Robotics integrates mechanical engineering, electronics, computer science, and artificial intelligence to create machines capable of performing complex tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention. Advances in sensor technology and machine learning have dramatically enhanced robot precision, adaptability, and efficiency across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics. Explore this article to discover how robotics is revolutionizing your world and shaping the future of technology.
Table of Comparison
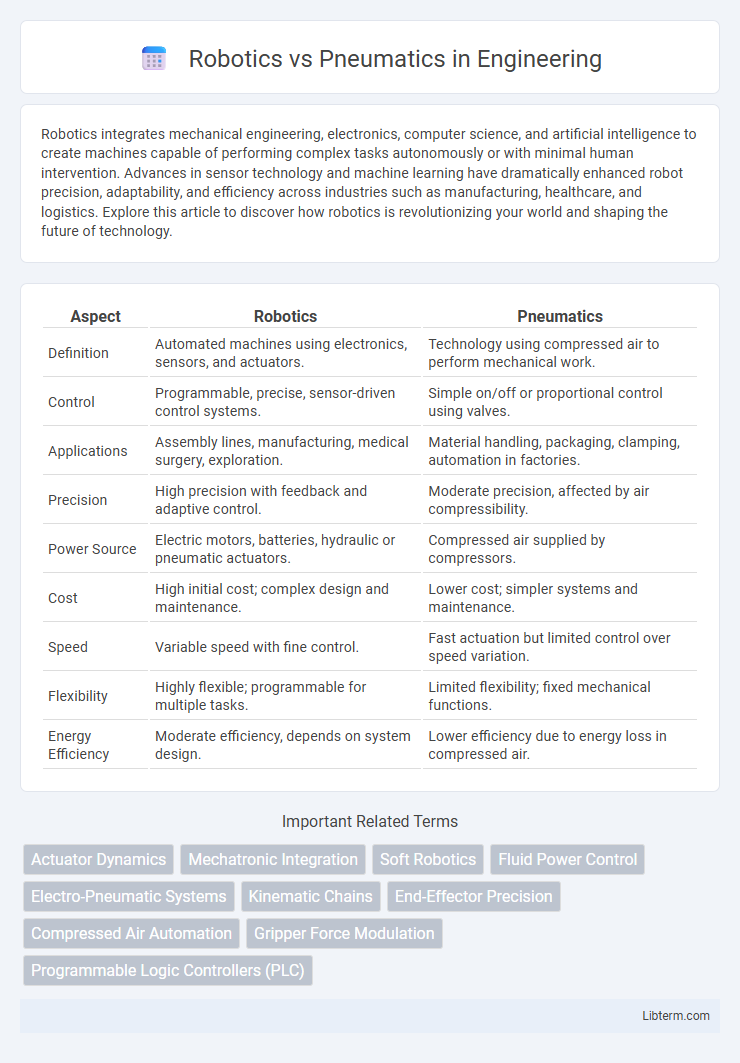
| Aspect | Robotics | Pneumatics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated machines using electronics, sensors, and actuators. | Technology using compressed air to perform mechanical work. |
| Control | Programmable, precise, sensor-driven control systems. | Simple on/off or proportional control using valves. |
| Applications | Assembly lines, manufacturing, medical surgery, exploration. | Material handling, packaging, clamping, automation in factories. |
| Precision | High precision with feedback and adaptive control. | Moderate precision, affected by air compressibility. |
| Power Source | Electric motors, batteries, hydraulic or pneumatic actuators. | Compressed air supplied by compressors. |
| Cost | High initial cost; complex design and maintenance. | Lower cost; simpler systems and maintenance. |
| Speed | Variable speed with fine control. | Fast actuation but limited control over speed variation. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; programmable for multiple tasks. | Limited flexibility; fixed mechanical functions. |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate efficiency, depends on system design. | Lower efficiency due to energy loss in compressed air. |
Introduction: Understanding Robotics and Pneumatics
Robotics involves the design and use of programmable machines capable of performing complex tasks autonomously or semi-autonomously, utilizing sensors, actuators, and control systems to mimic human functions. Pneumatics operates through the use of compressed air to power mechanical motion and control systems, primarily in industrial automation for simple, repetitive actions. Understanding the key principles and applications of both technologies highlights their complementary roles in enhancing efficiency and precision across manufacturing and automation sectors.
