systems, agricultural equipment, and motorcycles where efficient mechanical power transmission and durability are essential. Both systems play critical roles in manufacturing, construction, and transportation industries, tailored to specific operational requirements.
Choosing the Right Drive System
Choosing the right drive system involves evaluating the specific needs of your application, where hydraulic drives excel in providing smooth, variable torque and precise control, making them ideal for heavy-duty and industrial machinery. Chain drives offer efficient power transmission with simplicity and cost-effectiveness, suitable for moderate loads and applications requiring less maintenance. Consider factors like load capacity, maintenance requirements, operational environment, and cost when deciding between hydraulic drive and chain drive systems.
Hydraulic drive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com