EtherNet/IP is an industrial networking protocol that enables seamless communication between devices in automation systems using standard Ethernet technology. It supports real-time control and data exchange, improving efficiency and interoperability across manufacturing processes. Discover how EtherNet/IP can optimize Your industrial operations by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
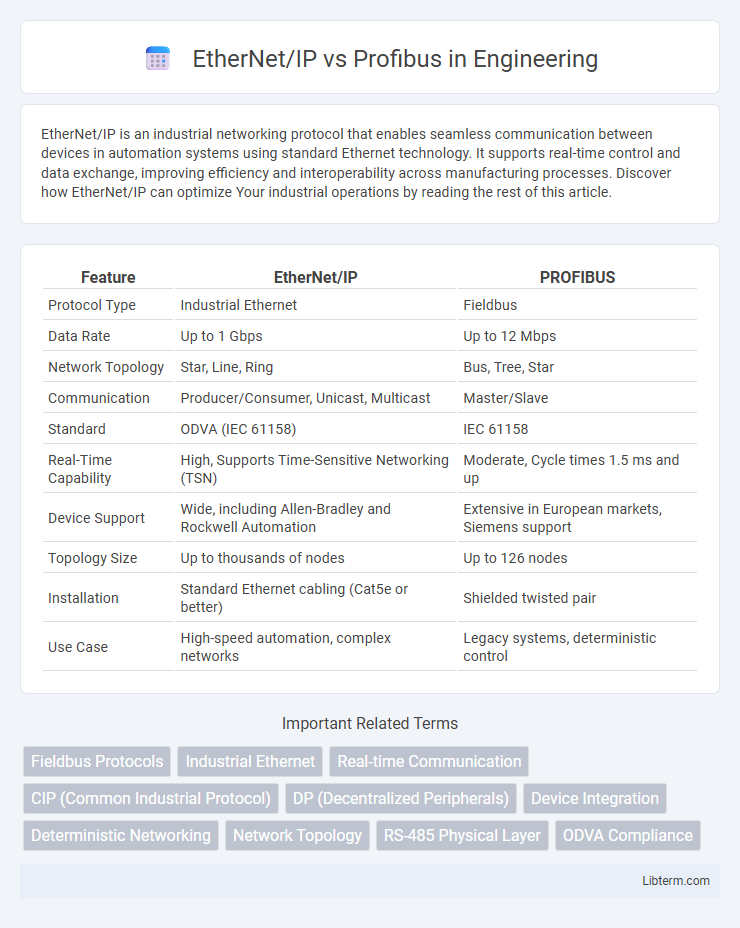
| Feature | EtherNet/IP | PROFIBUS |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Industrial Ethernet | Fieldbus |
| Data Rate | Up to 1 Gbps | Up to 12 Mbps |
| Network Topology | Star, Line, Ring | Bus, Tree, Star |
| Communication | Producer/Consumer, Unicast, Multicast | Master/Slave |
| Standard | ODVA (IEC 61158) | IEC 61158 |
| Real-Time Capability | High, Supports Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) | Moderate, Cycle times 1.5 ms and up |
| Device Support | Wide, including Allen-Bradley and Rockwell Automation | Extensive in European markets, Siemens support |
| Topology Size | Up to thousands of nodes | Up to 126 nodes |
| Installation | Standard Ethernet cabling (Cat5e or better) | Shielded twisted pair |
| Use Case | High-speed automation, complex networks | Legacy systems, deterministic control |
Introduction to EtherNet/IP and Profibus
EtherNet/IP is an industrial protocol utilizing standard Ethernet technology for real-time control and data exchange, supporting IP-based networks in industrial automation. Profibus, a fieldbus protocol developed by Siemens, enables deterministic communication for automation devices, widely used in manufacturing processes requiring precise timing. Both protocols facilitate interoperability and efficient device communication but differ in network infrastructure and application flexibility.
