A honeytoken is a security mechanism designed to lure cyber attackers by planting fake data or credentials that appear valuable but serve as traps for detecting unauthorized access. These decoys help your organization identify breaches early and understand attacker behavior without risking actual sensitive information. Explore the rest of this article to learn how honeytokens can enhance your cybersecurity strategy effectively.
Table of Comparison
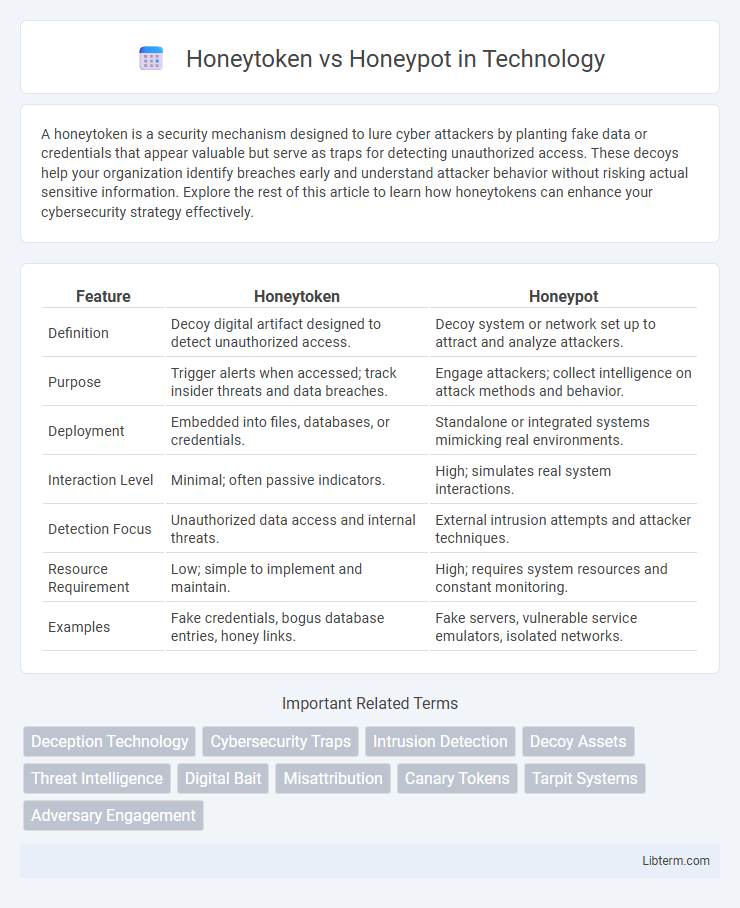
| Feature | Honeytoken | Honeypot |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Decoy digital artifact designed to detect unauthorized access. | Decoy system or network set up to attract and analyze attackers. |
| Purpose | Trigger alerts when accessed; track insider threats and data breaches. | Engage attackers; collect intelligence on attack methods and behavior. |
| Deployment | Embedded into files, databases, or credentials. | Standalone or integrated systems mimicking real environments. |
| Interaction Level | Minimal; often passive indicators. | High; simulates real system interactions. |
| Detection Focus | Unauthorized data access and internal threats. | External intrusion attempts and attacker techniques. |
| Resource Requirement | Low; simple to implement and maintain. | High; requires system resources and constant monitoring. |
| Examples | Fake credentials, bogus database entries, honey links. | Fake servers, vulnerable service emulators, isolated networks. |
Introduction to Honeytoken and Honeypot
Honeytokens are decoy data or digital artifacts designed to detect unauthorized access and alert security teams upon interaction, while honeypots are isolated, purposely vulnerable systems used to attract and analyze cyber attackers. Honeytokens can take the form of fake credentials, files, or database entries that trigger alerts when accessed, enhancing intrusion detection without the need for complex infrastructure. Honeypots simulate real environments to study attacker behavior and gather threat intelligence, providing valuable insights for strengthening network defenses.
