Rectifiers transform alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) by allowing current to flow in only one direction, essential for powering DC devices. Converters, on the other hand, modify electrical power from one form to another, such as changing AC voltage levels or converting DC to AC. Explore the article to understand how these devices impact your electrical systems and their practical applications.
Table of Comparison
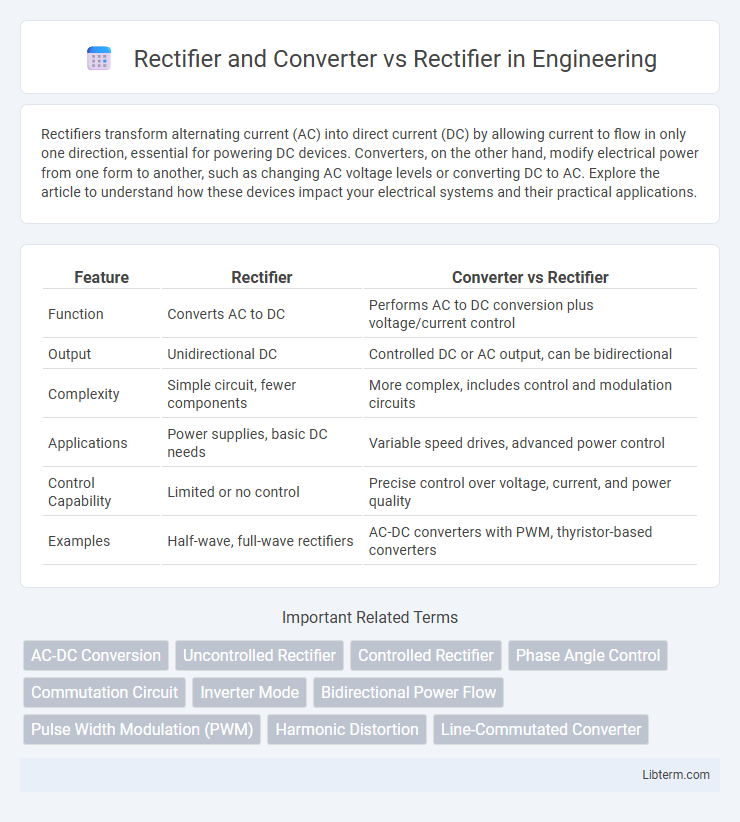
| Feature | Rectifier | Converter vs Rectifier |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Converts AC to DC | Performs AC to DC conversion plus voltage/current control |
| Output | Unidirectional DC | Controlled DC or AC output, can be bidirectional |
| Complexity | Simple circuit, fewer components | More complex, includes control and modulation circuits |
| Applications | Power supplies, basic DC needs | Variable speed drives, advanced power control |
| Control Capability | Limited or no control | Precise control over voltage, current, and power quality |
| Examples | Half-wave, full-wave rectifiers | AC-DC converters with PWM, thyristor-based converters |
Introduction to Rectifiers and Converters
Rectifiers convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) by allowing current flow in only one direction, essential for powering DC devices and circuits. Converters include rectifiers but also encompass other types of AC to DC or DC to DC conversion processes, enabling various voltage and current transformations for industrial and electronic applications. Understanding the differences helps in selecting appropriate power electronics components for efficient energy management and regulation.
Understanding Rectifiers: Basic Principles
Rectifiers convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) using semiconductor devices like diodes, relying on principles of unidirectional current flow and voltage polarity. Converters encompass rectifiers but include additional functionalities such as voltage regulation, frequency conversion, and controlled polarity, often utilizing thyristors or transistors for enhanced control. Understanding rectifiers involves grasping concepts of half-wave and full-wave rectification, ripple factor, and efficiency, which form the foundational knowledge for more complex converter operations.
What is a Converter? Types and Functions
A converter is an electrical device that changes one form of electrical energy into another, such as AC to DC or DC to AC, playing a crucial role in power electronics and energy management systems. Types of converters include AC-DC converters (rectifiers), DC-AC converters (inverters), AC-AC converters (cycloconverters), and DC-DC converters, each designed for specific applications like voltage regulation, frequency conversion, or power factor correction. The primary function of converters is to ensure compatibility between different electrical systems by efficiently modifying voltage, current, or frequency, enabling seamless operation of electronic devices and renewable energy systems.
Core Differences Between Rectifiers and Converters
Rectifiers exclusively convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), ensuring unidirectional flow for powering DC devices, while converters encompass broader power conversion processes including AC to AC, DC to DC, and AC to DC transformations. Rectifiers are a subset of converters specifically designed for rectification, whereas converters use complex circuits or electronic switches to modify voltage levels, frequency, or current type. The core difference lies in rectifiers' singular function of producing DC output from AC input, whereas converters provide versatile power conversion tailored to various electrical application needs.
Key Applications of Rectifiers
Rectifiers are primarily used to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC), serving as essential components in power supplies for electronic devices, battery charging systems, and DC motor drives. Unlike converters that can change voltage levels or frequency, rectifiers focus on delivering stable DC output for applications such as welding equipment, radios, and LED lighting. Key applications also include power conditioning in renewable energy systems and providing DC voltage in telecommunications infrastructure.
Converter Applications Across Industries
Converters play a crucial role across various industries by transforming electrical energy from one form to another, enabling efficient power management in sectors such as automotive, renewable energy, and manufacturing. While rectifiers primarily convert AC to DC, converters encompass a broader range of functions including DC to AC (inverters), DC to DC, and AC to AC conversions, supporting applications like variable speed drives, solar power systems, and electric vehicle propulsion. Their adaptability to control voltage, current, and frequency makes converters essential for modern industrial automation, energy storage, and power distribution systems.
Advantages and Limitations of Rectifiers
Rectifiers efficiently convert alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC), making them essential in power supplies and electronic devices. They offer advantages such as simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reliable DC output for low-power applications. However, rectifiers have limitations including output voltage ripple, lower efficiency at high power levels, and the need for additional filtering to produce smooth DC voltage.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Converters
Converters offer the key benefit of converting electrical energy between AC and DC forms, enabling compatibility with diverse power systems and devices, unlike simple rectifiers which only convert AC to DC. They provide improved efficiency, voltage regulation, and reduced harmonic distortion, enhancing the stability and performance of power supplies. However, converters are typically more complex and costly, requiring advanced control circuits and generating electromagnetic interference, which can impact sensitive electronics if not properly managed.
How to Choose: Rectifier vs Converter
Choosing between a rectifier and a converter depends on the specific power conversion requirements; rectifiers primarily transform AC to DC for electronic devices, while converters can change voltage levels or convert AC to DC and vice versa in more complex applications. Rectifiers are optimal for applications like power supplies in electronic circuits, enabling stable DC output with minimal ripple, whereas converters suit scenarios needing voltage regulation, frequency alteration, or bi-directional power flow such as in renewable energy systems and motor drives. Technical factors such as input voltage type, desired output waveform, efficiency, and load characteristics guide the decision-making process to ensure the chosen device meets operational demands effectively.
Future Trends in Rectifier and Converter Technology
Future trends in rectifier and converter technology emphasize higher efficiency, reduced power losses, and enhanced thermal management through wide bandgap semiconductors like SiC and GaN. Integration of advanced digital control systems enables precise voltage regulation and real-time fault detection, improving overall system reliability and performance. Emerging applications in electric vehicles and renewable energy systems drive innovation in compact, high-frequency power conversion designs, optimizing size and weight for next-generation power electronics.
Rectifier and Converter Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com