Sarcoidosis and berylliosis are both inflammatory lung diseases characterized by granuloma formation, but they differ in their causes and treatment approaches. Sarcoidosis is idiopathic, often affecting multiple organs, while berylliosis results from exposure to beryllium particles in occupational settings. Explore the article to understand the distinctions, symptoms, and management strategies crucial for your health awareness.
Table of Comparison
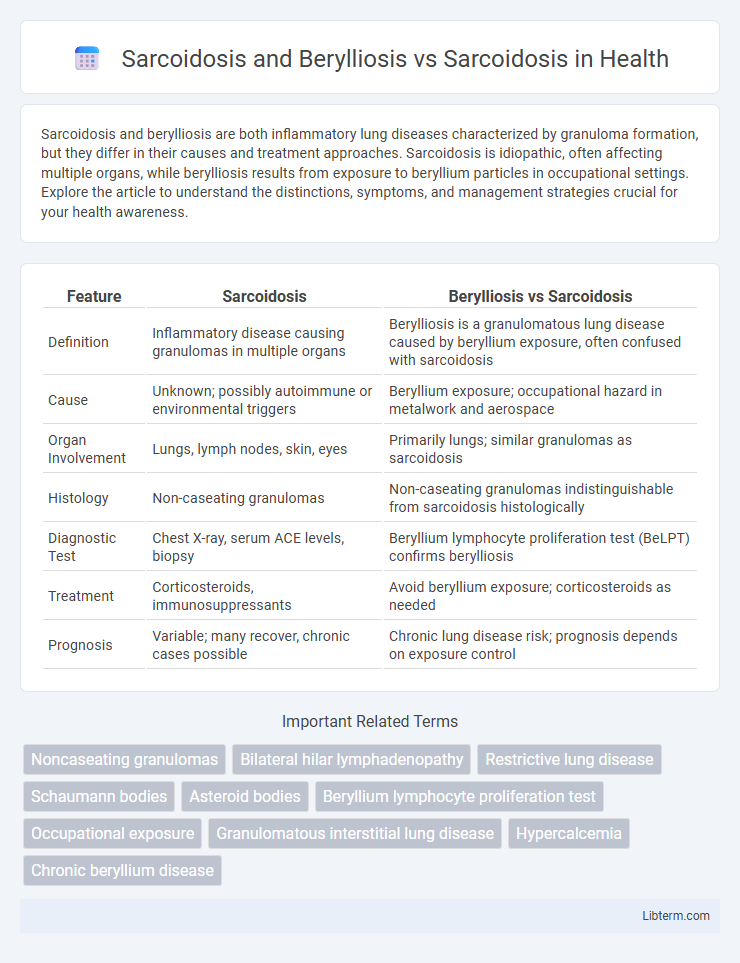
| Feature | Sarcoidosis | Berylliosis vs Sarcoidosis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflammatory disease causing granulomas in multiple organs | Berylliosis is a granulomatous lung disease caused by beryllium exposure, often confused with sarcoidosis |
| Cause | Unknown; possibly autoimmune or environmental triggers | Beryllium exposure; occupational hazard in metalwork and aerospace |
| Organ Involvement | Lungs, lymph nodes, skin, eyes | Primarily lungs; similar granulomas as sarcoidosis |
| Histology | Non-caseating granulomas | Non-caseating granulomas indistinguishable from sarcoidosis histologically |
| Diagnostic Test | Chest X-ray, serum ACE levels, biopsy | Beryllium lymphocyte proliferation test (BeLPT) confirms berylliosis |
| Treatment | Corticosteroids, immunosuppressants | Avoid beryllium exposure; corticosteroids as needed |
| Prognosis | Variable; many recover, chronic cases possible | Chronic lung disease risk; prognosis depends on exposure control |
Introduction to Sarcoidosis and Berylliosis
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease characterized by non-caseating granulomas, predominantly affecting the lungs and lymph nodes, with an unknown etiology. Berylliosis, or chronic beryllium disease, mimics sarcoidosis clinically and histologically but results from exposure to beryllium dust or fumes, triggering a hypersensitivity reaction. Differentiating sarcoidosis from berylliosis relies on occupational history, beryllium lymphocyte proliferation test (BeLPT), and imaging findings to ensure accurate diagnosis and management.
Overview of Sarcoidosis: Etiology and Pathogenesis
Sarcoidosis is a granulomatous inflammatory disease characterized by the formation of non-caseating granulomas primarily affecting the lungs and lymphatic system. Its etiology remains unclear, with genetic predisposition and immune system dysregulation contributing to abnormal T-cell activation and macrophage accumulation. In contrast, berylliosis results from exposure to beryllium, leading to a hypersensitivity granulomatous reaction with similar pathological features but distinct environmental causation.
