ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is a critical process in data management that involves extracting data from various sources, transforming it into a suitable format, and loading it into a target database or data warehouse for analysis. Mastering ETL enables your organization to maintain clean, consistent, and actionable data across diverse systems. Discover how ETL workflows can optimize your data integration by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
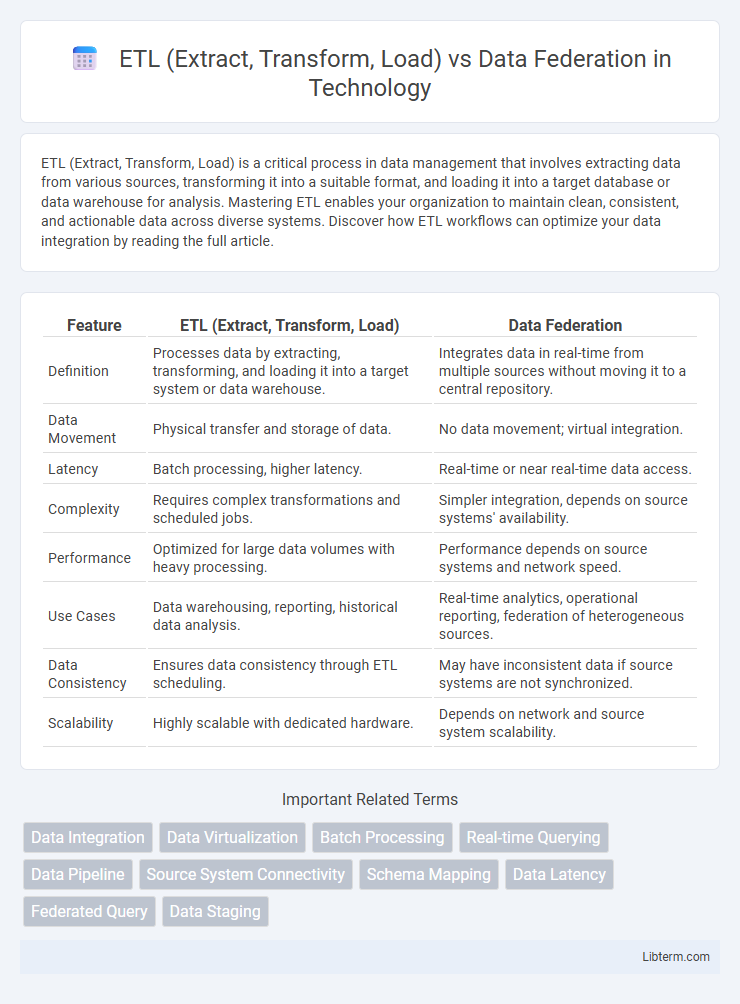
| Feature | ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) | Data Federation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Processes data by extracting, transforming, and loading it into a target system or data warehouse. | Integrates data in real-time from multiple sources without moving it to a central repository. |
| Data Movement | Physical transfer and storage of data. | No data movement; virtual integration. |
| Latency | Batch processing, higher latency. | Real-time or near real-time data access. |
| Complexity | Requires complex transformations and scheduled jobs. | Simpler integration, depends on source systems' availability. |
| Performance | Optimized for large data volumes with heavy processing. | Performance depends on source systems and network speed. |
| Use Cases | Data warehousing, reporting, historical data analysis. | Real-time analytics, operational reporting, federation of heterogeneous sources. |
| Data Consistency | Ensures data consistency through ETL scheduling. | May have inconsistent data if source systems are not synchronized. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable with dedicated hardware. | Depends on network and source system scalability. |
Introduction to ETL and Data Federation
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is a data integration process that extracts data from multiple sources, transforms it into a consistent format, and loads it into a centralized data warehouse for analysis. Data Federation enables real-time access to data across disparate systems by creating a virtual database layer without physically moving the data. ETL emphasizes data consolidation and preparation, while Data Federation focuses on dynamic data retrieval and integration for on-demand querying.
