Modbus and EtherNet/IP are widely used industrial communication protocols essential for seamless data exchange between devices on factory floors and automation systems. Modbus offers simplicity and compatibility with legacy equipment, while EtherNet/IP provides high-speed, real-time control over standard Ethernet networks. Discover how these protocols can optimize Your industrial processes by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
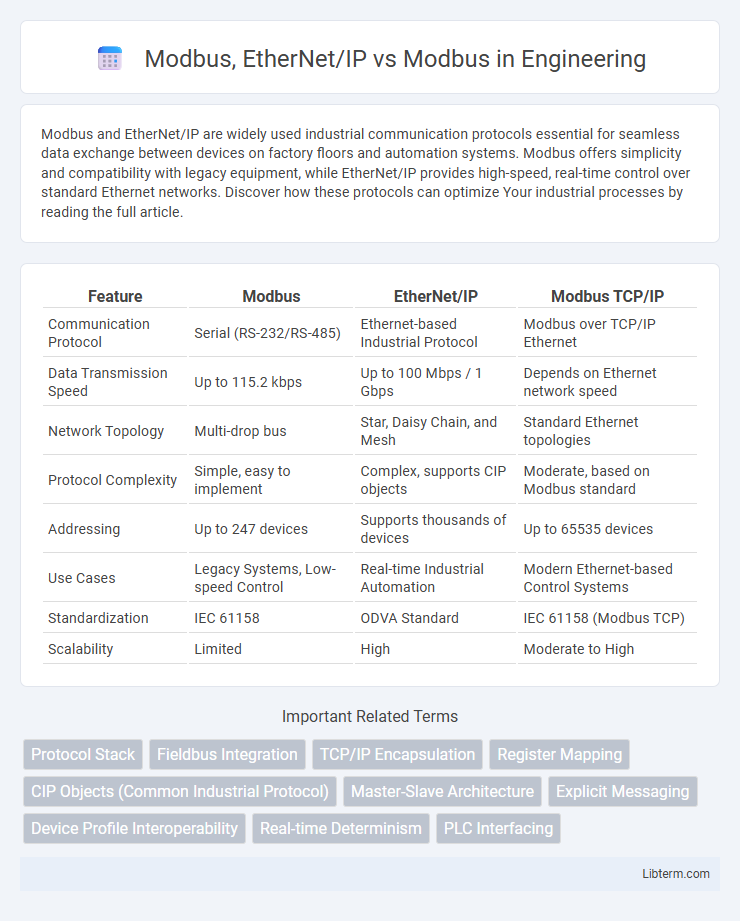
| Feature | Modbus | EtherNet/IP | Modbus TCP/IP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication Protocol | Serial (RS-232/RS-485) | Ethernet-based Industrial Protocol | Modbus over TCP/IP Ethernet |
| Data Transmission Speed | Up to 115.2 kbps | Up to 100 Mbps / 1 Gbps | Depends on Ethernet network speed |
| Network Topology | Multi-drop bus | Star, Daisy Chain, and Mesh | Standard Ethernet topologies |
| Protocol Complexity | Simple, easy to implement | Complex, supports CIP objects | Moderate, based on Modbus standard |
| Addressing | Up to 247 devices | Supports thousands of devices | Up to 65535 devices |
| Use Cases | Legacy Systems, Low-speed Control | Real-time Industrial Automation | Modern Ethernet-based Control Systems |
| Standardization | IEC 61158 | ODVA Standard | IEC 61158 (Modbus TCP) |
| Scalability | Limited | High | Moderate to High |
Introduction to Modbus Communication Protocol
Modbus is a widely used communication protocol in industrial automation for transmitting information between electronic devices, designed for simplicity and robustness. EtherNet/IP extends Modbus by integrating standard Ethernet technology, enabling faster data transfer and seamless network scalability in complex systems. Understanding Modbus's serial communication foundation and its evolution into Ethernet-based systems highlights its critical role in modern industrial environments.
Key Features of Modbus
Modbus is a widely used industrial communication protocol known for its simplicity, ease of implementation, and flexibility in serial communication via RS-232, RS-485, and TCP/IP. Key features of Modbus include a master-slave architecture, support for multiple data types such as coils, discrete inputs, input registers, and holding registers, and a straightforward addressing system that allows efficient device communication in automation systems. Compared to EtherNet/IP, Modbus offers lightweight protocol overhead, making it ideal for low-bandwidth and legacy system integration in manufacturing and process industries.
