Bourdon tube pressure gauges are precise instruments used to measure pressure in various industrial applications by converting pressure into mechanical displacement through a curved tube. Their durable design and accuracy make them ideal for monitoring systems in HVAC, automotive, and manufacturing sectors. Discover how understanding Bourdon tube pressure gauges can enhance your equipment maintenance and performance by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
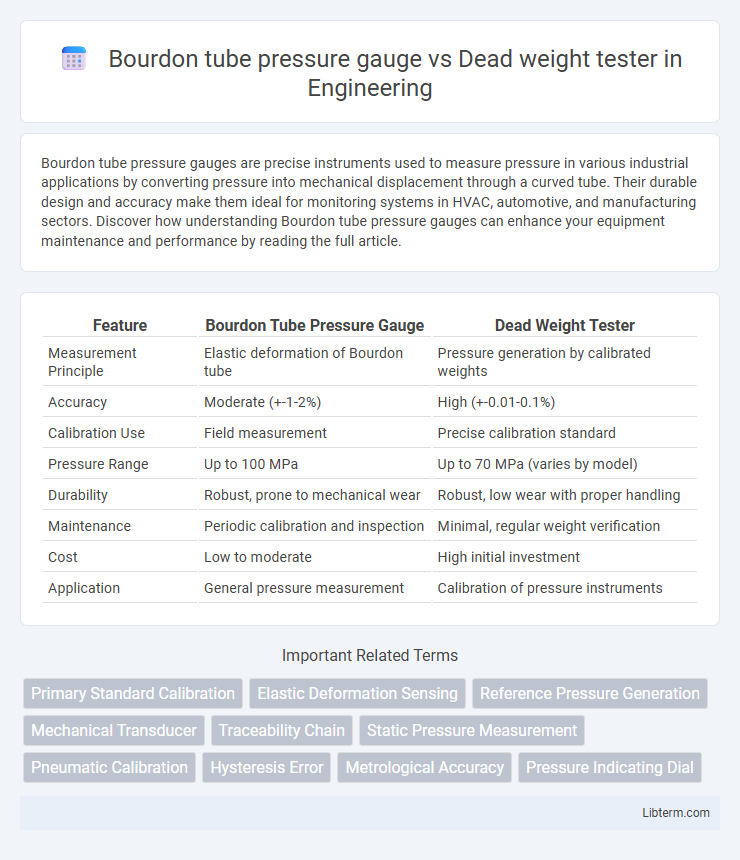
| Feature | Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauge | Dead Weight Tester |
|---|---|---|
| Measurement Principle | Elastic deformation of Bourdon tube | Pressure generation by calibrated weights |
| Accuracy | Moderate (+-1-2%) | High (+-0.01-0.1%) |
| Calibration Use | Field measurement | Precise calibration standard |
| Pressure Range | Up to 100 MPa | Up to 70 MPa (varies by model) |
| Durability | Robust, prone to mechanical wear | Robust, low wear with proper handling |
| Maintenance | Periodic calibration and inspection | Minimal, regular weight verification |
| Cost | Low to moderate | High initial investment |
| Application | General pressure measurement | Calibration of pressure instruments |
Introduction to Pressure Measurement Devices
Bourdon tube pressure gauges measure pressure through the elastic deformation of a curved tube, offering real-time analog readings in industrial applications. Dead weight testers provide highly accurate pressure standards by applying known weights to a piston, essential for calibrating and validating other pressure measurement devices. Both tools play crucial roles in ensuring precise pressure monitoring and calibration across various engineering and manufacturing processes.
Overview of Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauges
Bourdon tube pressure gauges operate by converting pressure-induced deformation of a curved, elastic tube into mechanical displacement, providing visual pressure readings. These gauges are widely used for measuring medium to high pressures in various industrial applications due to their robustness and reliability. Unlike dead weight testers, which serve as precision calibration instruments by applying known weights to measure pressure, Bourdon gauges function primarily as practical, real-time pressure indicators.
