Powder coating provides a durable, high-quality finish that resists scratches, chips, and corrosion better than traditional paint. This eco-friendly process uses finely ground particles electrostatically applied and cured under heat to create a smooth, even surface. Discover how powder coating can enhance your project's longevity and appearance by exploring the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
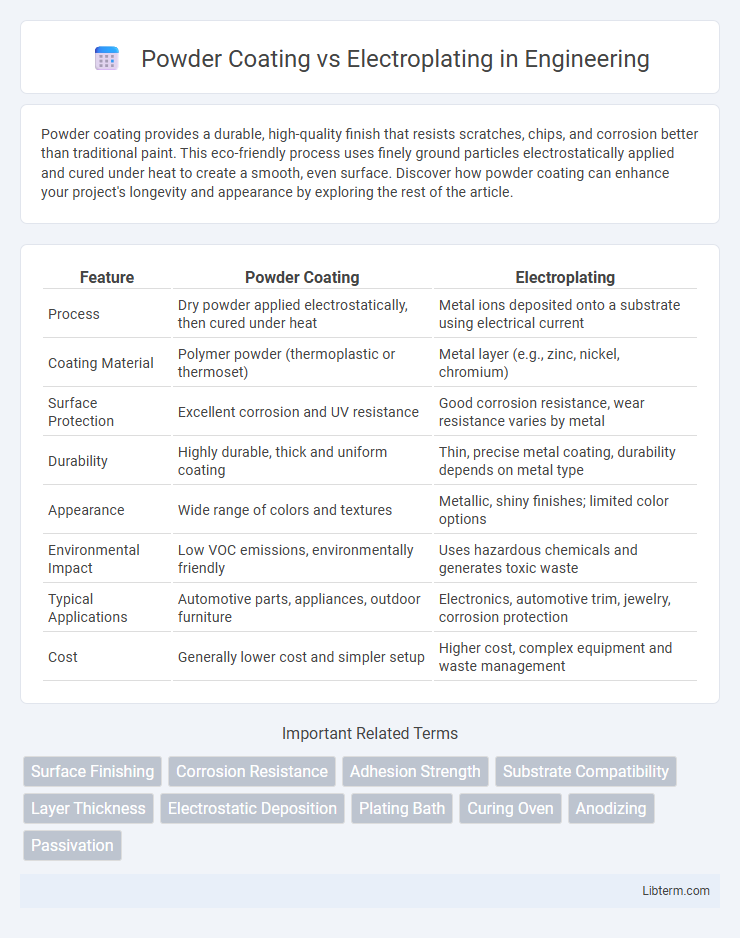
| Feature | Powder Coating | Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Dry powder applied electrostatically, then cured under heat | Metal ions deposited onto a substrate using electrical current |
| Coating Material | Polymer powder (thermoplastic or thermoset) | Metal layer (e.g., zinc, nickel, chromium) |
| Surface Protection | Excellent corrosion and UV resistance | Good corrosion resistance, wear resistance varies by metal |
| Durability | Highly durable, thick and uniform coating | Thin, precise metal coating, durability depends on metal type |
| Appearance | Wide range of colors and textures | Metallic, shiny finishes; limited color options |
| Environmental Impact | Low VOC emissions, environmentally friendly | Uses hazardous chemicals and generates toxic waste |
| Typical Applications | Automotive parts, appliances, outdoor furniture | Electronics, automotive trim, jewelry, corrosion protection |
| Cost | Generally lower cost and simpler setup | Higher cost, complex equipment and waste management |
Introduction to Surface Finishing Techniques
Powder coating and electroplating are two prominent surface finishing techniques used to enhance material durability and aesthetic appeal. Powder coating involves applying a dry powder that is cured under heat to form a protective, corrosion-resistant layer, while electroplating deposits a thin metal layer onto a surface through an electrochemical process for improved conductivity and appearance. Both methods offer unique benefits depending on requirements such as environmental resistance, cost-effectiveness, and desired finish quality.
What is Powder Coating?
Powder coating is a dry finishing process where finely ground particles of pigment and resin are electrostatically charged and sprayed onto a grounded metal surface. The coated object is then heated in an oven, causing the powder to melt and form a smooth, durable, and protective layer that resists corrosion, chipping, and fading. This environmentally friendly method produces a thick, uniform finish without the use of solvents, making it a popular choice for automotive, industrial, and household applications.
What is Electroplating?
Electroplating is a metal finishing process that uses an electric current to deposit a thin layer of metal onto the surface of a conductive object, enhancing its corrosion resistance, appearance, and durability. Common metals used in electroplating include chromium, nickel, gold, and silver, providing various functional and decorative benefits. This process is widely applied in industries such as automotive, electronics, and jewelry manufacturing to improve surface properties and extend the lifespan of components.
Application Processes Compared
Powder coating involves applying a dry powder electrostatically onto a surface and then curing it under heat to form a durable, protective finish ideal for metals and automotive parts. Electroplating uses an electrochemical process to deposit a thin metal layer, such as chromium or nickel, onto a substrate, enhancing corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. While powder coating offers a thicker, uniform coating with environmental benefits due to no solvent emissions, electroplating provides precise, thin metal layers suited for electrical conductivity and intricate component finishes.
Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Powder coating offers superior durability with a thick, uniform layer that resists chipping, scratching, and fading, making it highly effective for long-term corrosion resistance in harsh environments. Electroplating provides a thin, metallic finish that enhances corrosion resistance by creating a protective barrier, though it is more susceptible to wear and requires periodic maintenance. Both methods improve metal protection, but powder coating generally outperforms electroplating in impact resistance and longevity under corrosive conditions.
Cost Analysis: Powder Coating vs Electroplating
Powder coating generally offers lower overall costs compared to electroplating due to reduced material waste and energy consumption during application. Electroplating involves expensive metal salts and requires complex wastewater treatment, increasing operational expenses. For high-volume production, powder coating reduces labor and environmental costs, making it a more economical choice in many industrial applications.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Powder coating produces fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and hazardous waste compared to electroplating, making it a more environmentally friendly option. Electroplating involves toxic chemicals like chromium and cyanide, posing significant occupational health risks and requiring strict disposal protocols. Both processes demand safety precautions, but powder coating's dry application reduces exposure to harmful substances and environmental contamination.
Appearance and Finish Quality
Powder coating provides a smooth, uniform finish with excellent resistance to chipping, fading, and scratching, making it ideal for outdoor and high-wear applications. Electroplating offers a highly reflective, metallic appearance with a thin, durable coating that can enhance corrosion resistance and decorative appeal. The choice depends on desired aesthetics--powder coating delivers a matte or satin finish, while electroplating achieves a glossy, polished surface.
Best Use Cases for Each Method
Powder coating excels in providing a durable, corrosion-resistant finish ideal for outdoor furniture, automotive parts, and industrial equipment exposed to harsh weather conditions. Electroplating is best suited for enhancing electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance on intricate metal components, such as electronic connectors, jewelry, and aerospace parts. Selecting between powder coating and electroplating depends on the required surface properties, environmental exposure, and precision of the finish.
Choosing the Right Technique for Your Project
Powder coating offers a durable, corrosion-resistant finish ideal for outdoor and heavy-use metal applications, providing an environmentally friendly, solvent-free process with vibrant color options. Electroplating delivers a thin, electrically-deposited metal layer that enhances conductivity, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal, commonly used for precision components and decorative finishes. Selecting the right technique depends on factors like desired durability, corrosion protection, surface smoothness, environmental impact, and project budget.
Powder Coating Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com