Controlled environments ensure precise regulation of temperature, humidity, and light, optimizing conditions for plant growth and industrial processes. These systems enhance efficiency, reduce waste, and improve overall quality by maintaining consistent parameters. Discover how controlled settings can transform your operations by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
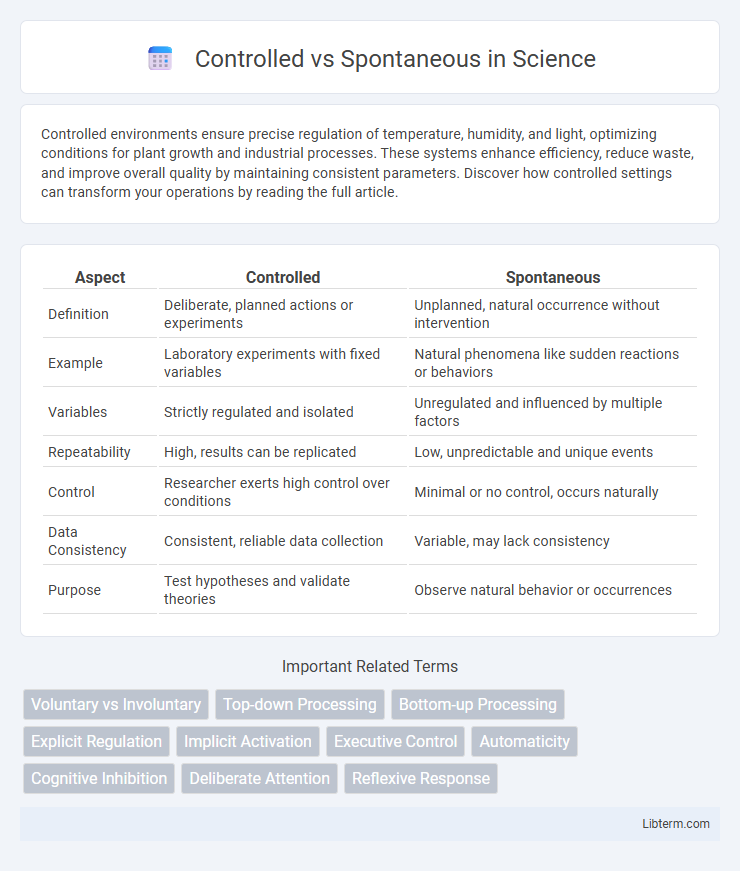
| Aspect | Controlled | Spontaneous |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Deliberate, planned actions or experiments | Unplanned, natural occurrence without intervention |
| Example | Laboratory experiments with fixed variables | Natural phenomena like sudden reactions or behaviors |
| Variables | Strictly regulated and isolated | Unregulated and influenced by multiple factors |
| Repeatability | High, results can be replicated | Low, unpredictable and unique events |
| Control | Researcher exerts high control over conditions | Minimal or no control, occurs naturally |
| Data Consistency | Consistent, reliable data collection | Variable, may lack consistency |
| Purpose | Test hypotheses and validate theories | Observe natural behavior or occurrences |
Understanding Controlled and Spontaneous Processes
Controlled processes require conscious, deliberate attention and typically involve slower, effortful cognition, such as problem-solving or decision-making tasks. Spontaneous processes operate automatically and quickly, often without conscious awareness, enabling immediate responses like habitual actions or intuitive judgments. Understanding the distinction between these processes is crucial for optimizing cognitive performance and managing attention in varied contexts.
Key Differences Between Controlled and Spontaneous
Controlled communication involves deliberate planning, structured content, and formal settings, ensuring clear message delivery and minimizing misunderstandings. Spontaneous communication is characterized by its natural, unstructured flow, often occurring in informal situations, promoting genuine interaction and real-time feedback. Key differences include the level of preparation, predictability, and flexibility in response, with controlled communication emphasizing precision and spontaneous communication fostering authenticity.
Benefits of Controlled Actions
Controlled actions enhance precision and consistency, leading to improved decision-making and task efficiency in professional and personal contexts. They reduce errors and increase reliability by allowing for deliberate planning, monitoring, and adjustment of behaviors. This methodical approach supports goal achievement and optimizes performance under pressure or complex conditions.
Advantages of Spontaneous Behavior
Spontaneous behavior offers advantages such as increased creativity and adaptability, allowing individuals to respond flexibly to unforeseen situations. It enhances authentic expression and fosters genuine social connections by reducing premeditated or scripted interactions. This natural approach often leads to quicker decision-making and promotes emotional resilience in dynamic environments.
When to Choose Control Over Spontaneity
Choosing control over spontaneity is essential in situations requiring precision, consistency, and risk management, such as project management, financial planning, or medical procedures. In high-stakes environments like aviation or legal processes, enforcing control ensures adherence to protocols and minimizes errors. Organizations prioritize controlled decision-making to achieve predictable outcomes, maintain quality standards, and comply with regulatory requirements.
Risks of Excessive Control
Excessive control in management stifles creativity and innovation, leading to decreased employee morale and engagement. It increases the risk of burnout as rigid oversight limits autonomy and flexibility, causing stress and reduced job satisfaction. Over-controlled environments often result in poor decision-making due to micromanagement and lack of empowerment.
Pitfalls of Pure Spontaneity
Pure spontaneity often leads to impulsive decisions that lack strategic foresight, causing inconsistent outcomes and potential negative consequences. Without a controlled framework, spontaneous actions may result in overlooked risks, fragmented efforts, and inefficiency in achieving long-term goals. Balancing spontaneity with structure ensures creativity thrives while maintaining direction and accountability.
Balancing Control and Spontaneity
Balancing control and spontaneity is essential for effective decision-making and creativity, blending structured planning with adaptive flexibility. Controlled actions leverage deliberate thought and predictable outcomes, while spontaneous decisions encourage innovation and responsiveness to unforeseen opportunities. Optimizing this balance enhances productivity by maintaining focus without stifling improvisation and dynamic problem-solving.
Real-Life Examples: Controlled vs Spontaneous Situations
Controlled situations, such as planned meetings or rehearsed presentations, allow individuals to prepare responses and manage outcomes effectively, enhancing clarity and professionalism. Spontaneous scenarios, like impromptu conversations or unexpected questions during interviews, require quick thinking and adaptability, often revealing genuine reactions and creativity. Real-life examples include job interviews conducted with scripted questions versus natural networking events where dialogue evolves unpredictably.
Practical Tips for Harmonizing Both Approaches
Balancing controlled and spontaneous approaches enhances creativity and productivity by integrating structured planning with flexible improvisation. Practical tips include setting clear goals and timelines while allowing moments for free-form brainstorming to encourage innovation. Using time-blocking methods combined with open-ended sessions can help harmonize discipline and spontaneity effectively.
Controlled Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com