Vitalistic philosophy emphasizes the importance of a life force or vital energy that distinguishes living beings from inanimate matter, influencing health and well-being. This perspective shapes alternative medicine practices by focusing on holistic healing rather than just physical symptoms. Explore the rest of this article to understand how vitalistic principles can impact your approach to health and vitality.
Table of Comparison
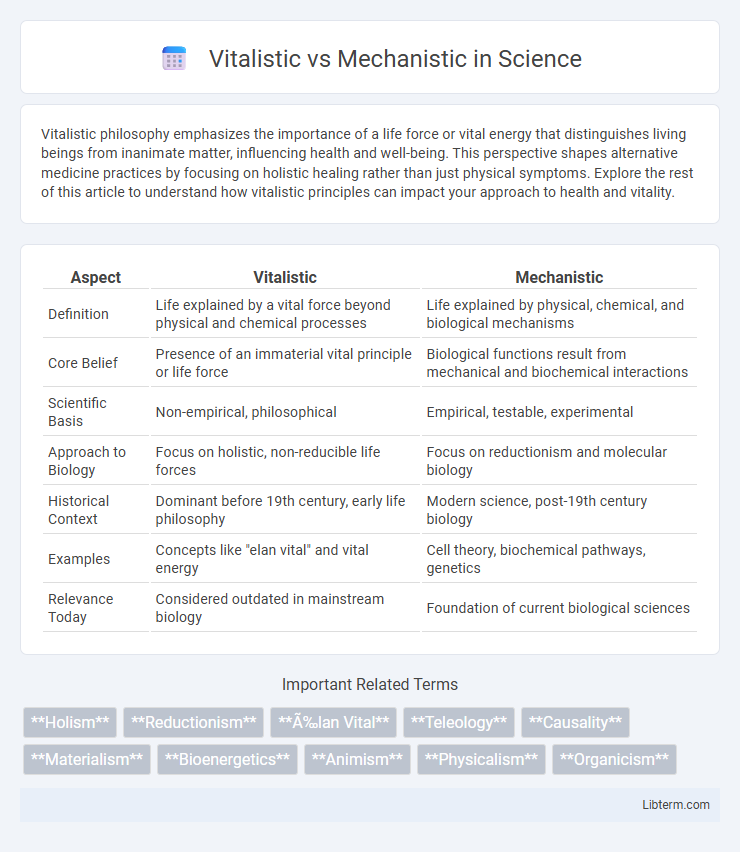
| Aspect | Vitalistic | Mechanistic |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Life explained by a vital force beyond physical and chemical processes | Life explained by physical, chemical, and biological mechanisms |
| Core Belief | Presence of an immaterial vital principle or life force | Biological functions result from mechanical and biochemical interactions |
| Scientific Basis | Non-empirical, philosophical | Empirical, testable, experimental |
| Approach to Biology | Focus on holistic, non-reducible life forces | Focus on reductionism and molecular biology |
| Historical Context | Dominant before 19th century, early life philosophy | Modern science, post-19th century biology |
| Examples | Concepts like "elan vital" and vital energy | Cell theory, biochemical pathways, genetics |
| Relevance Today | Considered outdated in mainstream biology | Foundation of current biological sciences |
Introduction to Vitalism and Mechanism
Vitalism posits that living organisms possess a non-material vital force distinguishing them from inanimate objects, emphasizing the presence of unique life energy beyond physical and chemical processes. Mechanism interprets life through the lens of physical laws and biochemical reactions, viewing organisms as complex machines governed solely by mechanical principles. This fundamental contrast shapes ongoing debates in biology and philosophy regarding the nature of life and the origin of biological functions.
Historical Origins of Vitalistic and Mechanistic Theories
Vitalistic theories originated in the 17th and 18th centuries, rooted in the belief that living organisms are governed by a unique vital force beyond physical and chemical laws, with early proponents such as Johann Friedrich Blumenbach and Hans Driesch emphasizing life's irreducibility. Mechanistic theories emerged during the Scientific Revolution, influenced by Rene Descartes and later scientists, who viewed organisms as complex machines operating solely through mechanical and chemical processes. The historical shift from vitalism to mechanism marked a critical transition in biology, moving from metaphysical explanations to empirical, mechanistic understandings of life functions.