Overview of EtherNet/IP
EtherNet/IP is an industrial network protocol that uses standard Ethernet and TCP/IP technology for real-time communication, providing seamless integration with existing Ethernet infrastructures. It supports automated control systems by enabling device-level data exchange and is widely adopted in manufacturing and process industries for its scalability and high-speed performance. Unlike Modbus, which primarily focuses on serial communication or Modbus TCP/IP, EtherNet/IP offers a comprehensive application layer built on CIP (Common Industrial Protocol) to facilitate complex industrial control functions.
Modbus vs EtherNet/IP: Main Differences
Modbus and EtherNet/IP are industrial communication protocols with key differences in speed, complexity, and application. Modbus operates on serial communication or TCP/IP for simple, low-level device interactions, while EtherNet/IP uses standard Ethernet infrastructure supporting higher bandwidth and real-time control in complex automation systems. EtherNet/IP offers advanced features like object-oriented data models and extensive device interoperability, contrasting Modbus's straightforward register-based data exchange.
Performance Comparison: Modbus and EtherNet/IP
Modbus primarily operates on serial communication protocols, providing reliable but slower data transfer rates up to 115.2 kbps, whereas EtherNet/IP leverages standard Ethernet infrastructure offering significantly higher speeds up to 100 Mbps or more. EtherNet/IP supports real-time control and large data packets with enhanced network scalability, making it suitable for complex industrial automation systems, while Modbus excels in simpler, low-bandwidth environments. The deterministic performance of EtherNet/IP ensures lower latency and better synchronization compared to Modbus, which experiences higher communication delays due to its master-slave polling mechanism.
Scalability and Network Architecture
Modbus offers simplicity and ease of integration in smaller, point-to-point or serial networks but faces scalability limitations when expanding to large, complex systems due to its master-slave architecture. EtherNet/IP supports scalable network architectures with features like star, ring, and mesh topologies, enabling high-performance communication over standard Ethernet infrastructure ideal for extensive industrial automation systems. The protocol's ability to handle numerous devices and support real-time data exchange enhances system scalability compared to Modbus, making EtherNet/IP suitable for large-scale, distributed control networks.
Integration and Compatibility Issues
Modbus and EtherNet/IP differ significantly in integration and compatibility, with Modbus being a simpler protocol widely supported by diverse legacy industrial devices, enabling easier integration in traditional systems. EtherNet/IP offers advanced features and high-speed communication but often encounters compatibility challenges with older equipment due to its reliance on Ethernet infrastructure and more complex object-oriented data models. Choosing between them depends on the existing network environment, with Modbus favoring straightforward integration in mixed-device setups and EtherNet/IP optimized for modern, Ethernet-based industrial automation systems.
Security Considerations for Modbus and EtherNet/IP
Modbus traditionally lacks built-in security features, making it vulnerable to interception and unauthorized access, whereas EtherNet/IP incorporates enhanced security protocols such as CIP Security for improved authentication and encryption. The absence of inherent encryption in Modbus necessitates additional security measures like VPNs or firewalls to protect data integrity and confidentiality. EtherNet/IP's design aligns better with modern industrial network security requirements, offering protection against cyber threats through robust device identity verification and secure communication channels.
Typical Industrial Applications
Modbus is widely used in applications requiring simple, reliable serial communication for programmable logic controllers (PLCs), remote terminal units (RTUs), and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. EtherNet/IP excels in complex industrial automation environments needing high-speed, real-time data exchange among advanced devices like motor drives, sensors, and robotics on Ethernet networks. Both protocols support manufacturing processes, but EtherNet/IP offers enhanced scalability and interoperability for sophisticated industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) solutions.
Choosing the Right Protocol: Modbus or EtherNet/IP
Choosing the right protocol between Modbus and EtherNet/IP depends on the specific industrial communication needs and network infrastructure. Modbus offers simplicity and wide compatibility with serial and TCP/IP communication, making it ideal for small to medium-scale automation systems. EtherNet/IP provides enhanced performance, scalability, and support for complex real-time data and device integration within Ethernet-based networks, suitable for large-scale industrial environments.
Modbus, EtherNet/IP Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com