Project Portfolio Management (PPM) is essential for aligning projects with an organization's strategic goals, ensuring optimal resource allocation and risk management. Effective PPM enhances decision-making by providing a comprehensive view of all ongoing initiatives, boosting overall project success rates. Discover how mastering PPM can transform your project outcomes in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
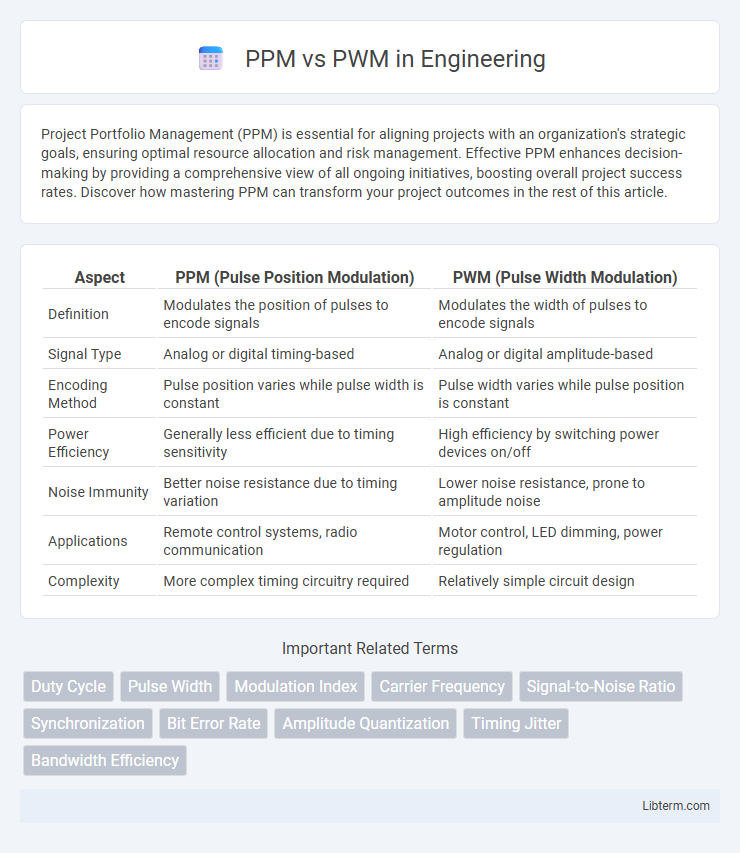
| Aspect | PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) | PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Modulates the position of pulses to encode signals | Modulates the width of pulses to encode signals |
| Signal Type | Analog or digital timing-based | Analog or digital amplitude-based |
| Encoding Method | Pulse position varies while pulse width is constant | Pulse width varies while pulse position is constant |
| Power Efficiency | Generally less efficient due to timing sensitivity | High efficiency by switching power devices on/off |
| Noise Immunity | Better noise resistance due to timing variation | Lower noise resistance, prone to amplitude noise |
| Applications | Remote control systems, radio communication | Motor control, LED dimming, power regulation |
| Complexity | More complex timing circuitry required | Relatively simple circuit design |
Introduction to PPM and PWM
Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) encodes information by varying the position of pulses within a fixed time frame, making it highly resistant to signal interference in communication systems. Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) controls the width of each pulse to represent data, commonly used for controlling power delivered to electrical devices like motors and LEDs. Both modulation techniques are essential in digital signal processing, with PPM preferred for noise immunity and PWM favored for efficient power control.
Definition of PPM (Pulse Position Modulation)
Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) is a modulation technique where the position of a pulse within a fixed time frame represents the information being transmitted. Unlike Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), which varies the duration of the pulse, PPM changes the timing of the pulse to encode data, offering advantages in noise immunity and synchronization precision. PPM is widely used in optical communications, radio control systems, and telemetry due to its efficient use of bandwidth and reduced susceptibility to signal distortion.
Definition of PWM (Pulse Width Modulation)
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is a technique used to encode a message into a pulsing signal by varying the width of the pulses while maintaining a constant frequency. It is widely utilized in applications like motor speed control, LED dimming, and power delivery due to its efficiency in controlling power output. PWM signals switch between on and off states rapidly, with the ratio of the on-time to the total period (duty cycle) determining the effective voltage and power delivered to the load.
Key Differences Between PPM and PWM
PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) encodes information by varying the position of each pulse within a fixed time frame, while PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) varies the width of each pulse to represent data. PPM is commonly used in radio control systems due to its robustness against noise, whereas PWM is widely applied in power delivery and motor speed control for efficient energy modulation. The timing precision in PPM leads to less signal distortion, while PWM offers simpler implementation and better resolution in controlling power levels.
Advantages of PPM
Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) offers significant advantages over Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) in signal integrity and noise resilience, making it ideal for remote control systems and communication signals. PPM encodes information in the timing of pulses rather than their width, reducing susceptibility to amplitude fluctuations and signal distortion in noisy environments. The increased robustness of PPM enhances data transmission accuracy and reliability, especially in applications such as model aircraft control and industrial automation.
Advantages of PWM
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) offers precise control over motor speed and brightness by varying the duty cycle, resulting in higher energy efficiency compared to Pulse Position Modulation (PPM). PWM reduces power loss and generates less heat in electronic components, making it ideal for power-sensitive applications such as LED dimming and motor control. Its ability to maintain consistent frequency while adjusting power output enhances system stability and responsiveness.
Common Applications of PPM
Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) is widely used in remote control systems for radio-controlled models, such as drones and aircraft, due to its resistance to signal interference and improved noise immunity. It is also favored in optical communication and telemetry systems where precise timing information is crucial for accurate data transmission. The ability of PPM to maintain synchronization and reduce error rates makes it ideal for scenarios requiring robust, reliable wireless communication.
Common Applications of PWM
Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) is widely used in applications such as motor speed control, LED dimming, and power delivery regulation due to its efficient energy usage and precise control capabilities. Unlike Pulse Position Modulation (PPM), which modulates signal timing and is common in communication systems like RC transmitters, PWM varies the duty cycle of a fixed frequency signal to adjust power. This makes PWM ideal for embedded systems, power inverters, and audio signal modulation where consistent frequency and adjustable power output are crucial.
Performance Comparison: PPM vs PWM
Pulse Position Modulation (PPM) offers higher noise immunity and better power efficiency compared to Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), making it ideal for long-distance communication and battery-powered systems. PWM excels in simpler implementation and precise control of power delivery, especially in motor speed and LED brightness applications, with faster response times. Performance-wise, PPM outperforms PWM in environments with significant signal interference, while PWM provides superior resolution and modulation speed in low-noise conditions.
Choosing Between PPM and PWM
Choosing between PPM (Pulse Position Modulation) and PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) depends on the specific application requirements and signal characteristics. PWM is widely preferred for controlling motor speed and LED brightness due to its precise duty cycle adjustment and energy efficiency. PPM is advantageous in radio control systems and multiplexed signal transmissions, offering simpler synchronization and reduced susceptibility to noise interference.
PPM Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com