Drill-based practice enhances skill retention by promoting repetition and focused learning, essential for mastering any discipline. This method sharpens your proficiency through consistent, targeted exercises, helping to identify and correct mistakes quickly. Explore the rest of the article to learn how to effectively incorporate drill-based techniques into your routine for optimal results.
Table of Comparison
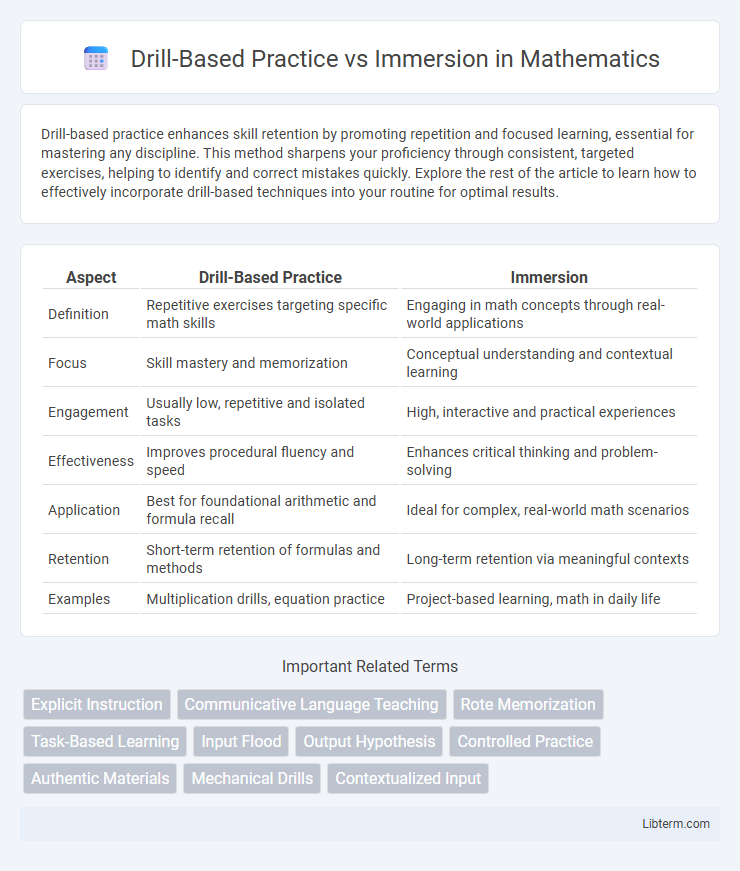
| Aspect | Drill-Based Practice | Immersion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repetitive exercises targeting specific math skills | Engaging in math concepts through real-world applications |
| Focus | Skill mastery and memorization | Conceptual understanding and contextual learning |
| Engagement | Usually low, repetitive and isolated tasks | High, interactive and practical experiences |
| Effectiveness | Improves procedural fluency and speed | Enhances critical thinking and problem-solving |
| Application | Best for foundational arithmetic and formula recall | Ideal for complex, real-world math scenarios |
| Retention | Short-term retention of formulas and methods | Long-term retention via meaningful contexts |
| Examples | Multiplication drills, equation practice | Project-based learning, math in daily life |
Understanding Drill-Based Practice
Drill-based practice reinforces learning through repetitive exercises, promoting skill mastery by enhancing muscle memory and automatic recall. This method is effective for foundational knowledge acquisition, such as grammar rules, vocabulary, and mathematical operations. Research shows consistent drills increase retention rates and improve speed in applying learned concepts.
What is Language Immersion?
Language immersion is an educational approach where learners are surrounded by the target language in authentic contexts, promoting natural acquisition through meaningful communication rather than repetitive drills. This method emphasizes exposure to language in real-life scenarios, enabling learners to develop intuitive understanding and fluency. Immersion environments often include activities such as conversations, storytelling, and cultural experiences that facilitate organic language learning.
Core Differences Between Drill-Based Practice and Immersion
Drill-based practice emphasizes repetitive exercises targeting specific language structures or vocabulary to build accuracy and automaticity, while immersion involves surrounding oneself with natural language use to develop fluency and contextual understanding. Drill methods prioritize controlled, incremental learning often supported by explicit feedback, whereas immersion relies on implicit acquisition through meaningful communication and exposure. The core difference lies in drill-based practice focusing on isolated skill mastery, contrasted with immersion's holistic, experiential learning environment.
Benefits of Drill-Based Practice
Drill-based practice enhances long-term retention and automaticity by reinforcing specific skills through repetitive exercises. It allows targeted focus on grammar, vocabulary, and pronunciation, leading to measurable progress and confidence in language use. This method is particularly effective for foundational learning and preparing for standardized language assessments.
Advantages of Immersion Learning
Immersion learning accelerates language acquisition by surrounding learners with authentic context and natural communication, which enhances comprehension and speaking skills. This method promotes cultural understanding and real-life application, leading to higher retention rates compared to repetitive drill-based practice. Immersion environments engage multiple senses simultaneously, fostering deeper cognitive connections and intuitive language use.
Limitations of Drill-Based Approaches
Drill-based practice often limits language learners by focusing heavily on repetition and memorization, which can hinder the development of spontaneous communication skills. This approach typically neglects contextual understanding and cultural nuances, essential for fluency in real-life situations. Consequently, learners may struggle with adapting language use dynamically outside structured practice environments.
Challenges Faced in Immersion Settings
Immersion settings often present challenges such as cognitive overload, where learners struggle to process new language input in real-time without explicit guidance. Limited vocabulary and grammatical knowledge can hinder comprehension, leading to frustration and decreased motivation. Inconsistent exposure and lack of structured feedback further impede language acquisition efficiency compared to drill-based practice.
Which Method Suits Different Learners?
Drill-based practice benefits learners who thrive on repetition, structure, and gradual mastery of language components such as grammar and vocabulary, making it ideal for beginners and those aiming for precise language accuracy. Immersion suits learners who prefer contextual learning through real-life experiences and communication, fostering natural language acquisition and fluency development, especially effective for conversational skills and cultural understanding. Selecting the method depends on individual goals, learning styles, and proficiency levels, with many finding a blended approach enhances overall language competence.
Blending Drill and Immersion for Optimal Results
Blending drill-based practice with immersion leverages the strengths of both methods to enhance language acquisition effectively. Drill-based practice reinforces fundamental grammar and vocabulary through repetition, while immersion provides contextual learning and cultural exposure for natural language use. Integrating structured drills within an immersive environment accelerates retention and fluency, optimizing overall language proficiency.
Final Thoughts: Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting the right language learning method depends on individual goals and learning styles, as drill-based practice enhances grammar and vocabulary retention through repetition, while immersion fosters natural language acquisition and cultural understanding. For learners seeking rapid conversational fluency, immersion provides real-world context and intuitive usage, whereas drill-based practice is ideal for mastering specific language structures and test preparation. Balancing both approaches can optimize fluency by leveraging structured practice and authentic exposure.
Drill-Based Practice Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com