Thermal spraying is a versatile coating process that applies molten or semi-molten materials onto surfaces to enhance durability, corrosion resistance, and wear protection. This technique is widely used in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and manufacturing to extend the lifespan of critical components. Discover how thermal spraying can improve Your equipment's performance by exploring the insights in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
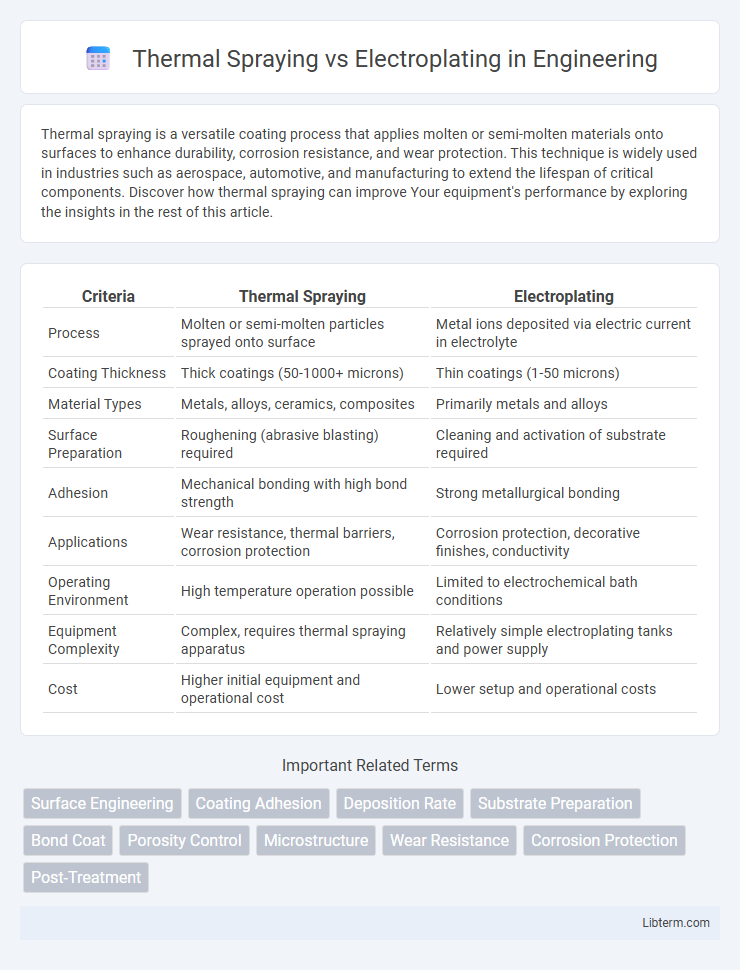
| Criteria | Thermal Spraying | Electroplating |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Molten or semi-molten particles sprayed onto surface | Metal ions deposited via electric current in electrolyte |
| Coating Thickness | Thick coatings (50-1000+ microns) | Thin coatings (1-50 microns) |
| Material Types | Metals, alloys, ceramics, composites | Primarily metals and alloys |
| Surface Preparation | Roughening (abrasive blasting) required | Cleaning and activation of substrate required |
| Adhesion | Mechanical bonding with high bond strength | Strong metallurgical bonding |
| Applications | Wear resistance, thermal barriers, corrosion protection | Corrosion protection, decorative finishes, conductivity |
| Operating Environment | High temperature operation possible | Limited to electrochemical bath conditions |
| Equipment Complexity | Complex, requires thermal spraying apparatus | Relatively simple electroplating tanks and power supply |
| Cost | Higher initial equipment and operational cost | Lower setup and operational costs |
Introduction to Surface Coating Technologies
Thermal spraying and electroplating are pivotal surface coating technologies used to enhance material properties such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and thermal insulation. Thermal spraying involves the deposition of molten or semi-molten materials onto a substrate, creating a thick, robust coating ideal for high-temperature applications. Electroplating uses an electrochemical process to deposit a thin metal layer, offering precise control over coating thickness and excellent surface finish for decorative and functional purposes.
