Belt drives offer an efficient and cost-effective method for power transmission between rotating shafts, commonly used in machinery and automotive applications. Their flexibility, quiet operation, and ability to absorb shock loads make them ideal for various industrial settings. Discover how belt drives can enhance Your mechanical systems by exploring the detailed insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
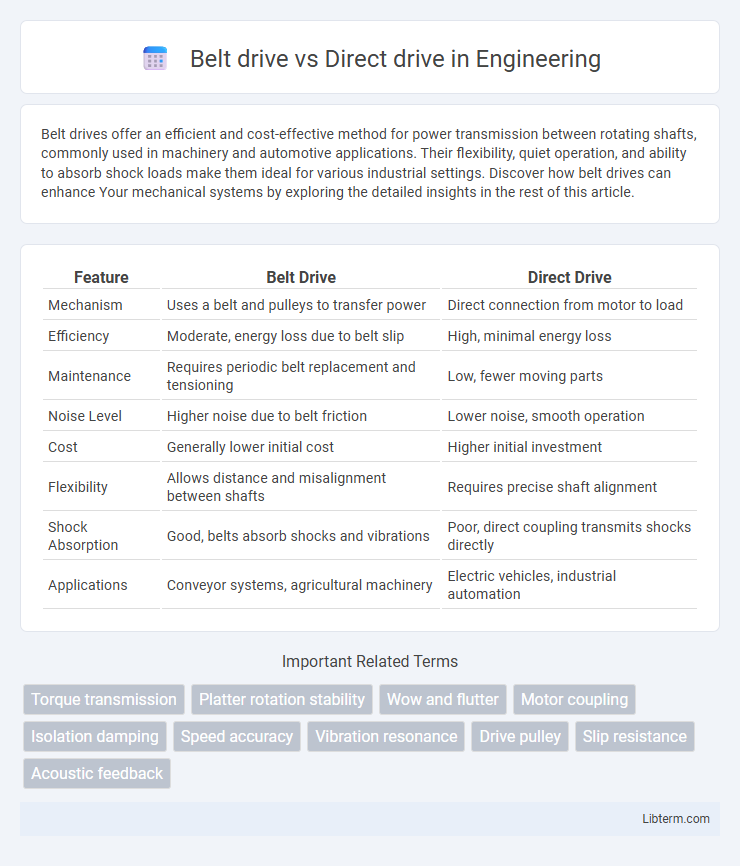
| Feature | Belt Drive | Direct Drive |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanism | Uses a belt and pulleys to transfer power | Direct connection from motor to load |
| Efficiency | Moderate, energy loss due to belt slip | High, minimal energy loss |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic belt replacement and tensioning | Low, fewer moving parts |
| Noise Level | Higher noise due to belt friction | Lower noise, smooth operation |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher initial investment |
| Flexibility | Allows distance and misalignment between shafts | Requires precise shaft alignment |
| Shock Absorption | Good, belts absorb shocks and vibrations | Poor, direct coupling transmits shocks directly |
| Applications | Conveyor systems, agricultural machinery | Electric vehicles, industrial automation |
Introduction to Belt Drive and Direct Drive Systems
Belt drive systems use a flexible belt to transfer rotational motion between pulleys, providing smooth operation and vibration reduction, commonly found in automotive engines and industrial machinery. Direct drive systems connect the motor directly to the driven component, eliminating intermediary mechanisms for improved efficiency, responsiveness, and reduced maintenance, often utilized in electric vehicles and precision equipment. Understanding the mechanical differences highlights the trade-offs in torque transmission, speed control, and durability between belt drive and direct drive technologies.
How Belt Drive Works
Belt drive systems operate by transmitting power from a rotating pulley connected to the motor to another pulley on the driven component via a flexible belt, creating motion through frictional contact. The belt tension and pulley diameter influence torque and speed, enabling smooth, vibration-dampened power transfer suited for various machinery. This mechanism reduces noise and absorbs shocks, enhancing durability and efficiency in applications like turntables, conveyor belts, and automotive engines.
How Direct Drive Works
Direct drive systems function by connecting the motor shaft directly to the load, eliminating intermediary components such as belts or gears, which reduces energy loss and mechanical wear. This setup ensures precise torque transmission and quieter operation, making it ideal for applications requiring high efficiency and low maintenance. The absence of belts also enhances reliability and responsiveness, as the motor's rotational speed is instantly transferred to the driven device.
Key Differences Between Belt Drive and Direct Drive
Belt drive systems utilize a flexible belt to transfer power between pulleys, offering smooth operation and reduced vibration, while direct drive connects the motor directly to the load, enhancing efficiency and reducing maintenance needs. Belt drives typically provide better shock absorption and quieter performance, making them ideal for applications requiring noise reduction, whereas direct drives excel in precision and power transmission with minimal energy loss. The choice between belt drive and direct drive hinges on factors like system complexity, maintenance frequency, impact tolerance, and overall efficiency requirements.
Performance Comparison: Speed, Power, and Efficiency
Belt drive systems typically offer smoother acceleration and quieter operation but may experience slight power loss due to belt slip, affecting overall speed and efficiency compared to direct drive systems. Direct drive mechanisms provide superior power transfer with minimal energy loss, resulting in higher speed capabilities and more consistent performance under load. Efficiency in direct drive often surpasses belt drive by reducing mechanical complexity and maintenance needs, making it ideal for applications demanding precise power and speed control.
Maintenance and Durability Considerations
Belt drive systems require regular maintenance such as belt tension adjustments and periodic replacements due to wear and slippage, impacting long-term durability. Direct drive mechanisms offer superior durability with fewer moving parts, reducing the need for maintenance and minimizing mechanical failures. Choosing between belt drive and direct drive depends on balancing maintenance requirements with expected lifespan and operational conditions.
Noise and Vibration Levels
Belt drive systems generally produce lower noise and vibration levels due to the cushioning effect of the belt, which absorbs shocks and reduces mechanical impacts. Direct drive setups, lacking intermediary components, often generate higher noise and vibration because the motor is directly connected to the load, transmitting any motor imperfections immediately. Manufacturers frequently prefer belt drives for applications requiring quieter operation and smoother performance.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Value
Belt drive systems typically have a lower initial investment due to cheaper components and simpler manufacturing, making them attractive for budget-conscious buyers. Direct drive systems often involve higher upfront costs but deliver superior long-term value with reduced maintenance expenses and improved energy efficiency. Evaluating total cost of ownership highlights that direct drives can offer better ROI through durability and lower operational costs despite their initial price premium.
Best Applications for Belt Drive vs Direct Drive
Belt drives excel in applications requiring vibration isolation and torque flexibility, such as HVAC systems, conveyors, and automotive engines, where shock absorption and noise reduction are crucial. Direct drives are ideal for precision machinery and high-speed applications like robotics, CNC machines, and electric vehicles, offering minimal maintenance and higher efficiency due to the direct motor-to-load connection. Choosing between belt drive and direct drive depends on factors like torque variability, speed requirements, and the necessity for smooth, quiet operation.
Which Drive System Is Right for You?
Belt drive systems offer quieter operation and smoother movement, making them ideal for users seeking low-maintenance and reduced noise, especially in home or office environments. Direct drive systems provide higher torque, greater efficiency, and minimal power loss, which suits those requiring fast, powerful, and precise performance, commonly favored in professional or industrial settings. Choosing between belt drive and direct drive depends on your priorities such as noise level, maintenance, power output, and application intensity.
Belt drive Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com