Core Principles of Vitalism
Vitalism centers on the belief that living organisms possess a unique vital force that cannot be explained by physical or chemical processes alone, distinguishing life from inanimate matter. This vital force is often described as an intrinsic energy responsible for growth, development, and healing, emphasizing that biological functions transcend mechanistic explanations. Core principles of vitalism include the idea that life cannot arise from non-life (abiogenesis), and that biological phenomena must be understood through qualitative, holistic perspectives rather than purely quantitative, mechanistic approaches.
Fundamental Concepts of Mechanism
Mechanism centers on the principle that all natural phenomena can be explained through physical causes and interactions governed by laws of physics and chemistry. It posits that living organisms function similarly to machines, with biological processes reducible to mechanical operations such as chemical reactions and physical forces. This fundamental concept emphasizes a deterministic and materialistic view of life, contrasting sharply with vitalistic beliefs in an intrinsic life force beyond physical explanations.
Vitalism in Modern Science and Medicine
Vitalism, emphasizing the presence of a unique life force beyond physical and chemical processes, has largely been replaced by mechanistic views in modern science and medicine, yet it still influences holistic and integrative health practices. Concepts rooted in vitalism persist in fields such as homeopathy, naturopathy, and traditional Chinese medicine, where the focus remains on the body's inherent ability to heal and maintain balance. Research into biofields and electromagnetic therapies reflects a continued interest in exploring non-mechanistic explanations for biological functions.
Mechanistic Perspectives in Biological Systems
Mechanistic perspectives in biological systems emphasize the understanding of organisms through physical and chemical processes, treating living beings as complex machines governed by the laws of physics and chemistry. This approach employs reductionism to analyze biological functions by breaking them down into molecular and cellular components, facilitating advancements in fields like molecular biology and biotechnology. Mechanistic models enable precise predictions and manipulations of biological behaviors, supporting developments in medical treatments and bioengineering.
Key Figures and Influencers in Both Philosophies
Key figures in vitalism include Hans Driesch, who championed the concept of an immaterial life force, and Henri Bergson, known for his idea of elan vital driving evolution. Mechanistic philosophy is notably represented by Rene Descartes, who viewed organisms as complex machines, and Francis Crick, co-discoverer of DNA's structure, emphasizing biochemical processes. These influencers shaped the fundamental debates on whether life is governed by inherent vital forces or purely physical and chemical mechanisms.
Vitalistic vs Mechanistic: Comparative Analysis
Vitalistic theories emphasize a life force or vital principle that cannot be explained solely by physical or chemical processes, contrasting mechanistic views which interpret biological functions through mechanical and biochemical interactions. In a comparative analysis, vitalism asserts an intrinsic, non-material essence vital for life, whereas mechanism reduces all biological phenomena to physical laws and empirical evidence. The debate shapes foundational perspectives in biology, affecting approaches to physiology, medicine, and the philosophy of life sciences.
Impact on Contemporary Health Practices
Vitalistic perspectives emphasize the body's innate ability to heal and maintain health through vital forces or energy fields, influencing complementary therapies like homeopathy, acupuncture, and naturopathy. Mechanistic approaches view the body as a complex machine governed by biochemical and physiological processes, forming the foundation of modern Western medicine, including pharmacology and surgery. The integration of vitalistic principles with mechanistic models has led to holistic health practices that combine conventional treatments with alternative therapies for enhanced patient outcomes.
Future Directions: Integration or Divergence?
Future directions in the Vitalistic versus Mechanistic debate suggest potential integration through interdisciplinary research combining biological, philosophical, and technological insights, advancing holistic health models and synthetic biology. Innovations in systems biology and biomimetics are enabling a convergence that respects vitalistic principles of life forces while leveraging mechanistic frameworks for predictive and therapeutic applications. Divergence may persist in epistemological and methodological approaches, emphasizing subjective experience versus empirical quantification, shaping specialized fields and contrasting scientific paradigms.
Vitalistic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com