Core Concepts: Understanding ETL
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) is a data integration process that involves extracting data from multiple sources, transforming it into a suitable format, and loading it into a centralized data warehouse for analysis. Core concepts of ETL include data cleansing, enrichment, and schema transformation, which ensure data quality and consistency before loading. Unlike Data Federation, which queries data in real-time without moving it, ETL enables historical data storage and complex analytics by physically consolidating data.
Core Concepts: Understanding Data Federation
Data Federation enables real-time data access by creating a virtual database layer that integrates data from multiple disparate sources without physically moving it, unlike ETL which involves extracting, transforming, and loading data into a centralized repository. This approach reduces data redundancy and latency, allowing users to query integrated data on-demand across diverse systems. Core to Data Federation is the abstraction of underlying data heterogeneity, providing a unified and consistent view of distributed data sources for seamless business intelligence.
Key Differences Between ETL and Data Federation
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) involves physically extracting data from source systems, transforming it into a structured format, and loading it into a target data warehouse, ensuring data consistency and historical storage. Data federation enables real-time access to data from multiple heterogeneous sources by creating a virtual database without moving or storing the data, allowing for dynamic querying across diverse systems. The key differences lie in ETL's batch-oriented data processing and storage versus data federation's on-demand, federated query execution without data replication.
Use Cases for ETL Solutions
ETL solutions excel in scenarios requiring complex data transformation, cleansing, and integration from multiple heterogeneous sources into a centralized data warehouse or data lake for deep analytics and reporting. Industries with high data volume and strict data quality demands, such as finance, healthcare, and retail, rely on ETL for batch processing, data migration, and historical data consolidation. ETL is preferred when consistent, reusable data pipelines and compliance with governance policies are critical, enabling reliable, structured datasets for business intelligence and machine learning models.
Use Cases for Data Federation
Data Federation enables real-time querying across multiple disparate data sources without physical data movement, ideal for scenarios requiring immediate access to up-to-date data such as live dashboard reporting and agile analytics. Unlike ETL, which consolidates data into a data warehouse through batch processing, Data Federation suits environments where data freshness and reduced latency are critical, including federated search, data virtualization, and cases with strict data governance. Enterprises with heterogeneous data landscapes leverage Data Federation to integrate data on-demand, minimizing storage costs while maintaining a unified data view for operational intelligence.
Performance Comparison: ETL vs Data Federation
ETL processes typically offer higher performance by physically extracting, transforming, and loading data into a centralized repository, enabling faster query execution and analytics. Data federation provides real-time access to distributed data sources without data movement, but often suffers from slower performance due to on-the-fly data integration and query processing overhead. ETL is preferred for large-scale batch processing and complex transformations, while data federation suits scenarios requiring real-time data access with minimal latency.
Data Integration and Real-Time Capabilities
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) enables comprehensive data integration by consolidating and transforming data into a centralized repository, supporting complex analytics but often with batch processing delays. Data Federation offers real-time data integration by querying multiple heterogeneous data sources on-demand without physical data movement, delivering up-to-date insights across distributed systems. Organizations prioritize ETL for deep data transformation and historical analysis, while Data Federation excels in scenarios requiring immediate access to diverse, live data streams for operational intelligence.
Scalability and Maintenance Considerations
ETL processes provide high scalability by handling large-scale data extraction and transformation through batch processing, but often require complex maintenance due to scheduled jobs and data storage needs. Data Federation offers real-time data integration with lower maintenance overhead, as it queries data directly across multiple sources without physical data movement, yet scalability may be limited by source system performance and network latency. Choosing between ETL and Data Federation depends on the volume of data, latency requirements, and the available resources for ongoing system maintenance.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and data federation depends on factors like data volume, latency requirements, and integration complexity. ETL is ideal for large datasets needing thorough cleansing and transformation, ensuring high data quality in a centralized repository. Data federation suits scenarios requiring real-time access to distributed data sources without physical data movement, optimizing agility and reducing storage demands.
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com