Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive materials to precisely cut through metals, stone, glass, and composites without generating heat. This technique preserves material integrity and offers intricate shapes with minimal waste, making it ideal for industries requiring precision and durability. Discover how waterjet cutting can enhance your manufacturing processes by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
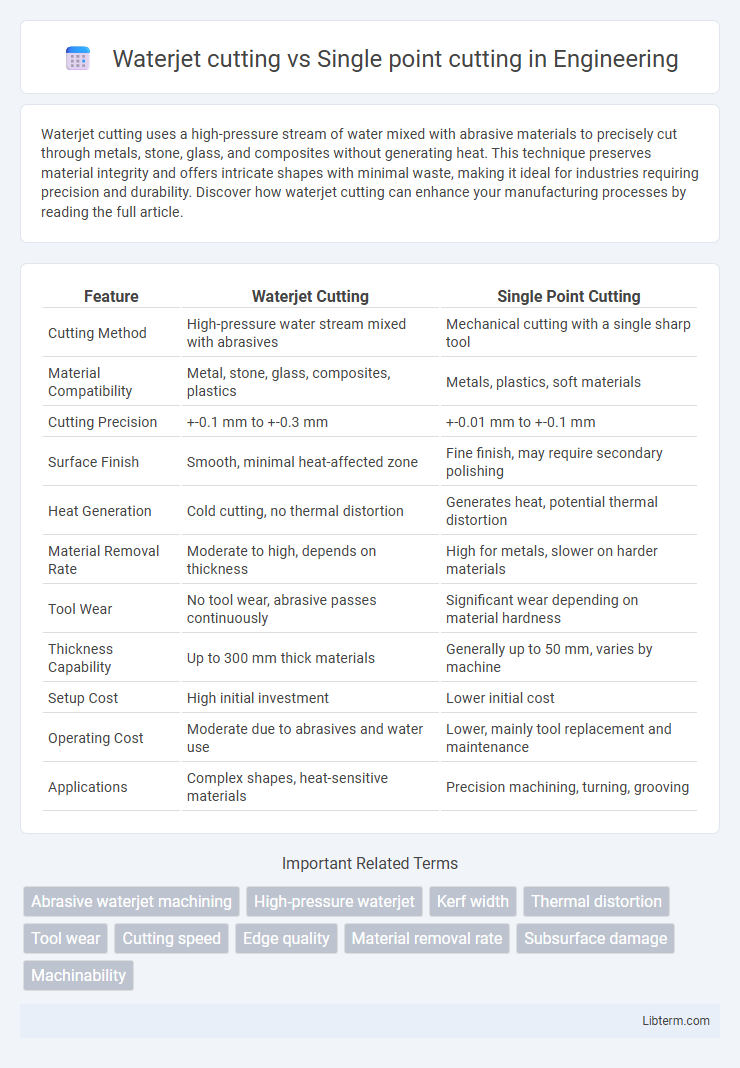
| Feature | Waterjet Cutting | Single Point Cutting |
|---|---|---|
| Cutting Method | High-pressure water stream mixed with abrasives | Mechanical cutting with a single sharp tool |
| Material Compatibility | Metal, stone, glass, composites, plastics | Metals, plastics, soft materials |
| Cutting Precision | +-0.1 mm to +-0.3 mm | +-0.01 mm to +-0.1 mm |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, minimal heat-affected zone | Fine finish, may require secondary polishing |
| Heat Generation | Cold cutting, no thermal distortion | Generates heat, potential thermal distortion |
| Material Removal Rate | Moderate to high, depends on thickness | High for metals, slower on harder materials |
| Tool Wear | No tool wear, abrasive passes continuously | Significant wear depending on material hardness |
| Thickness Capability | Up to 300 mm thick materials | Generally up to 50 mm, varies by machine |
| Setup Cost | High initial investment | Lower initial cost |
| Operating Cost | Moderate due to abrasives and water use | Lower, mainly tool replacement and maintenance |
| Applications | Complex shapes, heat-sensitive materials | Precision machining, turning, grooving |
Introduction to Cutting Technologies
Waterjet cutting utilizes high-pressure water mixed with abrasives to precisely slice through a variety of materials without generating heat, making it ideal for heat-sensitive components. Single point cutting employs a single sharp tool to remove material through mechanical force, commonly used in turning and shaping processes on lathes. Both technologies offer distinct advantages in manufacturing, with waterjet cutting excelling in versatility and cold cutting, while single point cutting provides superior precision for metal machining.
