Modbus is a widely-used communication protocol in industrial automation, enabling devices like sensors, controllers, and instruments to communicate efficiently. Its simple and open architecture supports seamless integration across various systems, ensuring reliable data exchange and control. Explore the rest of this article to understand how Modbus can optimize Your industrial communication network.
Table of Comparison
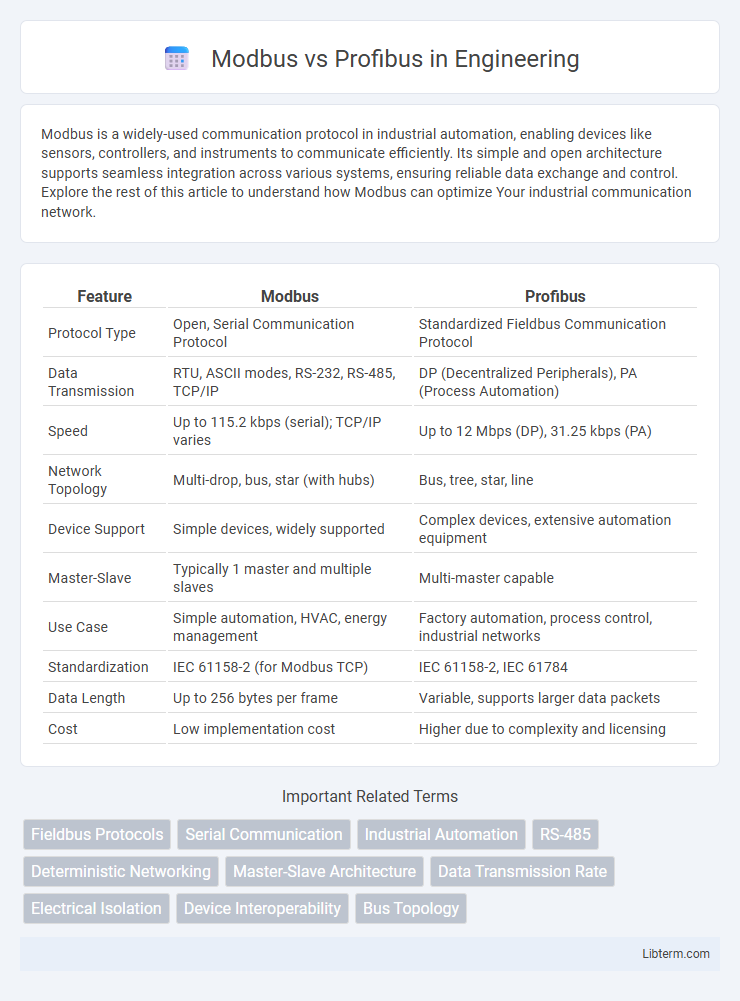
| Feature | Modbus | Profibus |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol Type | Open, Serial Communication Protocol | Standardized Fieldbus Communication Protocol |
| Data Transmission | RTU, ASCII modes, RS-232, RS-485, TCP/IP | DP (Decentralized Peripherals), PA (Process Automation) |
| Speed | Up to 115.2 kbps (serial); TCP/IP varies | Up to 12 Mbps (DP), 31.25 kbps (PA) |
| Network Topology | Multi-drop, bus, star (with hubs) | Bus, tree, star, line |
| Device Support | Simple devices, widely supported | Complex devices, extensive automation equipment |
| Master-Slave | Typically 1 master and multiple slaves | Multi-master capable |
| Use Case | Simple automation, HVAC, energy management | Factory automation, process control, industrial networks |
| Standardization | IEC 61158-2 (for Modbus TCP) | IEC 61158-2, IEC 61784 |
| Data Length | Up to 256 bytes per frame | Variable, supports larger data packets |
| Cost | Low implementation cost | Higher due to complexity and licensing |
Introduction to Modbus and Profibus
Modbus is a widely used communication protocol in industrial automation, known for its simplicity and open architecture, enabling seamless data exchange between electronic devices and control systems. Profibus, developed by Siemens, offers high-speed, deterministic communication ideal for complex automation tasks, supporting multiple device classes and flexible topologies. Both protocols facilitate interoperability in industrial networks but differ significantly in performance, scalability, and application scope.
