Flat belts provide efficient power transmission in various industrial applications due to their flexibility and smooth operation. They are ideal for long-distance, high-speed drives and reduce vibration and noise compared to other belt types. Explore the benefits and applications of flat belts to enhance your machinery's performance.
Table of Comparison
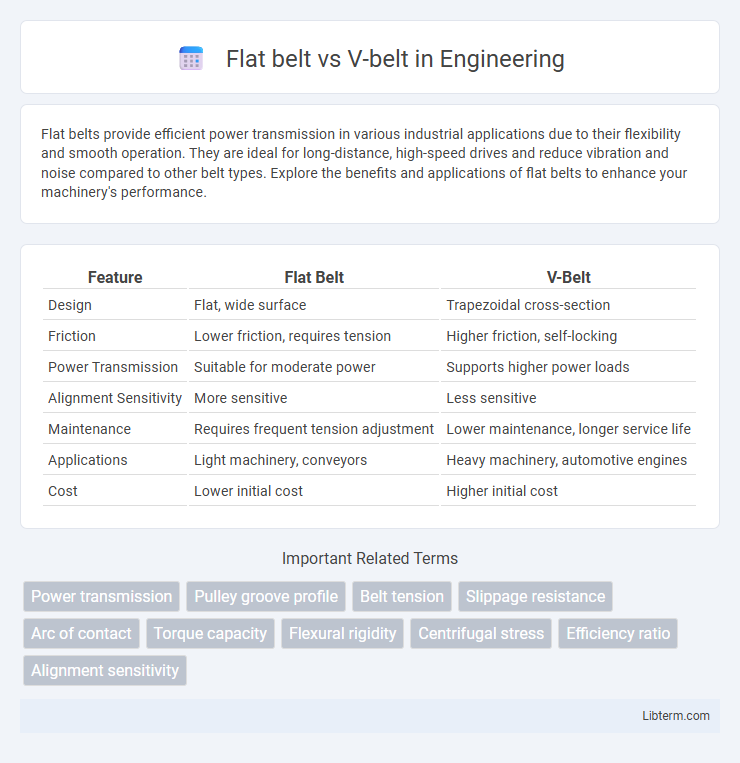
| Feature | Flat Belt | V-Belt |
|---|---|---|
| Design | Flat, wide surface | Trapezoidal cross-section |
| Friction | Lower friction, requires tension | Higher friction, self-locking |
| Power Transmission | Suitable for moderate power | Supports higher power loads |
| Alignment Sensitivity | More sensitive | Less sensitive |
| Maintenance | Requires frequent tension adjustment | Lower maintenance, longer service life |
| Applications | Light machinery, conveyors | Heavy machinery, automotive engines |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
Introduction: Understanding Flat Belts and V-Belts
Flat belts are continuous loops of flexible material with a smooth surface, commonly made from leather, rubber, or synthetic compounds, used primarily for high-speed, low-torque power transmission in industrial machinery. V-belts feature a trapezoidal cross-section designed to fit into matching pulley grooves, providing higher friction and better grip, which suits applications requiring higher torque and reduced slippage. Both types serve distinct mechanical purposes, impacting efficiency, load capacity, and maintenance in conveyor systems and various automotive or manufacturing equipment.
Design and Construction Differences
Flat belts feature a simple, broad, and smooth surface made from leather or synthetic materials, providing low friction and efficient power transmission. V-belts have a trapezoidal cross-section with multiple layers of reinforced fibers and rubber, designed to fit snugly into pulley grooves and increase friction for better grip. The construction of V-belts allows them to transmit higher torque and handle misalignment better compared to flat belts, which excel in high-speed and low-torque applications.
Working Principle of Flat Belts
Flat belts operate by transmitting power through friction between the flat surface of the belt and the pulley, relying on tension and the contact area to prevent slipping. They are typically used in applications requiring high-speed transmission and smooth, quiet operation. Unlike V-belts that use their wedging action in pulley grooves for grip, flat belts depend solely on the belt's tension and flat pulley surfaces to maintain efficient power transfer.
Working Principle of V-Belts
V-belts operate by wedging into the groove of a pulley, creating a strong frictional grip that transmits torque efficiently between the driver and driven shafts. Their trapezoidal cross-section increases the contact surface area and enhances the belt's grip, reducing slippage under load. This design allows V-belts to handle higher power transmission with better alignment and damping compared to flat belts.
Efficiency: Power Transmission Capabilities
Flat belts offer high efficiency in power transmission due to their larger contact surface area, minimizing slippage and energy loss, making them ideal for high-speed applications with light to moderate loads. V-belts provide better power transmission capabilities under high load conditions by increasing friction through their wedging action in the pulley groove, ensuring less slippage and improved torque transfer. Efficiency in power transmission depends on application specifics, with flat belts excelling in speed and smooth operation, while V-belts deliver superior grip and durability for heavier loads.
Application Areas and Common Uses
Flat belts are commonly used in high-speed, low-torque applications such as conveyor systems, printing machines, and textile equipment due to their ability to handle large distances with minimal slippage. V-belts are preferred in heavy-duty, high-torque environments like automotive engines, industrial machinery, and agricultural equipment because of their superior grip and power transmission efficiency. The choice between flat belts and V-belts depends on the specific application requirements, including load capacity, speed, and alignment conditions.
Advantages of Flat Belts
Flat belts offer higher efficiency and better speed range compared to V-belts due to their larger contact surface and lower friction. Their design allows for smoother operation with less slippage, reducing wear and extending the lifespan of the belt and pulleys. Flat belts also provide easier maintenance and alignment, making them ideal for high-speed applications and systems requiring precise motion control.
Advantages of V-Belts
V-belts offer superior power transmission efficiency and better grip due to their trapezoidal cross-section, reducing slippage in high-torque applications. Their design allows for greater flexibility and adaptability to varying pulley sizes, enhancing durability and longer service life compared to flat belts. V-belts also require less maintenance and provide quieter operation, making them ideal for industrial machinery and automotive engines.
Maintenance and Durability Comparison
Flat belts require regular tension adjustments and alignment checks to prevent slippage and wear, whereas V-belts generally maintain tension longer due to their wedge-shaped design, reducing the frequency of maintenance. V-belts exhibit superior durability under high load and harsh conditions because their design distributes stress more evenly and resists heat and abrasion better than flat belts. Maintenance costs for flat belts are often higher over time, as they wear out faster and need more frequent replacement compared to the longer-lasting V-belts.
Which Belt Type to Choose?
Flat belts provide high-speed power transmission with minimal slippage and are ideal for applications requiring smooth, consistent motion and less torque. V-belts offer superior grip and torque transmission, making them suitable for heavy-duty machinery and applications with higher load demands. Choose flat belts for light to medium loads and efficiency at high speeds, while V-belts are preferable for durability and higher power transmission in demanding environments.
Flat belt Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com