SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems enable real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes, while HMI (Human-Machine Interface) provides the crucial graphical interface for operators to interact with machines and data. Understanding the integration and functionality of SCADA and HMI can significantly enhance the efficiency and safety of your industrial operations. Explore the rest of the article to discover how these technologies transform modern automation.
Table of Comparison
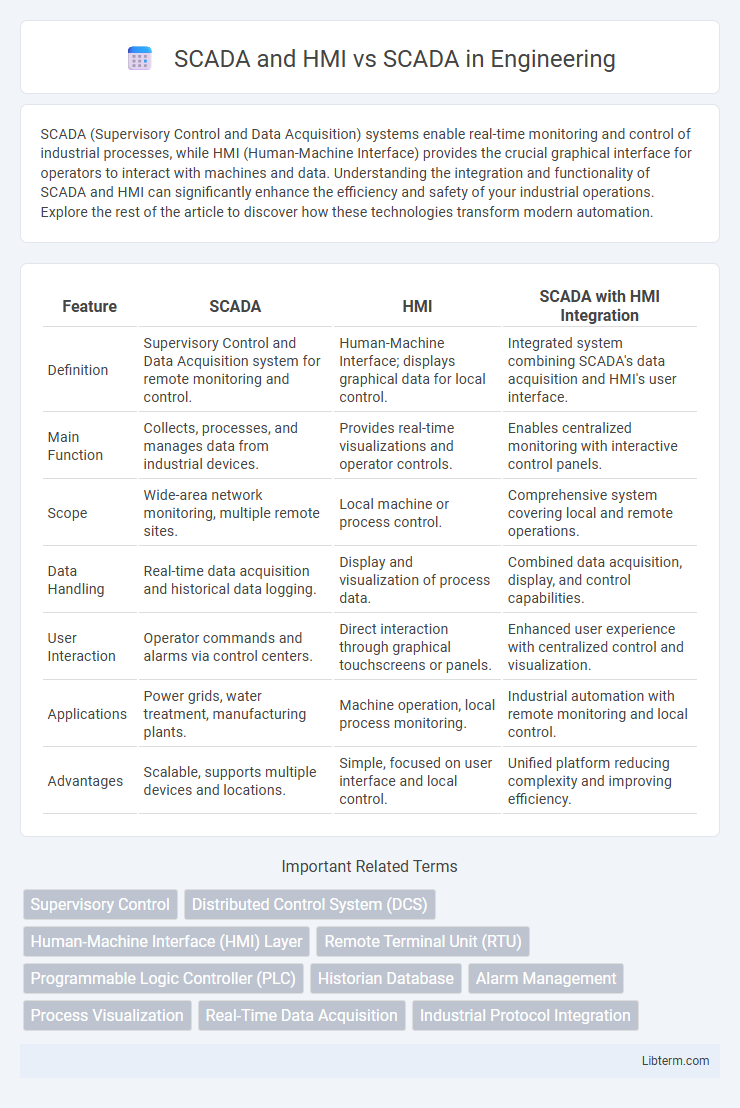
| Feature | SCADA | HMI | SCADA with HMI Integration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition system for remote monitoring and control. | Human-Machine Interface; displays graphical data for local control. | Integrated system combining SCADA's data acquisition and HMI's user interface. |
| Main Function | Collects, processes, and manages data from industrial devices. | Provides real-time visualizations and operator controls. | Enables centralized monitoring with interactive control panels. |
| Scope | Wide-area network monitoring, multiple remote sites. | Local machine or process control. | Comprehensive system covering local and remote operations. |
| Data Handling | Real-time data acquisition and historical data logging. | Display and visualization of process data. | Combined data acquisition, display, and control capabilities. |
| User Interaction | Operator commands and alarms via control centers. | Direct interaction through graphical touchscreens or panels. | Enhanced user experience with centralized control and visualization. |
| Applications | Power grids, water treatment, manufacturing plants. | Machine operation, local process monitoring. | Industrial automation with remote monitoring and local control. |
| Advantages | Scalable, supports multiple devices and locations. | Simple, focused on user interface and local control. | Unified platform reducing complexity and improving efficiency. |
Introduction to SCADA and HMI Systems
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems enable real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes through centralized data collection and analysis. HMI (Human-Machine Interface) serves as the graphical user interface within SCADA systems, allowing operators to interact with machinery and visualize critical operational data. Together, SCADA and HMI optimize industrial automation by enhancing process efficiency, data accuracy, and decision-making capabilities in sectors such as manufacturing, energy, and utilities.
