Signal attenuation refers to the gradual loss of signal strength as it travels through a medium, such as fiber optic cables or air. This reduction impacts data transmission quality, causing slower speeds and potential errors in communication systems. Discover how understanding signal attenuation can help you optimize your network's performance in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
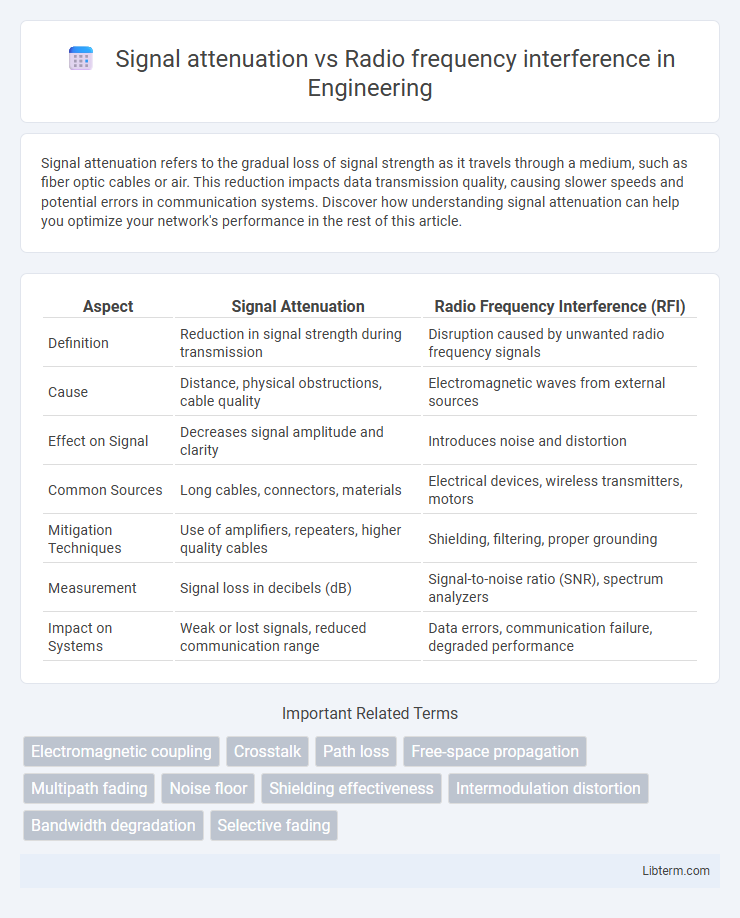
| Aspect | Signal Attenuation | Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduction in signal strength during transmission | Disruption caused by unwanted radio frequency signals |
| Cause | Distance, physical obstructions, cable quality | Electromagnetic waves from external sources |
| Effect on Signal | Decreases signal amplitude and clarity | Introduces noise and distortion |
| Common Sources | Long cables, connectors, materials | Electrical devices, wireless transmitters, motors |
| Mitigation Techniques | Use of amplifiers, repeaters, higher quality cables | Shielding, filtering, proper grounding |
| Measurement | Signal loss in decibels (dB) | Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), spectrum analyzers |
| Impact on Systems | Weak or lost signals, reduced communication range | Data errors, communication failure, degraded performance |
Introduction to Signal Attenuation and Radio Frequency Interference
Signal attenuation refers to the gradual loss of signal strength as it travels through a medium, commonly impacting communication systems by reducing clarity and range. Radio frequency interference (RFI) occurs when unwanted electromagnetic signals disrupt the transmission or reception of radio waves, leading to degraded performance or data loss. Understanding both phenomena is crucial for optimizing wireless communication, as attenuation affects signal quality over distance while RFI introduces noise from external electronic sources.
Defining Signal Attenuation
Signal attenuation refers to the loss of signal strength as it travels through a transmission medium, causing a reduction in signal amplitude and quality. It is primarily influenced by factors such as distance, medium type, and environmental conditions, leading to weaker signals over long distances. Unlike radio frequency interference, which introduces unwanted noise or disruptions, attenuation specifically denotes the degradation of signal power during propagation.
