Effective testing ensures that your software performs reliably under various conditions, identifying bugs before deployment. It enhances product quality, user satisfaction, and reduces maintenance costs by catching issues early. Explore this article to discover comprehensive testing strategies tailored for your development needs.
Table of Comparison
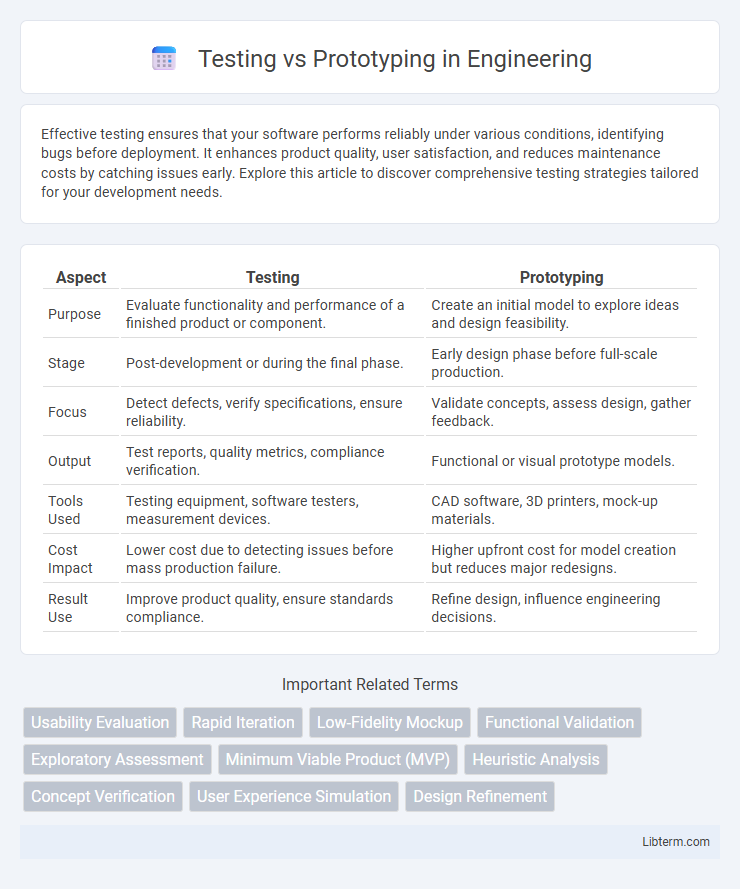
| Aspect | Testing | Prototyping |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate functionality and performance of a finished product or component. | Create an initial model to explore ideas and design feasibility. |
| Stage | Post-development or during the final phase. | Early design phase before full-scale production. |
| Focus | Detect defects, verify specifications, ensure reliability. | Validate concepts, assess design, gather feedback. |
| Output | Test reports, quality metrics, compliance verification. | Functional or visual prototype models. |
| Tools Used | Testing equipment, software testers, measurement devices. | CAD software, 3D printers, mock-up materials. |
| Cost Impact | Lower cost due to detecting issues before mass production failure. | Higher upfront cost for model creation but reduces major redesigns. |
| Result Use | Improve product quality, ensure standards compliance. | Refine design, influence engineering decisions. |
Understanding the Basics: Testing vs Prototyping
Testing involves evaluating a product or system to identify defects, ensure functionality, and validate performance against requirements. Prototyping creates an early model or sample to explore design concepts, gather user feedback, and refine ideas before full-scale production. Both processes serve distinct purposes: testing verifies the implementation, while prototyping focuses on conceptual validation and iterative improvement.
Key Differences Between Testing and Prototyping
Testing evaluates a product's functionality, performance, and user experience by identifying defects and ensuring it meets specified requirements, while prototyping creates an early model to visualize design concepts and gather user feedback. Testing is typically performed on near-final versions to validate and verify, whereas prototyping is conducted in initial design phases to explore ideas and iterate quickly. The key difference lies in testing aiming to confirm quality and conformity, whereas prototyping focuses on experimentation and development of design solutions.
The Role of Prototyping in Product Development
Prototyping plays a crucial role in product development by allowing designers to create tangible models that validate concepts, identify design flaws, and gather user feedback early in the process. Unlike testing, which evaluates functional aspects of a nearly finished product, prototyping emphasizes exploration and iteration to refine features and enhance user experience. This approach reduces development risks, shortens time-to-market, and ensures alignment with customer needs before committing to full-scale production.
Testing: Ensuring Functionality and Reliability
Testing verifies software functionality by systematically identifying defects and ensuring each component performs as intended under various conditions. It enhances reliability through rigorous validation methods such as unit tests, integration tests, and system tests, which detect bugs early in the development cycle. Effective testing reduces risks, improves user satisfaction, and assures product stability before deployment.
When to Prototype and When to Test
Prototyping is ideal during early design stages to explore ideas, validate concepts, and gather user feedback before committing to development. Testing is crucial once a prototype or product reaches a functional stage, allowing teams to identify bugs, usability issues, and performance bottlenecks through structured user trials and quality assurance processes. Deciding when to prototype or test depends on project phase, goals, and risk tolerance--prototype early to shape product direction, test later to ensure reliability and user satisfaction.
Types of Prototypes: Low-Fidelity vs High-Fidelity
Low-fidelity prototypes consist of simple sketches or paper models that emphasize conceptual design and user interaction without detailed visuals, enabling quick adjustments and early feedback. High-fidelity prototypes offer near-complete functionality and polished interfaces that closely resemble the final product, allowing for comprehensive usability testing and detailed validation. Selecting between low-fidelity and high-fidelity prototypes depends on project goals, timeline, and required fidelity in user experience evaluation.
Common Testing Methods in Product Design
Common testing methods in product design include usability testing, A/B testing, and functional testing, each targeting specific aspects of user experience and performance. Usability testing evaluates how real users interact with a prototype or product to identify pain points and improve interface design. A/B testing compares two versions of a product to determine which performs better based on user engagement metrics, while functional testing ensures all components operate correctly under various conditions.
Benefits of Early Prototyping
Early prototyping accelerates user feedback by providing tangible models that highlight design flaws and usability issues before full-scale development. Rapid iteration through prototypes reduces overall project costs and minimizes risks by validating concepts early in the design process. This approach improves stakeholder alignment and ensures the final product meets user needs more accurately, enhancing overall product quality.
Challenges in Testing and Prototyping
Testing faces challenges such as identifying all potential defects, ensuring comprehensive coverage, and replicating real-world conditions to validate functionality. Prototyping struggles with balancing fidelity and resource constraints while capturing user feedback accurately to refine designs effectively. Both processes require careful iteration to minimize risks and align the final product with user needs and technical specifications.
Integrating Testing and Prototyping in Agile Workflows
Integrating testing and prototyping in Agile workflows accelerates feedback loops and improves product quality by validating functionality early and iteratively. Prototyping enables rapid experimentation and user experience validation, while continuous testing ensures code reliability and performance throughout development cycles. This synergy reduces defects, enhances adaptability, and aligns deliverables with evolving customer requirements in Agile environments.
Testing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com