Understanding the Role of SCADA
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems enable real-time monitoring and control of industrial processes by gathering data from sensors and devices across large-scale operations. HMI (Human-Machine Interface) serves as the user interface within SCADA, providing operators with visualizations, controls, and alarm management to interact with the system effectively. Understanding the role of SCADA involves recognizing its function as the backbone for data acquisition and centralized control, whereas HMI translates this data into actionable insights for decision-making.
What is HMI and How Does it Work?
HMI (Human-Machine Interface) is a user interface that connects operators to industrial machinery and processes, enabling real-time monitoring and control through graphical displays, touchscreens, and input devices. It translates complex data from SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems into intuitive visuals, allowing users to interact with automation systems efficiently. Unlike SCADA, which focuses on data collection and analysis across multiple sites, HMI provides localized control and direct interaction with equipment on the factory floor.
SCADA and HMI: Key Differences
SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems provide centralized monitoring and control of industrial processes through data collection, analysis, and real-time visualization. HMI (Human-Machine Interface) serves as the interactive interface that allows operators to communicate with machinery by displaying operational data and enabling command inputs. The key difference lies in SCADA's comprehensive system-wide control and data management capabilities versus HMI's role as a user-friendly graphical display for operator interaction within the SCADA framework.
SCADA vs SCADA: Comparing Architecture and Functionality
SCADA systems integrate real-time data acquisition, communication infrastructure, and centralized control to monitor and manage industrial processes efficiently. In comparison, SCADA vs SCADA architecture differences often lie in the configuration of data acquisition units, network protocols, and scalability options tailored for specific industry needs. Functionality variations stem from software capabilities, including advanced analytics, alarm management, and remote access features that enhance system responsiveness and operational decision-making.
Integration of HMI in Modern SCADA Systems
Modern SCADA systems integrate Human-Machine Interface (HMI) technology to enhance real-time monitoring and control capabilities, providing operators with intuitive visualizations of complex industrial processes. This integration enables seamless data exchange, improved situational awareness, and faster decision-making by combining SCADA's supervisory functions with HMI's interactive graphical displays. Advanced SCADA-HMI solutions support scalable architecture, multi-protocol communication, and customizable dashboards, optimizing operational efficiency and system reliability in manufacturing, energy, and infrastructure sectors.
Advantages of Using SCADA with HMI
SCADA systems integrated with HMI offer enhanced real-time visualization and user-friendly control interfaces, improving operational efficiency and reducing response times during critical events. The combination provides operators with intuitive graphical displays, facilitating easier monitoring and faster troubleshooting of complex industrial processes. This synergy increases accuracy in data interpretation and supports better decision-making compared to SCADA systems without HMI capabilities.
Challenges in SCADA and HMI Implementation
SCADA systems face challenges including cybersecurity vulnerabilities, integration complexities with legacy equipment, and real-time data processing demands. HMI implementation struggles with user interface design that balances simplicity and functionality while ensuring operator responsiveness and error prevention. Both SCADA and HMI require rigorous testing and thorough training to optimize performance and minimize downtime in industrial automation environments.
Choosing the Right Solution: SCADA Only vs SCADA with HMI
Choosing between SCADA only and SCADA with HMI depends on the complexity and user interaction required in your system; SCADA alone excels in data acquisition and control, ideal for automated processes with minimal operator input. Adding an HMI enhances real-time visualization and intuitive user interfaces, improving operator decision-making and system monitoring. Systems requiring detailed graphical representations and user-friendly controls benefit significantly from integrating HMI with SCADA for optimized operational efficiency.
Future Trends in SCADA and HMI Technologies
Advancements in SCADA and HMI technologies emphasize enhanced interoperability, real-time data analytics, and AI-driven predictive maintenance to optimize industrial automation. Integration with IoT and cloud platforms enables scalable remote monitoring and improved cybersecurity measures. Future trends focus on augmented reality interfaces and adaptive machine learning algorithms to elevate operator efficiency and system responsiveness.
SCADA and HMI Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com