Needle bearings are a type of roller bearing characterized by their long, thin cylindrical rollers, which provide a high load-carrying capacity in a compact design. These bearings excel in applications where space is limited but high radial loads must be supported, such as in automotive transmissions and industrial machinery. Discover how needle bearings can enhance your equipment's performance by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
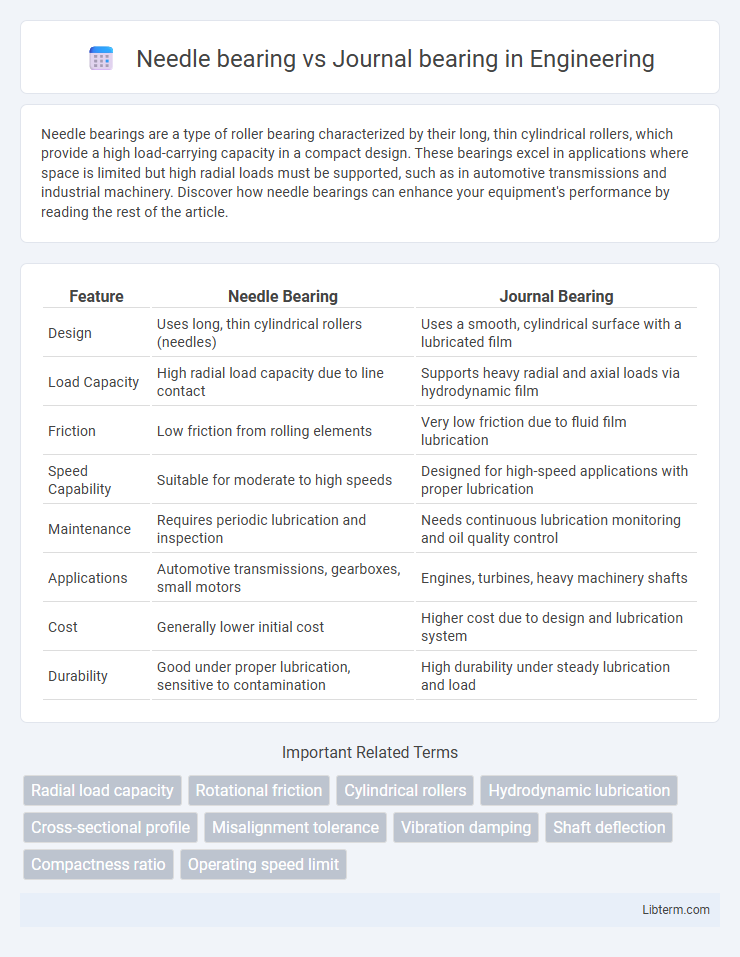
| Feature | Needle Bearing | Journal Bearing |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Uses long, thin cylindrical rollers (needles) | Uses a smooth, cylindrical surface with a lubricated film |
| Load Capacity | High radial load capacity due to line contact | Supports heavy radial and axial loads via hydrodynamic film |
| Friction | Low friction from rolling elements | Very low friction due to fluid film lubrication |
| Speed Capability | Suitable for moderate to high speeds | Designed for high-speed applications with proper lubrication |
| Maintenance | Requires periodic lubrication and inspection | Needs continuous lubrication monitoring and oil quality control |
| Applications | Automotive transmissions, gearboxes, small motors | Engines, turbines, heavy machinery shafts |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost | Higher cost due to design and lubrication system |
| Durability | Good under proper lubrication, sensitive to contamination | High durability under steady lubrication and load |
Introduction to Needle Bearings and Journal Bearings
Needle bearings utilize long, slim cylindrical rollers that reduce friction and support heavy radial loads in compact spaces, making them ideal for automotive transmissions and aerospace components. Journal bearings operate by creating a thin fluid film between a rotating shaft and a bearing surface, providing smooth rotational motion and excellent load distribution in engines and turbines. The distinct structural differences lead to varied applications, where needle bearings excel in high-load, low-speed scenarios and journal bearings are preferred for high-speed, continuous operation environments.