Overview of Modbus Protocol
Modbus protocol is a widely adopted communication standard used in industrial automation for connecting electronic devices. It operates on a master-slave or client-server architecture, enabling efficient data exchange between controllers and field devices such as sensors and actuators. The protocol supports serial communication standards like RS-232, RS-485, and Ethernet, making it versatile and compatible with various network configurations.
Overview of Profibus Protocol
Profibus Protocol, a widely adopted industrial communication standard, offers high-speed data exchange and real-time control capabilities ideal for automation systems. It supports various device profiles and network topologies, enabling seamless integration of sensors, actuators, and controllers across manufacturing environments. Profibus utilizes a deterministic Token Passing method, ensuring reliable and predictable communication critical for process control and factory automation applications.
Key Differences Between Modbus and Profibus
Modbus is a simple, open protocol primarily used for communication in serial networks with a master-slave architecture, offering easy implementation and widespread compatibility. Profibus supports higher data transfer rates, uses a more complex token-passing method, and enables real-time communication with decentralized control, making it suitable for industrial automation requiring precise timing. The key differences between Modbus and Profibus lie in their communication methods, data speeds, and network complexity, with Profibus offering enhanced performance and scalability for demanding environments.
Communication Methods and Network Topologies
Modbus primarily uses a master-slave communication method with serial communication protocols like RS-232 or RS-485, supporting simple point-to-point or multi-drop bus topologies. Profibus employs a token-passing mechanism in a master-slave or master-master arrangement, typically utilizing RS-485 or fiber optic physical layers with star, tree, or ring network topologies for enhanced reliability. While Modbus favors straightforward communication with minimal overhead, Profibus offers higher data rates and robust error-checking suited for complex industrial automation networks.
Data Transmission Speed and Performance
Modbus typically supports data transmission speeds up to 115.2 kbps, making it suitable for simpler, slower industrial applications. Profibus offers significantly higher speeds, ranging from 9.6 kbps to 12 Mbps, which enhances performance in complex automation systems requiring real-time data exchange. The higher bandwidth of Profibus enables faster communication cycles and improved system responsiveness compared to Modbus.
Compatibility and Integration
Modbus offers broad compatibility across various industrial devices due to its simple, open protocol widely supported by numerous manufacturers, facilitating seamless integration in mixed-device environments. Profibus, with its more complex, standardized communication system, excels in process automation settings but may require specialized hardware and configuration, limiting integration flexibility compared to Modbus. Both protocols support robust industrial communication, but Modbus's ease of use and device interoperability make it preferable for heterogeneous networks, while Profibus is favored in highly structured, automation-centric systems.
Security Features and Reliability
Modbus, widely used in industrial automation, offers basic security features primarily through password protection but lacks inherent encryption, making it vulnerable to cyberattacks. Profibus provides enhanced reliability with robust error detection and fault tolerance mechanisms, yet its security capabilities are limited without additional layers such as VPNs or firewalls. For critical industrial applications, Profibus is favored for its dependable communication, while Modbus requires supplemental security measures to ensure data integrity and protection against unauthorized access.
Application Areas and Industry Usage
Modbus is widely used in building automation, water treatment, and industrial environments due to its simplicity and compatibility with low-cost devices. Profibus finds extensive application in complex manufacturing processes, automotive production, and process automation where high-speed communication and reliable data exchange are critical. Industries like oil and gas, pharmaceuticals, and steel manufacturing favor Profibus for its robust performance in harsh environments and advanced diagnostics capabilities.
Choosing the Right Protocol for Your Automation Needs
Modbus offers simplicity, widespread use, and easy integration in industrial automation with support for serial and Ethernet communication, making it ideal for straightforward, cost-effective applications. Profibus provides higher speed, robust data handling, and real-time capabilities suitable for complex systems requiring deterministic performance and extensive device networks. Selecting the right protocol depends on factors such as network size, communication speed, device compatibility, and specific automation requirements, ensuring optimal efficiency and scalability.
Modbus Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com