Understanding Radio Frequency Interference (RFI)
Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) occurs when unwanted radio frequency signals disrupt the normal operation of electronic devices, causing degradation in communication quality. Unlike signal attenuation, which is the gradual loss of signal strength due to distance or obstacles, RFI introduces noise and distortion by overlapping or mixing with the desired signal frequencies. Understanding sources such as electronic appliances, wireless devices, and environmental factors is crucial for mitigating RFI and ensuring reliable signal transmission in wireless communication systems.
Key Differences Between Signal Attenuation and RFI
Signal attenuation refers to the gradual loss of signal strength as it travels through a medium, caused by factors such as distance, obstacles, and medium properties, whereas Radio Frequency Interference (RFI) involves unwanted electromagnetic signals disrupting communication by overlapping with the desired frequency. Attenuation results in weaker signal amplitude and reduced quality but does not introduce external noise, while RFI generates noise and distortion by interfering with the signal frequency spectrum. Understanding the key difference lies in attenuation being a natural signal degradation phenomenon, whereas RFI is an external disturbance compromising signal clarity and integrity.
Common Causes of Signal Attenuation
Signal attenuation commonly occurs due to physical obstructions such as walls, buildings, and trees that absorb or weaken radio waves during transmission. Environmental factors like moisture, rain, and atmospheric conditions also degrade signal strength by scattering or absorbing radio frequencies. Material properties including the density and composition of barriers further influence attenuation, reducing the effective range and quality of wireless communication signals.
Major Sources of Radio Frequency Interference
Major sources of radio frequency interference (RFI) include electrical machinery, wireless devices, power lines, and industrial equipment emitting electromagnetic noise that disrupts signal clarity. Signal attenuation differs as it involves the gradual loss of signal strength over distance or through obstacles, whereas RFI introduces external unwanted noise that degrades communication quality. Effective mitigation requires identifying these interference sources to enhance signal integrity and maintain reliable wireless network performance.
Effects of Signal Attenuation on Communication Systems
Signal attenuation causes a reduction in signal strength, leading to degraded communication quality and increased error rates in data transmission. This weakening of signals can result in loss of information, reduced coverage area, and poor voice or video call performance in communication systems. Signal attenuation is critical to address in wireless networks, as it directly impacts signal reliability and overall system efficiency.
Impact of RFI on Signal Quality and Performance
Radio frequency interference (RFI) significantly degrades signal quality by introducing noise that disrupts the clarity and integrity of communications, leading to increased bit error rates and reduced data throughput. Unlike signal attenuation, which gradually weakens the signal strength over distance, RFI causes unpredictable disturbances that can result in intermittent signal loss and compromised performance of wireless systems. Effective mitigation of RFI through filtering, shielding, and adaptive technologies is crucial to maintaining reliable signal transmission and optimal network efficiency.
Mitigation Techniques for Signal Attenuation and RFI
Mitigation techniques for signal attenuation include using signal amplifiers, installing repeaters, and selecting higher-quality cables with lower loss characteristics to maintain signal strength over long distances. To combat radio frequency interference (RFI), deploying shielded cables, implementing proper grounding practices, and utilizing filters such as bandpass or notch filters effectively reduce unwanted noise and improve signal clarity. Combining these strategies ensures improved communication reliability in wireless and wired networks.
Best Practices for Maintaining Reliable Signal Transmission
To maintain reliable signal transmission, minimize signal attenuation by using high-quality coaxial cables with low loss and ensuring proper cable length limitations to prevent weakening of the signal strength. Shielded cables and proper grounding effectively reduce radio frequency interference (RFI), which can cause noise and distortions in communication systems. Employing frequency filters and maintaining clear line-of-sight between transmitter and receiver further enhances signal integrity by mitigating interference and preserving optimal transmission quality.
Signal attenuation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com