Core Principles of Robotics Technology
Robotics technology centers on programmable machines capable of performing complex tasks through sensors, actuators, and control systems, emphasizing precision, adaptability, and autonomous decision-making. Pneumatics relies on compressed air to power mechanical motions, typically offering straightforward, repetitive movements with limited flexibility compared to robotics. The core principles of robotics integrate advanced software algorithms and feedback loops enabling dynamic interaction with environments, distinguishing it from the fixed, linear operations in pneumatic systems.
Fundamentals of Pneumatic Systems
Pneumatic systems operate using compressed air to transmit and control energy, relying on components such as compressors, valves, actuators, and air tanks. These systems provide precise motion control with rapid response times and are valued for their simplicity, cleanliness, and cost-effectiveness in industrial automation. Unlike robotics, which often integrates complex electronic controls and software for versatile tasks, pneumatic fundamentals emphasize reliable mechanical energy transfer through air pressure and flow regulation.
Key Differences Between Robotics and Pneumatics
Robotics involves the design, construction, and operation of programmable machines capable of performing complex tasks through sensors, actuators, and software control, while pneumatics uses compressed air to power mechanical motion in simpler, repetitive applications. Robotics systems offer high precision, adaptability, and integration with artificial intelligence, whereas pneumatic systems are valued for their cost-effectiveness, reliability, and ease of maintenance. The key differences lie in automation complexity, control methods, and application versatility, with robotics dominating advanced manufacturing and pneumatics excelling in basic industrial automation.
Applications of Robotics in Modern Industries
Robotics revolutionizes modern industries by automating tasks ranging from assembly lines in automotive manufacturing to precision surgery in healthcare, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Unlike pneumatics, which primarily powers simple mechanical motions through compressed air, robotics integrates advanced sensors, AI, and machine learning for complex decision-making and adaptability. This technological synergy in factories, warehouses, and laboratories drives productivity and innovation beyond traditional pneumatic systems.
Industrial Uses of Pneumatic Systems
Pneumatic systems dominate industrial applications due to their reliability, simplicity, and cost-effectiveness in powering tools, conveyors, and automation equipment. Commonly deployed in manufacturing, packaging, and assembly lines, pneumatics provide fast, precise control of movement with minimal maintenance requirements. Their ability to operate safely in hazardous environments makes them indispensable for industries requiring robust and efficient mechanical actuation.
Efficiency and Precision: Robotics vs Pneumatics
Robotics systems offer superior precision with advanced sensors and programmable controls, enabling exact movements and repeatability in complex tasks. Pneumatics provide efficient energy use in simple, high-speed applications but suffer from lower accuracy due to compressible air and mechanical limitations. Efficiency in robotics is driven by optimized algorithms and electric actuators, while pneumatics rely on rapid actuation but encounter energy losses and reduced control fidelity.
Cost Comparison: Upfront and Maintenance Considerations
Robotics systems typically involve higher upfront costs due to advanced sensors, control units, and programming requirements, whereas pneumatics offer a lower initial investment with simpler hardware. Maintenance expenses for robotics can be significant, driven by complex software updates and specialized repairs, while pneumatic systems incur lower maintenance costs given their straightforward mechanical components and easier troubleshooting. Evaluating total cost of ownership requires balancing robotics' higher automation capabilities against the economical and reliable nature of pneumatics in repetitive, less complex applications.
Safety and Reliability Factors
Robotics systems offer enhanced safety through precise control and programmable responses that minimize human error and hazardous exposure, while pneumatic systems rely on compressed air and mechanical components that can introduce risks like leaks or pressure failures. Reliability in robotics is boosted by advanced sensors and feedback loops enabling real-time fault detection, whereas pneumatics may experience inconsistent performance due to air quality and maintenance issues. Implementing robotics reduces downtime and accident rates by integrating fail-safes and redundant systems, compared to pneumatics which require rigorous inspections to ensure operational integrity.
Future Trends: The Evolution of Robotics and Pneumatics
Advancements in robotics focus on integrating artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance automation, precision, and adaptability across industries, while pneumatics evolve with energy-efficient and smart control systems for cost-effective actuation. Emerging trends highlight the convergence of robotics and pneumatics in collaborative robots (cobots) that utilize pneumatic components for lightweight, flexible movement alongside advanced robotic controls. Future developments prioritize sustainability, improved sensors, and real-time data analytics to optimize the performance and integration of both technologies in manufacturing and healthcare.
Robotics Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com