Demasculinization refers to the process by which typical male characteristics, behaviors, or roles are diminished or altered. This concept can be observed in social, psychological, and biological contexts, affecting identity, self-perception, and societal dynamics. Discover how demasculinization impacts various aspects of life and culture in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
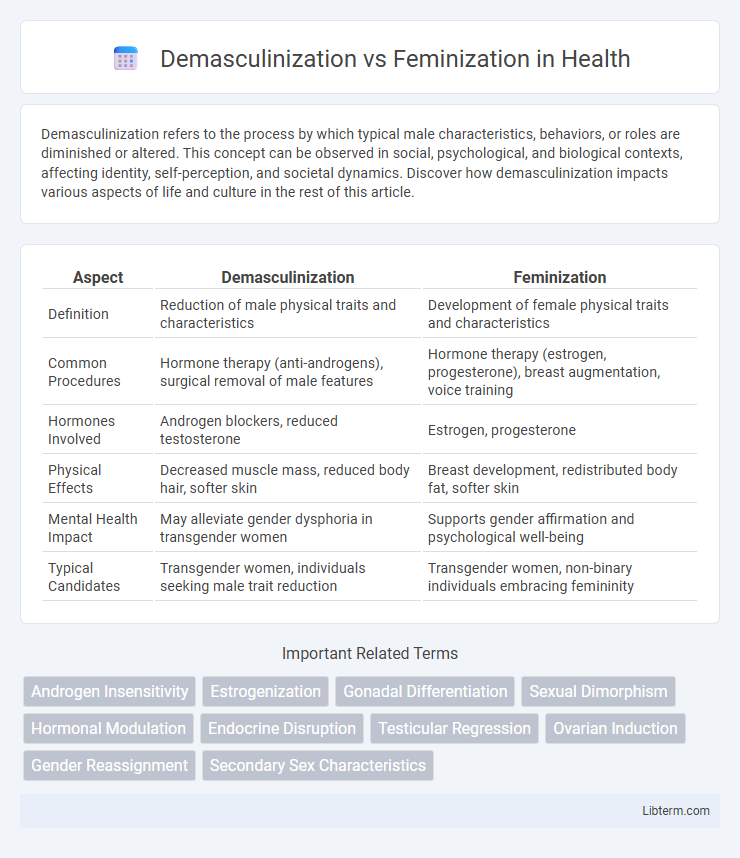
| Aspect | Demasculinization | Feminization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Reduction of male physical traits and characteristics | Development of female physical traits and characteristics |
| Common Procedures | Hormone therapy (anti-androgens), surgical removal of male features | Hormone therapy (estrogen, progesterone), breast augmentation, voice training |
| Hormones Involved | Androgen blockers, reduced testosterone | Estrogen, progesterone |
| Physical Effects | Decreased muscle mass, reduced body hair, softer skin | Breast development, redistributed body fat, softer skin |
| Mental Health Impact | May alleviate gender dysphoria in transgender women | Supports gender affirmation and psychological well-being |
| Typical Candidates | Transgender women, individuals seeking male trait reduction | Transgender women, non-binary individuals embracing femininity |
Understanding Demasculinization: Definition and Causes
Demasculinization refers to the reduction or loss of traditionally male characteristics in individuals, often caused by hormonal imbalances, environmental factors, or medical treatments such as anti-androgens. This process can manifest through decreased muscle mass, reduced body hair, and alterations in voice pitch, impacting physical and psychological traits associated with masculinity. Understanding the biological, social, and environmental causes of demasculinization aids in distinguishing it from feminization, which involves the development of female secondary sexual characteristics.
What is Feminization? Key Concepts and Examples
Feminization refers to the process through which traits, behaviors, or characteristics traditionally associated with femininity are adopted or emphasized in individuals or groups. Key concepts include gender expression, social roles, and cultural norms that shape perceptions of femininity, often involving increased emphasis on nurturing, empathy, and communication skills. Examples of feminization can be seen in workplace trends encouraging emotional intelligence, fashion emphasizing softer or more fluid aesthetics, and shifts in parental roles where caregiving responsibilities become more evenly shared.
Historical Perspectives on Gender Shifts
Historical perspectives on gender shifts reveal that demasculinization and feminization are complex processes influenced by cultural, social, and economic changes over centuries. Demasculinization often involved the diminishing emphasis on traditional masculine roles, particularly during industrialization and wartime when shifts in labor dynamics redefined gender expectations. Feminization, conversely, highlights how female-associated traits and roles gained prominence, notably during feminist movements of the 19th and 20th centuries that challenged patriarchal norms and advocated for gender equality.
Biological vs. Sociocultural Factors in Gender Identity
Biological factors in demasculinization and feminization of gender identity primarily involve hormonal influences, genetic variations, and neurobiological mechanisms impacting sex differentiation and brain structure. Sociocultural factors encompass gender norms, societal expectations, and cultural practices that shape individual gender expression and identity development through socialization processes. The interplay between biological predispositions and sociocultural environments creates a complex dynamic that influences variations in gender identity beyond simple binary categorizations.
Media Representation: Demasculinization and Feminization Trends
Media representation increasingly highlights demasculinization trends by portraying male characters with enhanced emotional sensitivity, vulnerability, and nurturing traits, challenging traditional hyper-masculine stereotypes. Simultaneously, feminization in media involves incorporating attributes historically associated with femininity, such as empathy and collaboration, into male roles, often blurring gender norms and promoting gender fluidity. These trends reflect broader societal shifts toward diverse masculinities and the deconstruction of rigid gender binaries in popular culture.
Psychological Impacts of Gender Role Changes
Demasculinization can lead to increased feelings of identity confusion, reduced self-esteem, and heightened anxiety as traditional male roles are challenged. Feminization, in contrast, may foster greater emotional expression and psychological flexibility but can also result in social stigma and internal conflict for those rigidly socialized in male gender norms. Psychological impacts of these gender role changes highlight the complexity of navigating evolving identity frameworks amid societal expectations.
The Role of Education in Shaping Gender Norms
Education plays a critical role in shaping gender norms by influencing perceptions of demasculinization and feminization through curriculum content and social interactions. Schools that promote gender-inclusive materials and challenge traditional stereotypes contribute to reducing rigid gender roles and encourage diverse expressions of identity. Early educational interventions focusing on equality and respect can foster environments that support both demasculinization and feminization as valid social constructs.
Societal Responses to Changing Gender Dynamics
Societal responses to demasculinization and feminization often reveal deep-rooted cultural tensions surrounding evolving gender roles. Communities may experience resistance or adaptation as traditional masculine traits are redefined or diminished while feminine qualities gain prominence in workplaces and media. This shift influences policy-making, workplace norms, and educational curricula, highlighting the complex interplay between gender identity and social expectations.
Demasculinization and Feminization in the Workplace
Demasculinization in the workplace refers to the reduction or elimination of traditionally masculine traits such as competitiveness, assertiveness, and hierarchy-driven leadership, fostering a more inclusive environment. Feminization emphasizes incorporating qualities historically associated with femininity like empathy, collaboration, and emotional intelligence, which enhance team dynamics and employee satisfaction. Both trends impact organizational culture by challenging gender norms and promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives.
Future Implications: Navigating Gender Identity in Modern Society
Demasculinization and feminization processes influence evolving gender identity paradigms, challenging traditional norms and promoting inclusivity. Emerging social policies and technological advancements support diverse gender expressions, fostering environments where non-binary and fluid identities gain recognition. Future implications include enhanced legal protections and personalized healthcare, driving a more equitable and adaptive society.
Demasculinization Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com