Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic approach used to identify the underlying causes of problems or incidents to prevent recurrence. By focusing on the source rather than symptoms, RCA enhances problem-solving efficiency and supports continuous improvement in various industries. Discover how mastering RCA techniques can transform your problem-solving skills by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
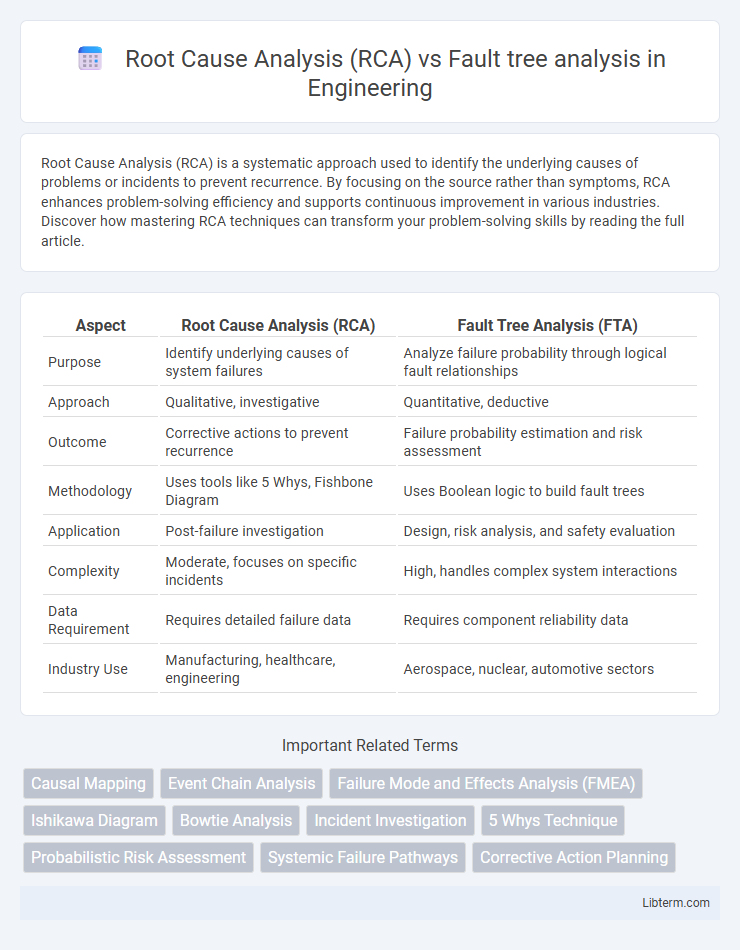
| Aspect | Root Cause Analysis (RCA) | Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify underlying causes of system failures | Analyze failure probability through logical fault relationships |
| Approach | Qualitative, investigative | Quantitative, deductive |
| Outcome | Corrective actions to prevent recurrence | Failure probability estimation and risk assessment |
| Methodology | Uses tools like 5 Whys, Fishbone Diagram | Uses Boolean logic to build fault trees |
| Application | Post-failure investigation | Design, risk analysis, and safety evaluation |
| Complexity | Moderate, focuses on specific incidents | High, handles complex system interactions |
| Data Requirement | Requires detailed failure data | Requires component reliability data |
| Industry Use | Manufacturing, healthcare, engineering | Aerospace, nuclear, automotive sectors |
Introduction to Root Cause Analysis (RCA) and Fault Tree Analysis (FTA)
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic method used to identify the underlying causes of faults or problems by tracing the sequence of events leading to an issue. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a top-down, deductive failure analysis technique that uses Boolean logic to map combinations of hardware or software failures causing a system fault. RCA focuses on understanding root causes to prevent recurrence, while FTA provides a graphical representation of potential fault paths to assess system reliability and risk.
