USB (Universal Serial Bus) technology revolutionizes data transfer and device connectivity by providing a fast, standardized interface for peripherals such as keyboards, printers, and external drives. It supports plug-and-play installation and hot-swapping, ensuring seamless integration with multiple operating systems and devices. Explore this article to learn how USB can enhance your technology experience and simplify your digital setup.
Table of Comparison
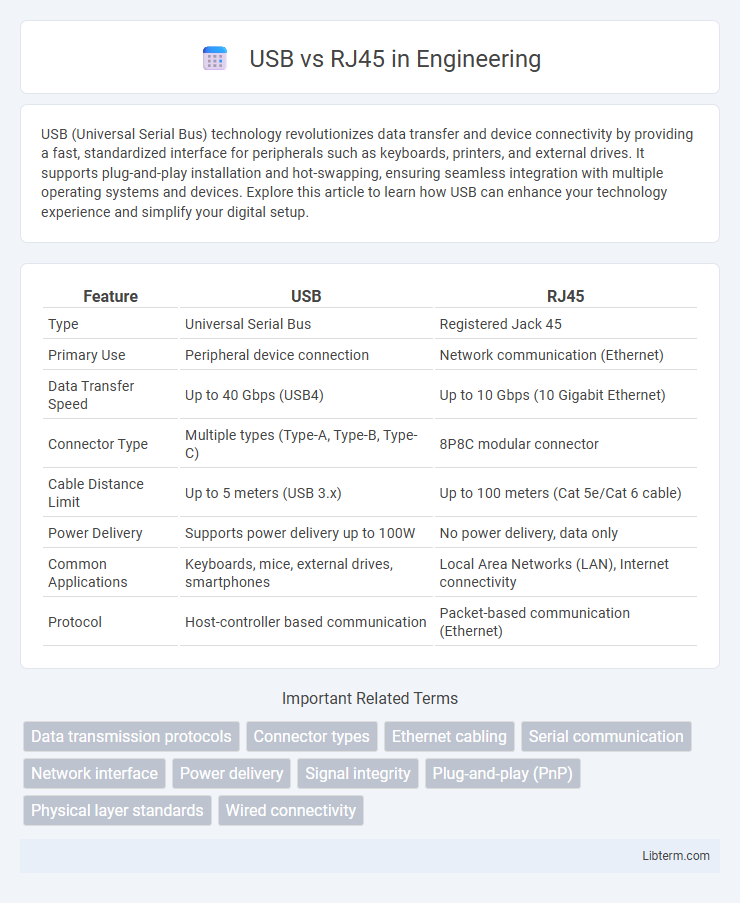
| Feature | USB | RJ45 |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Universal Serial Bus | Registered Jack 45 |
| Primary Use | Peripheral device connection | Network communication (Ethernet) |
| Data Transfer Speed | Up to 40 Gbps (USB4) | Up to 10 Gbps (10 Gigabit Ethernet) |
| Connector Type | Multiple types (Type-A, Type-B, Type-C) | 8P8C modular connector |
| Cable Distance Limit | Up to 5 meters (USB 3.x) | Up to 100 meters (Cat 5e/Cat 6 cable) |
| Power Delivery | Supports power delivery up to 100W | No power delivery, data only |
| Common Applications | Keyboards, mice, external drives, smartphones | Local Area Networks (LAN), Internet connectivity |
| Protocol | Host-controller based communication | Packet-based communication (Ethernet) |
Introduction: Understanding USB and RJ45
USB (Universal Serial Bus) is a widely used interface for connecting peripherals such as keyboards, mice, and external storage devices to computers, enabling fast data transfer and power supply through a standardized plug-and-play connection. RJ45 refers to the 8P8C connector commonly used for Ethernet networking, facilitating reliable wired communication in local area networks (LANs) with speeds ranging from 10 Mbps to 10 Gbps. Both USB and RJ45 serve distinct purposes in data connectivity, with USB geared toward device interfacing and power delivery, while RJ45 focuses on network communication infrastructure.
