Surface coating enhances the durability and appearance of materials by providing a protective layer against corrosion, wear, and environmental damage. This process is essential for extending the lifespan of industrial components, automotive parts, and household items. Discover how the right surface coating can improve Your product's performance and aesthetic appeal throughout the article.
Table of Comparison
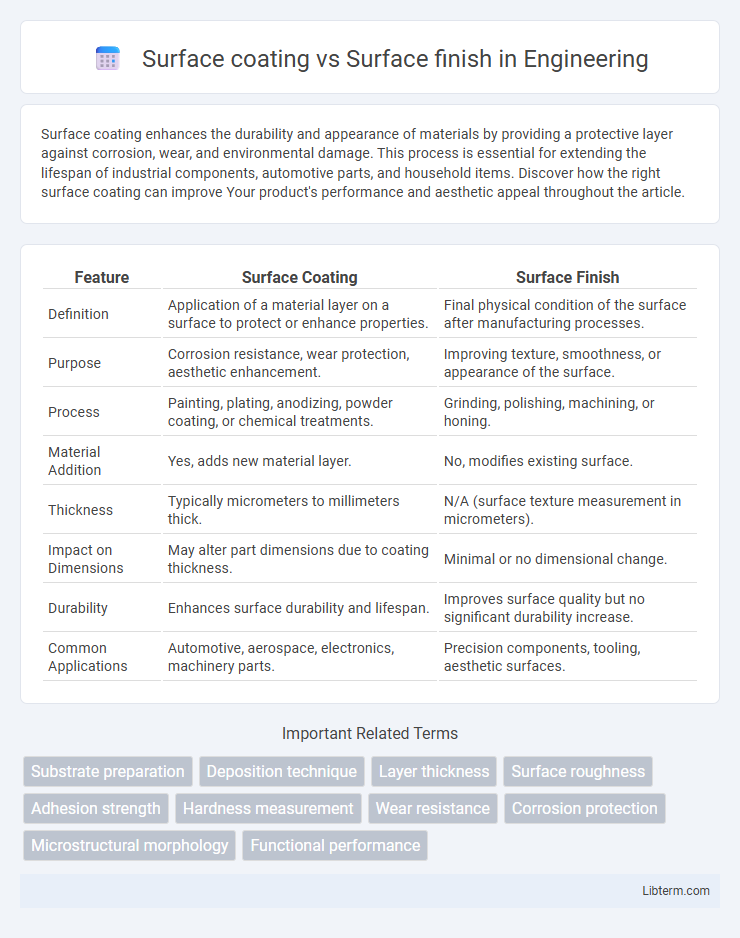
| Feature | Surface Coating | Surface Finish |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Application of a material layer on a surface to protect or enhance properties. | Final physical condition of the surface after manufacturing processes. |
| Purpose | Corrosion resistance, wear protection, aesthetic enhancement. | Improving texture, smoothness, or appearance of the surface. |
| Process | Painting, plating, anodizing, powder coating, or chemical treatments. | Grinding, polishing, machining, or honing. |
| Material Addition | Yes, adds new material layer. | No, modifies existing surface. |
| Thickness | Typically micrometers to millimeters thick. | N/A (surface texture measurement in micrometers). |
| Impact on Dimensions | May alter part dimensions due to coating thickness. | Minimal or no dimensional change. |
| Durability | Enhances surface durability and lifespan. | Improves surface quality but no significant durability increase. |
| Common Applications | Automotive, aerospace, electronics, machinery parts. | Precision components, tooling, aesthetic surfaces. |
Introduction to Surface Coating and Surface Finish
Surface coating involves applying a protective or decorative layer to a substrate, enhancing durability, corrosion resistance, and appearance, commonly used in automotive, aerospace, and industrial applications. Surface finish refers to the texture, smoothness, and topography of a material's surface, impacting friction, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal, typically measured by parameters like roughness average (Ra). Both processes are essential in manufacturing and material science for improving performance, extending lifespan, and meeting specific functional requirements.
Defining Surface Coating
Surface coating refers to the application of a material layer onto a substrate to enhance properties such as corrosion resistance, wear resistance, or aesthetics. This layer can be composed of paint, powder, metal, or polymer and serves functional and protective purposes by forming a barrier between the environment and the base material. Surface coating differs from surface finish, which primarily involves modifying the texture or smoothness of a surface without necessarily adding a protective layer.
Defining Surface Finish
Surface finish refers to the texture, smoothness, and appearance of a material's surface after manufacturing processes, measured by parameters such as roughness average (Ra) and waviness. It directly affects the material's performance characteristics like friction, wear resistance, and aesthetic appeal. Unlike surface coating, which adds a protective or decorative layer, surface finish is an inherent result of machining, grinding, or polishing techniques.
Key Differences Between Surface Coating and Surface Finish
Surface coating involves applying a protective or decorative layer, such as paint, powder, or plating, to enhance properties like corrosion resistance and durability. Surface finish refers to the texture or smoothness of a material's surface, often achieved through processes like polishing, grinding, or machining, impacting aesthetics and functionality. Key differences lie in coating being an added layer for protection or appearance, while finish pertains to the inherent surface condition affecting tactile and visual qualities.
Types of Surface Coatings
Surface coatings include paints, powder coatings, plating, anodizing, and polymer films, each designed to provide protection, corrosion resistance, or aesthetic enhancement to a substrate. Surface finish refers to the texture or smoothness achieved through processes like polishing, grinding, or blasting, often influencing adhesion and appearance but not providing protective layers. Common types of surface coatings such as epoxy, polyurethane, ceramic, and metallic coatings vary in durability, chemical resistance, and application methods, making them essential in industries from automotive to aerospace.
Types of Surface Finishes
Surface finishes include anodizing, powder coating, plating, and polishing, each offering distinct aesthetic and protective properties. Anodizing enhances corrosion resistance and surface hardness, while powder coating provides a durable, colorful layer resistant to chipping and fading. Plating methods like chrome or nickel improve both appearance and durability, and polishing produces a smooth, reflective surface ideal for decorative applications.
Applications of Surface Coating in Industry
Surface coating enhances material properties by applying protective layers to prevent corrosion, wear, and chemical damage in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and electronics. It improves durability, electrical conductivity, and aesthetic appeal, enabling components to withstand harsh environments and extend service life. Surface finish primarily refers to the texture and smoothness achieved after manufacturing, while surface coating adds functional layers for added protection and performance.
Applications of Surface Finish in Industry
Surface finish plays a critical role in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and medical devices by enhancing functionality through improved wear resistance, corrosion protection, and aesthetic appeal. Precise control over surface finish parameters like roughness and texture directly impacts component performance, fatigue life, and assembly fit. Unlike surface coating, which adds material layers, surface finish optimizes the inherent properties of the substrate to meet specific industrial requirements.
Factors Influencing Choice: Coating vs. Finish
The choice between surface coating and surface finish depends on factors such as durability requirements, environmental exposure, and aesthetic preferences. Surface coatings provide protective layers against corrosion, wear, and chemical damage, making them ideal for harsh conditions. Surface finishes focus more on texture and appearance, influencing factors like reflectivity, smoothness, and tactile feel, suitable for applications prioritizing visual quality and surface integrity.
Conclusion: Selecting the Right Solution
Selecting the right solution between surface coating and surface finish depends on the desired durability, appearance, and functional requirements of the product. Surface coatings provide robust protection against corrosion and wear, enhancing longevity in harsh environments. Surface finishes prioritize aesthetic appeal and texture refinement, making them ideal for applications where visual quality and tactile experience are paramount.
Surface coating Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com