Defining Honeytokens
Honeytokens are deceptive data elements or digital artifacts designed to detect unauthorized access attempts by triggering alerts when interacted with, unlike honeypots which are entire decoy systems or networks used to lure attackers. Honeytokens can be anything from fake database entries, API keys, or email addresses that do not serve any legitimate purpose but provide immediate evidence of malicious activity upon use. These tools play a crucial role in cybersecurity by providing early warning signs of breaches without requiring the attacker to interact with complex network environments.
What is a Honeypot?
A honeypot is a cybersecurity mechanism designed to attract, detect, and analyze unauthorized access by mimicking legitimate systems or data. It acts as a decoy resource, isolating attackers and collecting intelligence on their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs). Unlike honeytokens, which are discrete pieces of data, honeypots are fully interactive environments used to study attacker behavior and improve threat detection.
Key Differences Between Honeytoken and Honeypot
Honeytokens are digital bait, such as fake credentials or files, designed to detect unauthorized access by triggering alerts when used, whereas honeypots are decoy systems or networks created to lure attackers and analyze their tactics. Honeytokens operate on a smaller scale, targeting specific data points without requiring complex infrastructure, while honeypots involve deploying entire simulated environments to engage attackers over extended periods. The primary distinction lies in honeytokens' minimal resource requirement and quick alerting capability versus honeypots' comprehensive threat intelligence collection through prolonged attacker interaction.
Use Cases for Honeytokens
Honeytokens serve as deceptive digital artifacts such as fake credentials, database entries, or email addresses designed to detect unauthorized access and insider threats by alerting security teams when interacted with. Unlike honeypots, which are entire systems or networks deliberately exposed to lure attackers, honeytokens provide granular visibility into breach points and can be embedded in various environments including cloud storage, application logs, or code repositories. Organizations leverage honeytokens to monitor data exfiltration, identify compromised user accounts, and enhance insider threat detection without exposing production systems to risk.
Honeypot Applications in Cybersecurity
Honeypots serve as decoy systems designed to attract cyber attackers and analyze their tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) in real-time, enhancing threat intelligence for cybersecurity teams. These applications enable early detection of zero-day exploits, malware behavior, and insider threats by creating a controlled environment that mimics vulnerable assets. Implementing honeypots helps organizations strengthen incident response strategies, improve intrusion detection systems, and proactively mitigate advanced persistent threats (APTs).
Advantages of Deploying Honeytokens
Honeytokens provide a low-cost, easily deployable method for detecting unauthorized access and insider threats by embedding decoy data that triggers alerts when interacted with. Unlike honeypots, honeytokens do not require maintaining complex infrastructure and reduce the risk of attacker lateral movement within the network. Their versatility and stealthiness enhance threat intelligence by providing early warnings and actionable insights without attracting excessive attacker attention.
Risks and Limitations of Honeypots
Honeypots can expose organizations to risks such as attracting real attackers who may use the decoy system to pivot deeper into the network, increasing the potential for actual breaches. They require continuous monitoring and maintenance to avoid becoming liabilities or exploiting resources for malicious purposes. False positives and legal implications related to data collection also limit the effectiveness and safe deployment of honeypots compared to simpler honeytokens.
Choosing Between Honeytoken and Honeypot
Choosing between honeytoken and honeypot depends on the specific cybersecurity goals and infrastructure of an organization. Honeytokens, which are digital traps such as fake credentials or files, offer lightweight deception to detect unauthorized access without requiring significant resources. Honeypots, physical or virtual systems designed to mimic real targets, provide in-depth threat analysis and attacker behavior monitoring but require more maintenance and risk management.
Best Practices for Integrating Deception Technologies
Effective integration of honeytokens and honeypots requires clear segmentation within network architecture to isolate deception assets from production environments, reducing operational risk. Regularly updating and customizing honeytokens with unique data elements enhances their detectability against sophisticated attackers, while deploying honeypots with realistic service emulation increases engagement and threat intelligence quality. Implement continuous monitoring and automated alerting workflows to quickly analyze interaction patterns, enabling proactive response to intrusion attempts and improving overall cybersecurity posture.
Honeytoken Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com