Defining RCA: Principles and Applications
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) identifies the fundamental causes of problems through systematic investigation, emphasizing process improvement and prevention of recurrence. RCA principles include data collection, cause-and-effect analysis, and verification of root causes, ensuring targeted corrective actions. Applications of RCA span manufacturing, healthcare, and IT sectors, where understanding underlying issues enhances quality, safety, and operational efficiency.
Understanding Fault Tree Analysis: Structure and Purpose
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is a top-down, deductive failure analysis method used to identify the root causes of system failures through a graphical representation of fault paths. The structure of FTA begins with a defined undesirable event, represented as the "top event," and systematically breaks it down into immediate causes using logic gates such as AND and OR gates. This visual mapping facilitates understanding of the interrelationships between various faults and assists in quantifying the probability of the top event, making it a vital tool for risk assessment and reliability engineering compared to broader Root Cause Analysis (RCA) approaches.
Key Differences Between RCA and FTA
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) primarily focuses on identifying the underlying causes of a specific problem or failure by systematically tracing back through events and conditions. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) uses a top-down, deductive approach to model the combinations of hardware or software failures that lead to a predefined undesired event, employing Boolean logic to map fault relationships. The key difference lies in RCA's emphasis on root cause identification for corrective actions, while FTA is designed for reliability and safety assessment through structured fault mapping.
Step-by-Step Process of Root Cause Analysis
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) involves systematically identifying the fundamental cause of problems by collecting data, identifying causal factors, and implementing corrective actions to prevent recurrence. The step-by-step process includes defining the problem, gathering evidence, identifying possible causal factors, determining the root cause using tools like the "5 Whys," and developing corrective actions. Unlike Fault Tree Analysis, which uses a top-down, graphical approach to evaluate failure probabilities, RCA focuses on a detailed, investigative methodology to address underlying causes in complex systems.
Fault Tree Analysis Methodology Explained
Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) methodology involves a top-down, deductive approach to identify the root causes of system failures by mapping out fault events using Boolean logic gates like AND and OR. This structured diagram helps visualize the interrelationships between different hardware and software failures, human errors, and environmental factors leading to the undesired event. FTA enables risk assessment and critical failure point identification by quantifying the probability of top-level faults through minimal cut sets and qualitative and quantitative analysis.
When to Use RCA vs. When to Use FTA
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is best utilized when identifying the underlying reasons for a problem by examining cause-and-effect relationships, ideal for addressing recurring issues with complex human factors. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) is more effective for system-level risk assessment and failure analysis, especially in engineering contexts where logical Boolean relationships and system component failures must be traced. Use RCA when the goal is to improve processes and prevent future incidents; choose FTA to analyze system reliability and identify potential points of failure within technical systems.
Advantages and Limitations of RCA and FTA
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) offers a systematic approach to identifying the primary causes of problems, enhancing problem-solving accuracy by focusing on underlying issues rather than symptoms. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) provides a visual, deductive method to analyze failure probabilities and system reliability through logical relationships, enabling quantitative risk assessment. RCA's limitations include potential subjectivity and time consumption, while FTA can be complex to construct for large systems and depends on complete failure data for accuracy.
Real-World Examples: RCA and FTA in Action
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) effectively identified the systemic causes of Toyota's unintended acceleration issues, leading to improved safety protocols and design changes. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) was instrumental in the aerospace industry, specifically in NASA's investigation of the Challenger disaster, by systematically mapping out potential failure paths to prevent future catastrophes. Both methodologies provide complementary insights in complex problem-solving scenarios, enhancing reliability and safety across various industries.
Choosing the Right Analysis Method for Your Organization
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) focuses on identifying the primary causes of problems through systematic investigation, ideal for organizations seeking in-depth understanding of specific incidents. Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) employs a top-down, graphical approach to assess potential failures and their probabilities, best suited for complex systems requiring risk assessment. Selecting the right method depends on organizational goals, with RCA enhancing problem-solving clarity and FTA supporting reliability and safety evaluations in engineering contexts.
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com