What is Thermal Spraying?
Thermal spraying is a coating process where melted or heated materials are sprayed onto a surface to form a protective or functional layer. It involves techniques like plasma spraying, flame spraying, and arc spraying, which deposit metals, ceramics, or polymers for enhanced wear resistance and corrosion protection. This method offers thicker coatings and better adhesion compared to electroplating, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring durable surface treatments.
What is Electroplating?
Electroplating is a metal coating process that uses an electric current to deposit a thin layer of metal onto a conductive surface, enhancing corrosion resistance, durability, and appearance. This technique typically involves submerging the item in an electrolyte solution containing metal ions from the plating material. Compared to thermal spraying, electroplating offers precise thickness control and superior adhesion for applications requiring uniform metal coatings on complex geometries.
Key Differences Between Thermal Spraying and Electroplating
Thermal spraying involves applying a molten or semi-molten material onto a surface to create a coating, while electroplating uses an electrical current to deposit a metal layer from a solution. Thermal spraying provides thicker coatings with diverse material options, including ceramics and alloys, offering superior wear and corrosion resistance. Electroplating produces thinner, more uniform metal coatings, ideal for decorative finishes and improving electrical conductivity.
Material Compatibility and Applications
Thermal spraying offers broad material compatibility, including metals, ceramics, and polymers, making it suitable for high-temperature and wear-resistant coatings in aerospace and automotive industries. Electroplating is primarily effective with conductive substrates like metals, providing uniform, corrosion-resistant, and decorative finishes used extensively in electronics and jewelry. Selection depends on application requirements, where thermal spraying excels in heavy-duty protective layers and electroplating is ideal for precise, thin, and conductive coatings.
Surface Finish and Coating Thickness Comparison
Thermal spraying typically produces thicker coatings, ranging from 50 to 1,000 microns, with a rougher surface finish requiring additional machining for smoothness. Electroplating offers thinner coatings, usually between 5 to 25 microns, delivering a smoother and more uniform surface finish ideal for fine detailing. The choice between the two methods depends on the desired coating thickness and surface finish precision for the application.
Performance: Durability and Corrosion Resistance
Thermal spraying offers superior durability by applying thick, robust coatings that withstand high abrasion and impact, making it ideal for heavy-duty industrial applications. Electroplating provides excellent corrosion resistance through uniform metallic layers, often with precise thickness control suitable for electrical conductivity and decorative finishes. Both methods enhance surface properties, but thermal spraying excels in mechanical resilience while electroplating is preferred for consistent corrosion protection in less abrasive environments.
Environmental Impact and Safety Considerations
Thermal spraying reduces hazardous waste generation and uses fewer toxic chemicals compared to electroplating, lowering environmental contamination risks. Electroplating often involves heavy metals and acid baths, posing significant health hazards and complex disposal challenges. Safety measures in thermal spraying focus on controlling particulate emissions and heat exposure, while electroplating requires stringent handling of corrosive chemicals and wastewater treatment.
Cost Analysis: Thermal Spraying vs Electroplating
Thermal spraying generally incurs higher initial equipment and material costs compared to electroplating but offers lower operating expenses due to reduced waste and faster processing times. Electroplating demands costly chemicals and generates hazardous waste, increasing disposal and environmental compliance costs over time. Overall, thermal spraying can provide better cost-efficiency for large-scale or heavy-duty applications, while electroplating may be more economical for precise, thin coatings on smaller components.
Choosing the Right Coating Method for Your Needs
Thermal spraying offers superior wear resistance and thickness control for heavy-duty applications, while electroplating provides excellent corrosion protection and precise surface finishes for delicate components. Selection depends on factors such as substrate material, desired coating thickness, environmental exposure, and budget constraints. Evaluate application requirements and performance criteria to determine whether the durability of thermal spraying or the precision of electroplating best suits your project's needs.
Thermal Spraying Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com