Overview of Waterjet Cutting
Waterjet cutting uses a high-pressure stream of water mixed with abrasive materials to precisely cut through various metals, stone, glass, and composites without generating heat, preserving material integrity. It offers superior edge quality and minimal thermal distortion compared to single point cutting, which relies on a single cutting tool to mechanically shear material. The versatility of waterjet cutting extends to thick and hard materials unsuitable for traditional single point cutting, enhancing efficiency in complex industrial applications.
Fundamentals of Single Point Cutting
Single point cutting involves using a single cutting edge to remove material from a workpiece by shearing, commonly applied in turning, shaping, and milling operations. This process relies on controlling the cutting parameters such as feed rate, depth of cut, and cutting speed to achieve desired surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Unlike waterjet cutting, which uses a high-pressure abrasive stream, single point cutting generates heat and mechanical stresses that influence tool wear and microstructure of the machined surface.
Material Versatility and Suitability
Waterjet cutting excels in material versatility, capable of precisely cutting metals, stone, glass, composites, and plastics without altering material properties through heat. Single point cutting is best suited for softer materials like wood, plastics, and certain metals, offering precise contouring but limited to materials that withstand direct contact cutting without excessive wear. The choice between these techniques depends on the material's hardness, thermal sensitivity, and the required cutting precision for the application.
Precision and Accuracy Comparison
Waterjet cutting provides superior precision with tolerances typically around +-0.1 mm, ideal for complex shapes and materials sensitive to heat. Single point cutting, such as lathe or milling operations, offers high accuracy but often depends on tool condition and machine stiffness, resulting in slightly broader tolerances around +-0.2 mm. The non-thermal nature of waterjet cutting ensures minimal material distortion, enhancing accuracy compared to the mechanical contact and heat generation in single point cutting methods.
Speed and Efficiency Analysis
Waterjet cutting offers higher efficiency in processing complex shapes at speeds up to 50% faster than single point cutting, especially on thicker or harder materials. Single point cutting excels in precision for simple profiles but typically operates at slower feed rates due to mechanical constraints and tool wear. Overall, waterjet technology minimizes setup time and material waste, translating to greater productivity in industrial applications.
Surface Finish Quality
The informal sector often lacks legal protections, social security, and minimum wage guarantees, exposing workers to exploitation and poor working conditions. In contrast, the formal sector provides regulated employment with enforced labor laws, social benefits, and access to healthcare and pensions, promoting worker stability and well-being. The disparity significantly impacts social equity, as informal workers face higher vulnerability without formal rights or institutional support.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Waterjet cutting generates minimal dust and hazardous fumes, significantly reducing airborne pollutants and providing a safer working environment compared to single point cutting, which often produces harmful metal shavings and emissions. The use of water and abrasive materials in waterjet cutting eliminates the need for coolants and lubricants, minimizing chemical waste and reducing environmental impact. Single point cutting poses higher risks of operator injury due to sharp metal chips and potential exposure to high temperatures, while waterjet cutting offers a cooler, cleaner process with lower physical hazards.
Cost Implications and Operational Expenses
Waterjet cutting incurs higher initial equipment costs but offers lower consumable expenses compared to single point cutting, which requires frequent tool replacements and sharpening. Operational expenses favor waterjet cutting due to minimal thermal distortion and reduced material wastage, enhancing overall efficiency. Single point cutting involves higher downtime and labor costs associated with tool maintenance and slower processing speeds.
Choosing the Right Cutting Technique
Waterjet cutting offers precise, cold cutting suitable for heat-sensitive materials, providing versatility across metals, stone, and composites without causing thermal distortion. Single point cutting excels in high-precision machining of metals, especially for intricate shapes and tight tolerances, using tools like lathes or milling machines. Choosing the right technique depends on material type, required precision, thermal sensitivity, and production speed, with waterjet preferred for minimal thermal impact and single point cutting favored for detailed metalwork.
Waterjet cutting Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com