Dacryocystitis is an infection of the tear sac causing redness, swelling, and pain near the inner corner of the eye, while hordeolum, commonly known as a stye, is an acute infection of the eyelid's oil glands resulting in a tender, swollen lump. Both conditions require prompt attention to avoid complications like abscess formation or chronic inflammation. Learn more about symptoms, causes, and effective treatments for dacryocystitis and hordeolum in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
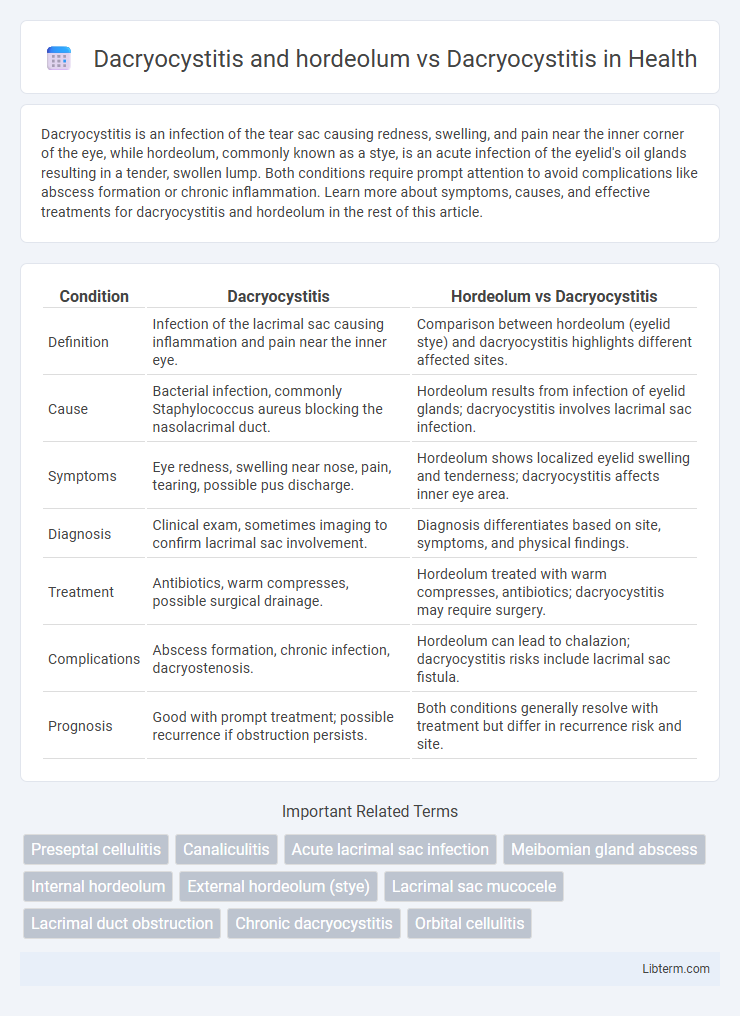
| Condition | Dacryocystitis | Hordeolum vs Dacryocystitis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Infection of the lacrimal sac causing inflammation and pain near the inner eye. | Comparison between hordeolum (eyelid stye) and dacryocystitis highlights different affected sites. |
| Cause | Bacterial infection, commonly Staphylococcus aureus blocking the nasolacrimal duct. | Hordeolum results from infection of eyelid glands; dacryocystitis involves lacrimal sac infection. |
| Symptoms | Eye redness, swelling near nose, pain, tearing, possible pus discharge. | Hordeolum shows localized eyelid swelling and tenderness; dacryocystitis affects inner eye area. |
| Diagnosis | Clinical exam, sometimes imaging to confirm lacrimal sac involvement. | Diagnosis differentiates based on site, symptoms, and physical findings. |
| Treatment | Antibiotics, warm compresses, possible surgical drainage. | Hordeolum treated with warm compresses, antibiotics; dacryocystitis may require surgery. |
| Complications | Abscess formation, chronic infection, dacryostenosis. | Hordeolum can lead to chalazion; dacryocystitis risks include lacrimal sac fistula. |
| Prognosis | Good with prompt treatment; possible recurrence if obstruction persists. | Both conditions generally resolve with treatment but differ in recurrence risk and site. |
Introduction to Dacryocystitis and Hordeolum
Dacryocystitis is an infection of the lacrimal sac, often caused by obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct leading to painful swelling near the inner corner of the eye. Hordeolum, commonly known as a stye, is an acute bacterial infection of the eyelid's sebaceous glands causing localized, tender swelling. Both conditions present with redness and inflammation but differ in location and underlying cause, requiring distinct treatment approaches to prevent complications.