Understanding the Dead Weight Tester
The Dead Weight Tester provides highly accurate pressure calibration by applying known weights to a piston, generating precise reference pressures used to verify and adjust other gauges, including Bourdon tube pressure gauges. Unlike the Bourdon tube gauge, which relies on the mechanical deformation of a curved tube under pressure to produce a reading, the Dead Weight Tester's accuracy stems from the direct measurement of force over a known area. This makes it an essential tool in calibration laboratories where traceability and exact pressure standards are critical for maintaining measurement reliability.
Key Differences Between Bourdon Tube Gauges and Dead Weight Testers
Bourdon tube pressure gauges measure pressure by the deformation of a curved tube, providing continuous real-time pressure readings suitable for various industrial applications. In contrast, dead weight testers function as calibration devices using known weights to generate accurate reference pressures, ensuring precision and traceability in calibration standards. Key differences lie in their operational purpose--Bourdon gauges for monitoring pressure and dead weight testers for precise calibration--along with accuracy levels, with dead weight testers offering superior measurement reliability.
Accuracy and Precision: A Comparative Analysis
Bourdon tube pressure gauges offer reliable accuracy within +-1-3% of full scale, making them suitable for general industrial applications, while dead weight testers provide superior precision with accuracy often better than +-0.01%, serving as primary standards for calibration. Dead weight testers utilize known masses to apply precise pressure, eliminating mechanical error sources inherent in Bourdon tubes, which can experience wear and hysteresis over time. The choice between the two depends on the required measurement fidelity, with dead weight testers favored for high-accuracy calibration and Bourdon gauges preferred for cost-effective, continuous pressure monitoring.
Applications and Use Cases
Bourdon tube pressure gauges are widely used in industrial processes for monitoring and controlling fluid pressure in hydraulic systems, HVAC units, and manufacturing equipment due to their durability and real-time pressure indication. Dead weight testers serve as precision pressure calibration devices in laboratories and maintenance facilities, ensuring accuracy by applying known weights to generate standard pressure levels for calibrating other instruments. The Bourdon tube gauge offers continuous operational feedback, while dead weight testers are essential for traceable calibration and validation of pressure measurement tools.
Calibration Methods and Standards
Bourdon tube pressure gauges are calibrated using comparative methods against known pressure standards, often referencing a dead weight tester to ensure accuracy and traceability to national metrology institutes. Dead weight testers provide primary calibration by applying precise, traceable weights to generate exact pressure values, serving as the gold standard for calibrating pressure measurement devices. Calibration standards such as ISO/IEC 17025 and ANSI/NCSL Z540.3 dictate the procedures and environmental conditions to maintain measurement reliability and validation during both Bourdon tube gauge and dead weight tester calibration.
Pros and Cons of Bourdon Tube Pressure Gauges
Bourdon tube pressure gauges offer durability, ease of use, and real-time pressure readings without requiring external power, making them ideal for general industrial applications. However, they can exhibit lower accuracy compared to dead weight testers, especially in calibration standards, and may be affected by mechanical wear and environmental vibrations. Despite these limitations, Bourdon gauges remain cost-effective and versatile instruments widely used for pressure monitoring in various systems.
Advantages and Limitations of Dead Weight Testers
Dead weight testers offer highly accurate and reliable pressure calibration by applying known weights to generate precise reference pressures, making them essential for verifying and calibrating Bourdon tube pressure gauges. Their main advantage lies in traceability and minimal measurement uncertainty, ideal for laboratory and field calibration tasks. Limitations include their bulkiness, sensitivity to environmental factors like vibration and temperature, and slower operation compared to direct-reading devices.
Choosing the Right Instrument for Your Needs
Bourdon tube pressure gauges offer real-time, mechanical pressure readings ideal for continuous monitoring in industrial and HVAC applications, providing durability and ease of installation. Dead weight testers serve as highly accurate calibration devices, using known weights to validate pressure instruments, making them essential for laboratories and quality control. Selecting the right instrument depends on whether ongoing measurement or precision calibration is the priority, aligning with specific operational requirements and accuracy standards.
Bourdon tube pressure gauge Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com