Core Technologies and Protocol Architecture
EtherNet/IP utilizes standard Ethernet technology with the Common Industrial Protocol (CIP) layered on top, enabling high-speed, real-time data exchange over TCP/IP and UDP. Profibus operates on a fieldbus communication system using deterministic serial communication with a master-slave protocol based on the OSI model's physical and data link layers. The protocol architecture of EtherNet/IP supports object-oriented messaging for device interoperability, while Profibus emphasizes cyclic and acyclic data transmission optimized for process automation and discrete manufacturing control.
Communication Speed and Data Throughput
EtherNet/IP offers significantly higher communication speed with data rates up to 1 Gbps compared to Profibus, which operates at a maximum of 12 Mbps. EtherNet/IP supports larger data throughput, enabling faster real-time data exchange suitable for complex industrial automation systems. Profibus, while reliable for slower control applications, is limited by its lower bandwidth and slower communication speed.
Network Topology and Scalability
EtherNet/IP supports star, tree, and linear bus topologies, offering high scalability with flexible network expansion and the ability to connect thousands of devices using standard Ethernet infrastructure. Profibus primarily uses linear bus topology with limited branch connections, making it less scalable for large or complex industrial networks. The IP-based architecture of EtherNet/IP facilitates easier integration with enterprise networks and supports higher data transfer rates compared to the serial communication of Profibus.
Device Compatibility and Integration
EtherNet/IP offers extensive device compatibility due to its use of standard Ethernet protocols, enabling seamless integration with a wide range of industrial devices and IT systems. Profibus, while widely supported in traditional manufacturing environments, can face limitations integrating with modern TCP/IP-based networks and devices. The open nature of EtherNet/IP simplifies device interoperability and reduces integration complexity compared to the more specialized and proprietary nature of Profibus.
Real-Time Performance and Determinism
EtherNet/IP offers high-speed communication with real-time performance achieved through CIP Sync and Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN), making it suitable for complex automation systems requiring precise synchronization. Profibus provides deterministic communication with fixed cycle times, utilizing token passing to ensure predictable data transfer, which is critical for process automation environments. While EtherNet/IP supports flexible network topologies and higher bandwidth, Profibus excels in ultra-reliable timing and minimal jitter, essential for tightly controlled manufacturing processes.
Installation, Maintenance, and Diagnostics
EtherNet/IP offers simplified installation with standard Ethernet cabling and connectors, reducing setup time and costs compared to Profibus, which requires specialized cables and terminators. Maintenance on EtherNet/IP benefits from widespread familiarity with Ethernet technology and the availability of extensive diagnostic tools that enable real-time network monitoring and swift fault identification, whereas Profibus diagnostics often depend on proprietary software and hardware interfaces. Diagnostic capabilities in EtherNet/IP include integrated IP-based troubleshooting features such as network traffic analysis and device status alerts, providing more granular and accessible data than Profibus, which utilizes segment-specific diagnostics primarily focused on signal integrity and device communication.
Security Features and Cybersecurity Considerations
EtherNet/IP offers advanced security features such as CIP Security, which includes authentication, encryption, and integrity checking, making it more resilient to cyber threats in industrial environments. Profibus, while widely used in automation, lacks built-in security protocols and relies heavily on network segmentation and external security measures to mitigate cyber risks. The increasing adoption of EtherNet/IP is driven by its enhanced cybersecurity capabilities, aligning with modern industrial IoT security standards and reducing vulnerabilities in critical infrastructure.
Suitability for Industrial Applications
EtherNet/IP offers high-speed communication and seamless integration with standard Ethernet infrastructure, making it ideal for complex industrial automation systems requiring real-time data exchange. Profibus, with its robust deterministic communication and long-standing reliability, is well-suited for process control and factory automation environments where legacy systems are prevalent. The choice between EtherNet/IP and Profibus depends on the specific application's need for speed, scalability, and compatibility with existing industrial networks.
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
EtherNet/IP typically incurs lower installation and maintenance costs due to its use of standard Ethernet infrastructure and widespread compatibility, reducing initial capital expenditure and ongoing operational expenses. Profibus often demands specialized hardware and proprietary components, which can raise upfront costs and complicate scalability, potentially diminishing return on investment over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership, EtherNet/IP's flexibility and ease of integration support faster deployment and improved ROI in dynamic industrial environments.
EtherNet/IP Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com