Key Differences Between Needle Bearings and Journal Bearings
Needle bearings feature cylindrical rollers that are much longer than their diameter, providing high load capacity and minimal friction in compact spaces ideal for high-speed applications. Journal bearings use a sliding motion between a shaft and a bearing surface, relying on a thin film of lubricant to reduce friction and support heavy radial loads in low to moderate speed environments. The primary difference lies in the rolling element of needle bearings versus the sliding contact in journal bearings, affecting their load distribution, friction characteristics, and maintenance requirements.
Construction and Design Features
Needle bearings feature numerous slender cylindrical rollers that provide a high load capacity and compact design, ideal for applications with limited radial space. Journal bearings consist of a plain bearing surface supporting a rotating shaft, typically relying on a lubricating film to reduce friction and wear. The distinct construction of needle bearings allows for better load distribution, whereas journal bearings emphasize simplicity and durability in rotating machinery.
Load Capacity and Performance
Needle bearings provide higher load capacity in compact spaces due to their elongated cylindrical rollers that distribute loads over a larger area, making them ideal for heavy radial loads and high-speed applications. Journal bearings, relying on a fluid film for operation, offer excellent performance under varying load conditions and reduce friction through continuous lubrication, enhancing durability in moderate to high-load environments. While needle bearings excel in stiffness and load support, journal bearings outperform in shock absorption and smooth rotational motion under fluctuating loads.
Friction and Efficiency Comparison
Needle bearings exhibit lower friction coefficients compared to journal bearings due to their rolling element design, which significantly reduces metal-to-metal contact and enhances mechanical efficiency in high-speed applications. Journal bearings, relying on a hydrodynamic lubrication film, can achieve low friction under proper lubrication but often experience higher friction losses at startup and low speeds due to boundary lubrication conditions. Efficiency in needle bearings is generally superior in dynamic loads, while journal bearings perform better in shock-absorbing and vibration-damping scenarios, influenced by their frictional characteristics and load distribution mechanisms.
Applications in Various Industries
Needle bearings are extensively used in automotive transmissions and aerospace applications due to their high load capacity and compact design, enabling efficient rotational motion in limited spaces. Journal bearings find widespread application in heavy machinery and power generation equipment, where they support high radial loads and provide smooth, continuous rotation for shafts under variable speed conditions. Both bearing types play critical roles in manufacturing, with needle bearings favored for precision equipment and journal bearings essential for industrial turbines and pumps.
Advantages of Needle Bearings
Needle bearings offer significant advantages such as higher load capacity in a compact design, which makes them ideal for applications with limited space and high radial loads. Their rolling elements reduce friction and wear compared to journal bearings, resulting in improved efficiency and longer service life. Needle bearings also provide better support for oscillating or reciprocating motions, enhancing performance in automotive and industrial machinery.
Advantages of Journal Bearings
Journal bearings offer advantages such as superior load-carrying capacity and excellent damping characteristics under heavy loads and high speeds. Their hydrodynamic lubrication creates a continuous oil film, reducing metal-to-metal contact and wear, which enhances durability and reliability in industrial machinery. Unlike needle bearings, journal bearings provide smoother operation and better vibration absorption in applications like turbines and large engines.
Common Issues and Maintenance Requirements
Needle bearings often face common issues such as lubrication failure, wear due to insufficient grease, and misalignment, which can lead to premature bearing seizure and increased friction. Journal bearings are prone to lubrication breakdown, overheating, and metal-to-metal contact, resulting in scoring and shaft damage; they require regular oil film monitoring and periodic inspection for signs of wear or contamination. Effective maintenance for needle bearings includes routine lubrication and alignment checks, while journal bearings demand consistent oil quality assessment, temperature monitoring, and vibration analysis to prevent mechanical failures.
Choosing the Right Bearing for Your Application
Needle bearings offer high load capacity and compact design ideal for applications with limited radial space, while journal bearings provide smooth operation and durability under heavy, continuous loads. Selecting the right bearing depends on factors like load type, speed, alignment tolerance, and maintenance requirements. For high-speed, oscillating movements, needle bearings excel, whereas journal bearings are preferred for heavy-duty, low-speed uses needing robust lubrication.
Needle bearing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com