Key Differences Between Dacryocystitis and Hordeolum
Dacryocystitis is an infection of the lacrimal sac, typically caused by obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, resulting in swelling and pain near the inner corner of the eye. Hordeolum, or stye, is an acute bacterial infection of the eyelid glands, presenting as a localized red, painful lump on the eyelid margin. The key differences include the anatomical location--dacryocystitis affects the lacrimal drainage system near the nose, while hordeolum affects eyelid glands--and the clinical presentation, with dacryocystitis causing lacrimal sac tenderness and possible discharge, whereas hordeolum involves superficial eyelid swelling and localized pustule formation.
Dacryocystitis: Overview and Causes
Dacryocystitis is an infection of the lacrimal sac, often caused by obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct, leading to tear stasis and bacterial proliferation, commonly with Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus species. In contrast, hordeolum (stye) is an acute purulent inflammation of the eyelid glands, typically affecting the Zeis or Meibomian glands, associated with localized pain and swelling. Understanding dacryocystitis requires recognizing its primary causes, which include congenital or acquired nasolacrimal duct obstruction, chronic sinusitis, trauma, and systemic infections, necessitating prompt treatment to prevent complications like orbital cellulitis.
Clinical Features of Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis presents with pain, redness, and swelling over the lacrimal sac area, often accompanied by tearing and discharge due to infection of the lacrimal sac. In contrast, hordeolum primarily affects the eyelid margin with localized eyelid swelling and tenderness related to an infected eyelash follicle or gland. Clinical features of dacryocystitis include acute onset of erythema and edema at the medial canthal region, mucopurulent discharge on palpation of the lacrimal sac, and possible fever, distinguishing it from superficial eyelid infections.
Hordeolum: Definition and Etiology
Hordeolum, commonly known as a stye, is an acute infection of the eyelid glands caused predominantly by Staphylococcus aureus, resulting in localized pain, swelling, and erythema. Unlike dacryocystitis, which involves inflammation of the lacrimal sac typically due to nasolacrimal duct obstruction, hordeolum affects the glands of Zeis or Moll along the eyelid margin. Understanding the bacterial etiology and glandular involvement in hordeolum is crucial for differentiating it from dacryocystitis and guiding appropriate management.
Distinguishing Symptoms: Dacryocystitis vs Hordeolum
Dacryocystitis presents with pain, swelling, and redness localized at the medial canthal area, often accompanied by tearing and purulent discharge due to lacrimal sac infection. Hordeolum, commonly known as a stye, manifests as a painful, erythematous lump on the eyelid margin, typically caused by an infected eyelash follicle or gland. Unlike hordeolum, dacryocystitis involves deeper lacrimal sac inflammation with symptoms such as localized tenderness and possibly fever, helping differentiate the two conditions clinically.
Diagnostic Strategies for Both Conditions
Dacryocystitis diagnosis involves clinical examination focusing on swelling and tenderness over the lacrimal sac, accompanied by dacryocystography or dacryoscintigraphy to assess nasolacrimal duct obstruction. Hordeolum diagnosis relies on identifying localized painful eyelid swelling, often with purulent material at the eyelash follicle, through slit-lamp examination. Imaging is rarely required in hordeolum but critical in dacryocystitis to differentiate from orbital cellulitis or abscess formation.
Treatment Approaches: Dacryocystitis vs Hordeolum
Treatment approaches for dacryocystitis primarily involve systemic antibiotics targeting common pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus species, with surgical intervention like dacryocystorhinostomy indicated in chronic or complicated cases to restore lacrimal drainage. In contrast, hordeolum management emphasizes local therapies including warm compresses to promote drainage, topical antibiotics like erythromycin or bacitracin for bacterial control, and incision or drainage for persistent abscess formation. Understanding the distinct etiologies--lacrimal sac infection in dacryocystitis versus eyelid gland infection in hordeolum--guides tailored treatment protocols optimizing patient outcomes.
Complications and Prognosis
Dacryocystitis can lead to complications such as orbital cellulitis, abscess formation, and chronic dacryocystitis if untreated, whereas hordeolum typically resolves without severe complications but may cause localized cellulitis or preseptal cellulitis. Prognosis for dacryocystitis depends on prompt management; acute cases respond well to antibiotics and drainage, but chronic forms may require surgery. Hordeolum has an excellent prognosis with conservative treatment, showing rapid resolution within one to two weeks.
Prevention and Patient Education
Preventing dacryocystitis involves maintaining proper eyelid hygiene and promptly treating any nasal or sinus infections that may contribute to lacrimal sac obstruction. For hordeolum, educating patients on avoiding eye rubbing, using warm compresses regularly, and ensuring good hand hygiene helps reduce stye formation and bacterial contamination. Emphasizing early symptom recognition and adherence to prescribed treatments significantly lowers the risk of recurrent infections in both conditions.
Dacryocystitis and hordeolum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com