Partitioning a hard drive allows you to organize data efficiently by dividing a single physical storage device into separate, manageable sections. This process can improve system performance, enable multiple operating systems, and simplify file management. Explore the full article to learn how partitioning can optimize your storage setup and enhance overall computer functionality.
Table of Comparison
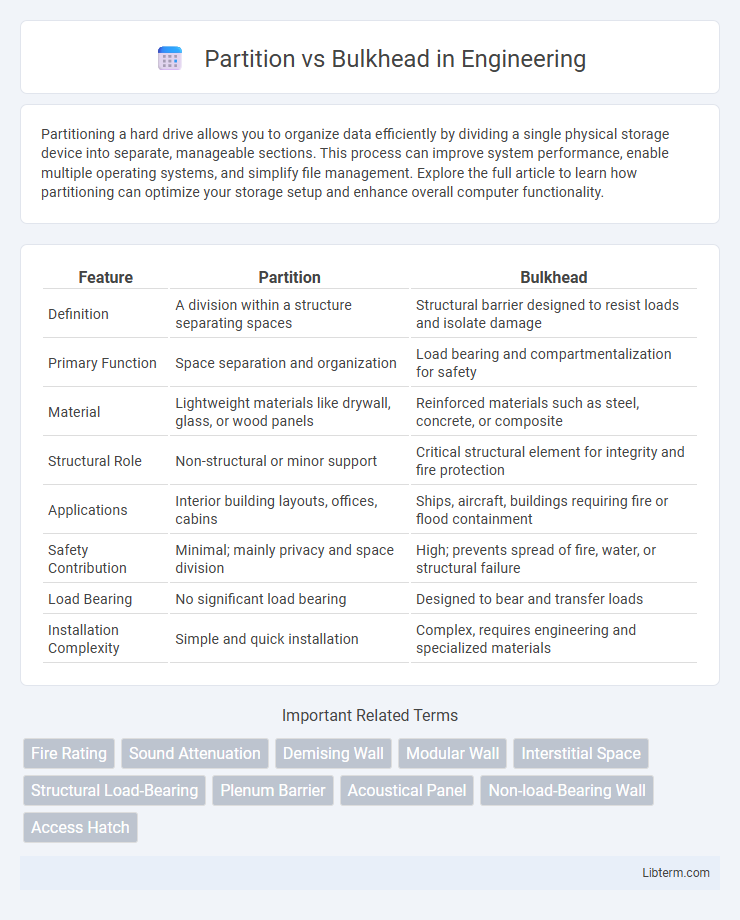
| Feature | Partition | Bulkhead |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A division within a structure separating spaces | Structural barrier designed to resist loads and isolate damage |
| Primary Function | Space separation and organization | Load bearing and compartmentalization for safety |
| Material | Lightweight materials like drywall, glass, or wood panels | Reinforced materials such as steel, concrete, or composite |
| Structural Role | Non-structural or minor support | Critical structural element for integrity and fire protection |
| Applications | Interior building layouts, offices, cabins | Ships, aircraft, buildings requiring fire or flood containment |
| Safety Contribution | Minimal; mainly privacy and space division | High; prevents spread of fire, water, or structural failure |
| Load Bearing | No significant load bearing | Designed to bear and transfer loads |
| Installation Complexity | Simple and quick installation | Complex, requires engineering and specialized materials |
Introduction to Partitions and Bulkheads
Partitions and bulkheads serve as structural divisions within ships and buildings, designed to enhance safety and functionality by compartmentalizing spaces. Partitions are typically non-load-bearing walls that provide separation of interior areas, improving organization and privacy without significantly contributing to the structural integrity. Bulkheads, in contrast, are load-bearing walls crucial for maintaining the vessel's or structure's stability, often acting as watertight barriers to prevent flooding and contain damage in emergencies.
Definition of Partition
Partition is a technique that divides a system into isolated segments to enhance fault tolerance and limit the impact of failures, ensuring system stability and uptime. Bulkhead, inspired by shipbuilding, isolates critical components so failures in one partition do not affect others, preventing cascading failures. Partitioning enables distributed processing by segregating workloads, which improves scalability and resource management in complex architectures.
Definition of Bulkhead
Bulkhead is a design principle that isolates components or systems to prevent failure from spreading, enhancing overall system resilience and reliability. Unlike partitioning, which divides workloads or data sets for organizational purposes, bulkheads create independent barriers that contain faults within specific sections. This concept is widely used in software architecture and engineering to improve fault tolerance and maintain operational stability.
Key Differences Between Partition and Bulkhead
Partitions divide a system or component into isolated sections to prevent failure from spreading, while bulkheads serve as physical barriers primarily in ships or aircraft to contain damage within a compartment. Partitions focus on logical or functional separation without necessarily bearing structural loads, whereas bulkheads are structural elements designed to withstand pressure and maintain integrity under stress. Furthermore, partitions are often flexible and adaptable for modular design, while bulkheads are rigid and critical for safety and stability.
Structural Functions and Applications
Partitions serve as internal dividers in buildings, creating distinct rooms and spaces to enhance privacy, organization, and usability. Bulkheads function as protective barriers, often used to isolate structural components or systems, ensuring safety and preventing damage in critical areas such as machinery rooms or hazardous zones. Both elements play crucial roles in architectural design, with partitions optimizing spatial layout and bulkheads reinforcing structural integrity.
Materials Used in Partitions vs Bulkheads
Partitions are typically constructed from lightweight materials like gypsum board, glass, wood, or metal studs, designed for easy installation and flexibility in interior layouts. Bulkheads are made using more robust materials such as steel, concrete, or fire-resistant drywall assemblies to provide structural support and fire containment within buildings. The material choice for bulkheads prioritizes durability and safety compliance, while partitions emphasize cost-effectiveness and adaptability.
Advantages of Using Partitions
Partitions enhance system reliability by isolating faults within specific zones, preventing errors from spreading across the entire infrastructure. They simplify maintenance and upgrades by allowing targeted interventions without disrupting other components. Partitions optimize resource allocation, improving performance and scalability in complex architectures.
Advantages of Using Bulkheads
Bulkheads provide superior fault isolation by containing failures within individual compartments, preventing cascading system-wide outages. Their design enhances reliability and availability in distributed systems, as each bulkhead operates independently and limits resource contention. This architecture also improves scalability by allowing targeted resource allocation and focused recovery processes for isolated components.
Common Industries Utilizing Partitions and Bulkheads
Common industries utilizing partitions and bulkheads include maritime shipping, aerospace, automotive, and construction, where these structural elements enhance safety and compartmentalization. In maritime vessels, bulkheads prevent flooding and maintain hull integrity, while partitions organize internal spaces for crew and cargo. Automotive and aerospace sectors employ partitions and bulkheads to improve crashworthiness and optimize cabin layouts, ensuring regulatory compliance and passenger protection.
Choosing Between Partition and Bulkhead: Factors to Consider
Choosing between partition and bulkhead depends on factors like system isolation requirements, fault tolerance levels, and resource allocation strategies. Partitions maximize system utilization by dividing resources logically within a shared environment, while bulkheads provide physical or logical segregation to prevent cascading failures. Consider workload characteristics, failure impact scope, and complexity of management when deciding the optimal approach.
Partition Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com