Key Differences Between USB and RJ45
USB (Universal Serial Bus) primarily supports data transfer and power delivery between computers and peripherals, with speeds ranging from 12 Mbps (USB 1.1) to 40 Gbps (USB4). RJ45 connectors are used for Ethernet networking, enabling wired LAN connections with data rates up to 10 Gbps (10 Gigabit Ethernet). USB interfaces connect devices like keyboards, mice, and external drives, while RJ45 interfaces link computers to network switches and routers for internet access.
How USB Works: Features and Functions
USB (Universal Serial Bus) functions as a standardized interface for data transfer and power supply between computers and peripheral devices, utilizing differential signaling for high-speed communication. It supports plug-and-play connectivity, enabling automatic device recognition and configuration without requiring manual driver installation in most cases. USB's data transfer rates range from 1.5 Mbps (USB 1.0) up to 40 Gbps (USB4), making it versatile for connecting devices like keyboards, storage drives, and multimedia equipment.
How RJ45 Works: Features and Applications
RJ45 connectors enable Ethernet communication by linking devices through twisted pair cables, transmitting data using differential signaling to reduce interference. These connectors support high-speed data rates up to 10 Gbps, making them ideal for wired networks, including LANs and industrial Ethernet systems. Common applications include connecting computers, routers, switches, and other networking hardware in offices, data centers, and smart home environments.
Speed and Performance Comparison
USB 3.1 Gen 2 supports data transfer speeds up to 10 Gbps, while RJ45 Ethernet ports vary widely, with standard Gigabit Ethernet offering 1 Gbps and 10 Gigabit Ethernet reaching 10 Gbps speeds. USB connections provide lower latency for peripheral devices but may experience bottlenecks due to shared bus architecture, whereas RJ45 Ethernet offers dedicated, stable network connections ideal for sustained high-throughput performance. For applications demanding consistent, low-latency network speeds, 10 Gigabit RJ45 Ethernet typically outperforms USB interfaces, especially under heavy multitasking or data-intensive scenarios.
Common Uses: USB vs RJ45 in Everyday Devices
USB ports are widely used for connecting peripherals like keyboards, mice, printers, external storage devices, and charging smartphones, making them essential for personal computers, laptops, and mobile devices. RJ45 connectors are primarily employed in networking equipment such as routers, switches, and computers to facilitate wired Ethernet connections, enabling fast and reliable internet access in homes and offices. While USB supports data transfer and power delivery for a broad range of devices, RJ45 is specialized for network communication with high-speed data exchange over LANs.
Compatibility and Connectivity
USB supports a wide range of devices including printers, external drives, and peripherals with plug-and-play compatibility across most modern computers. RJ45 connectors are specifically designed for Ethernet networking, enabling reliable wired internet connections with standardized compatibility across network devices. While USB offers greater versatility for various hardware connections, RJ45 provides stable, high-speed data transmission primarily for network environments.
Security Considerations for USB and RJ45
USB connections pose security risks due to their susceptibility to malware injection and unauthorized data access through physical device access points. RJ45 Ethernet interfaces provide more secure network communication with robust encryption protocols like WPA3 and secure authentication methods, reducing exposure to cyber threats. Network administrators often prefer RJ45 for sensitive environments due to its controlled access and lower risk of physical tampering compared to USB ports.
Pros and Cons of USB vs RJ45
USB offers high versatility and ease of use with plug-and-play capability, supporting data transfer and power delivery, but it typically has shorter cable lengths and can face interference in networking applications. RJ45, primarily used for Ethernet networking, provides stable, high-speed connections with low latency ideal for long-distance data transmission but requires structured cabling and lacks the power delivery functionality that USB offers. USB is better suited for peripherals and short-range connectivity, while RJ45 excels in reliable, wired network communication.
Choosing the Right Option: USB or RJ45?
Choosing between USB and RJ45 depends on the intended use: USB offers versatile connectivity for peripherals, supporting data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps with USB4, ideal for external devices and quick plug-and-play connections. RJ45, utilizing Ethernet standards like CAT6 and CAT7, provides reliable wired network connections with speeds ranging from 1 Gbps to 10 Gbps and low latency, essential for stable internet and local area network setups. For high-speed data communication, gaming, or internet access, RJ45 is preferable, whereas USB is better suited for connecting external storage, cameras, or other peripherals.
USB Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com