Understanding Berylliosis: Causes and Risk Factors
Berylliosis, also known as chronic beryllium disease (CBD), is a lung condition caused by exposure to beryllium, a lightweight metal used in aerospace, manufacturing, and nuclear industries, distinguishing it from sarcoidosis, which has an unknown etiology. The risk factors for developing berylliosis include occupational exposure to beryllium dust or fumes, genetic susceptibility related to the HLA-DPB1 gene, and prolonged inhalation of airborne particles in inadequately ventilated environments. Unlike sarcoidosis, which presents with non-caseating granulomas of unclear origin, berylliosis involves an immune-mediated granulomatous response specifically triggered by beryllium exposure, making occupational history critical in differential diagnosis.
Pathological Similarities: Granuloma Formation in Both Diseases
Sarcoidosis and berylliosis both exhibit pathological similarities characterized by non-caseating granuloma formation, primarily composed of aggregated macrophages and multinucleated giant cells. These granulomas disrupt normal lung architecture and are critical in the diagnostic differentiation from infectious granulomatous diseases. The shared immune-mediated granulomatous response underscores the importance of detailed occupational history and advanced imaging in distinguishing between sarcoidosis and berylliosis.
Key Clinical Features: Sarcoidosis vs Berylliosis
Sarcoidosis presents with non-caseating granulomas primarily affecting the lungs, lymph nodes, skin, and eyes, often accompanied by symptoms like cough, dyspnea, erythema nodosum, and uveitis. Berylliosis, caused by chronic exposure to beryllium, mimics sarcoidosis clinically and radiologically but is distinguished by a history of occupational exposure and positive beryllium lymphocyte proliferation test (BeLPT). Both diseases exhibit granulomatous inflammation; however, berylliosis typically involves exposure-specific epidemiology and a higher likelihood of restrictive lung disease with fibrosis.
Diagnostic Approaches: Differentiating the Two Conditions
Diagnostic approaches for sarcoidosis and berylliosis primarily involve clinical history, imaging, and histopathology to differentiate the two granulomatous lung diseases. High-resolution CT scans reveal bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy in sarcoidosis, while berylliosis often shows reticulonodular patterns associated with occupational exposure to beryllium. Definitive differentiation requires a beryllium lymphocyte proliferation test (BeLPT) to detect beryllium sensitization, which is not present in sarcoidosis, alongside tissue biopsy demonstrating noncaseating granulomas in both conditions.
Radiological Findings: Patterns in Sarcoidosis and Berylliosis
Radiological findings in sarcoidosis typically show bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy and a diffuse reticulonodular pattern predominantly in the upper lung zones. Berylliosis may exhibit similar radiographic features but often presents with more pronounced interstitial fibrosis and nodular infiltrates correlating with exposure history to beryllium. Differentiating patterns involve the presence of chronic beryllium disease marked by granulomatous inflammation resembling sarcoidosis, yet with potential for progressive fibrosis and calcified lymph nodes.
Laboratory and Histological Markers for Accurate Diagnosis
Sarcoidosis and berylliosis present with granulomatous inflammation, but distinguishing them relies heavily on laboratory and histological markers such as serum angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) levels, which are elevated in sarcoidosis, while lymphocyte proliferation tests using beryllium salts (BeLPT) are specific for berylliosis. Histologically, both diseases show non-caseating granulomas; however, berylliosis granulomas often contain birefringent particles detectable by electron microscopy indicative of beryllium exposure. Accurate diagnosis requires integrating clinical history with biomarker profiles, including BAL fluid lymphocytosis and genetic susceptibility markers like HLA-DPB1 alleles associated with berylliosis.
Treatment Strategies: Management of Sarcoidosis and Berylliosis
Treatment strategies for sarcoidosis primarily involve corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response, with immunosuppressive agents like methotrexate or azathioprine reserved for refractory cases. Berylliosis management requires immediate cessation of beryllium exposure alongside corticosteroids to control granulomatous inflammation, as ongoing exposure leads to disease progression despite therapy. Both conditions benefit from pulmonary function monitoring, but berylliosis necessitates stringent occupational health interventions to prevent further beryllium inhalation.
Prognosis and Long-Term Outcomes: What to Expect
Sarcoidosis typically presents with a variable prognosis, where many patients experience spontaneous remission within 2 to 5 years, although chronic forms can lead to pulmonary fibrosis and organ dysfunction. Berylliosis, or chronic beryllium disease, often results from prolonged exposure to beryllium and tends to have a more progressive course with persistent inflammation and granuloma formation, leading to irreversible lung damage and decreased pulmonary function. Long-term outcomes for berylliosis generally involve ongoing monitoring for exposure cessation and immunosuppressive therapy, whereas sarcoidosis management may range from observation in mild cases to corticosteroid treatment for advanced disease.
Sarcoidosis and Berylliosis Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com