Partnerships foster collaboration by combining strengths, resources, and expertise to achieve common goals efficiently. Building a strong partnership requires trust, clear communication, and shared vision to ensure mutual success. Discover how cultivating the right partnerships can transform your business by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
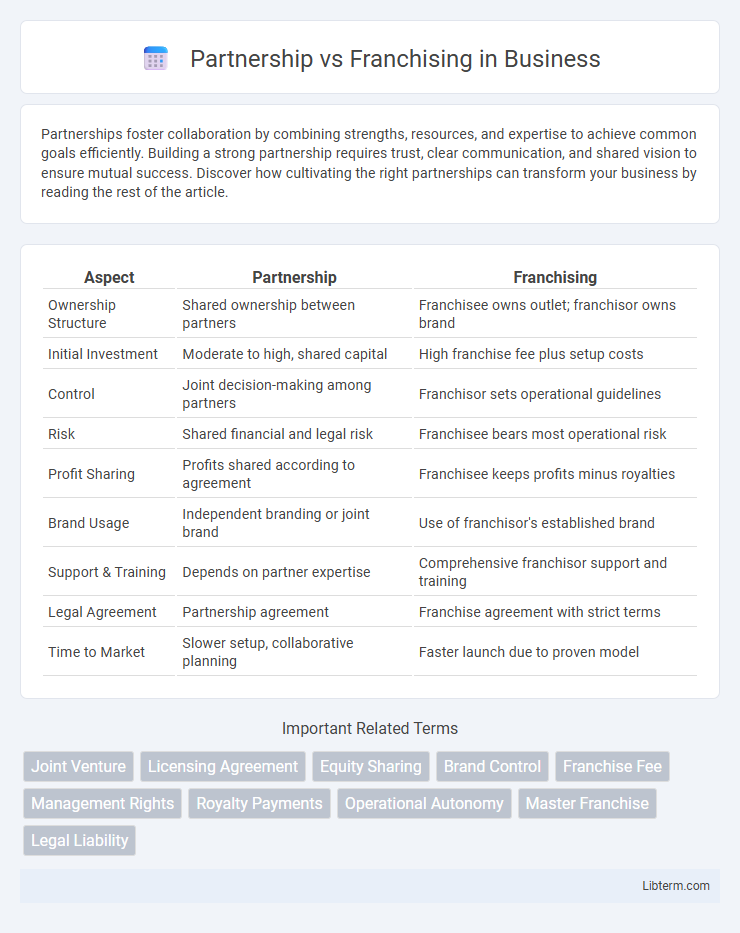
| Aspect | Partnership | Franchising |
|---|---|---|
| Ownership Structure | Shared ownership between partners | Franchisee owns outlet; franchisor owns brand |
| Initial Investment | Moderate to high, shared capital | High franchise fee plus setup costs |
| Control | Joint decision-making among partners | Franchisor sets operational guidelines |
| Risk | Shared financial and legal risk | Franchisee bears most operational risk |
| Profit Sharing | Profits shared according to agreement | Franchisee keeps profits minus royalties |
| Brand Usage | Independent branding or joint brand | Use of franchisor's established brand |
| Support & Training | Depends on partner expertise | Comprehensive franchisor support and training |
| Legal Agreement | Partnership agreement | Franchise agreement with strict terms |
| Time to Market | Slower setup, collaborative planning | Faster launch due to proven model |
Understanding Partnerships: Key Concepts
Partnerships involve two or more individuals or entities sharing ownership, profits, and responsibilities in a business venture, with legal obligations outlined in a partnership agreement. Unlike franchising, partnerships allow more flexibility in management decisions and profit distribution, as partners directly control the operations and brand. Key concepts include joint liability, fiduciary duties, equity sharing, and the importance of clear communication and trust among partners to ensure business success.
Franchising Explained: Core Principles
Franchising is a business model where the franchisor grants the franchisee the rights to operate a business using its brand, systems, and support. Key principles include standardized operations, ongoing training, marketing assistance, and fee-based agreements typically involving initial franchise fees and recurring royalties. This model ensures brand consistency and allows rapid expansion while providing entrepreneurs with a proven business framework and continuous support.
Legal Structure Differences
Partnerships involve two or more individuals sharing ownership, profits, and liabilities based on a partnership agreement, whereas franchising is a licensing arrangement where the franchisee operates under the franchisor's brand and business model. In partnerships, all partners typically have joint and several liabilities, while franchising limits the franchisee's liability to their own business operations. Legal requirements for partnerships include registration and adherence to partnership laws, whereas franchising involves compliance with franchise disclosure laws and contractual obligations defined by the franchising agreement.
Investment and Capital Requirements
Partnerships typically require lower initial investment as capital contributions are pooled from multiple partners, reducing individual financial burden. Franchising demands higher upfront costs, including franchise fees, royalties, and compliance with franchisor mandates, which can significantly increase capital requirements. Both models affect cash flow differently, with partnerships offering flexible funding options while franchising demands continuous financial commitments for brand use and operational support.
Level of Control and Decision-Making
Partnerships allow shared control and joint decision-making between partners, enabling flexible management and collaborative strategy development. Franchising grants the franchisor significant control over business operations, brand standards, and marketing, while the franchisee operates within established guidelines with limited autonomy. Decision-making in franchising is typically centralized, ensuring consistency across locations, whereas partnerships distribute decision authority more evenly among partners.
Risk Management and Liability
Partnerships involve shared liability among partners, exposing each individual to personal financial risk for business debts and legal obligations, which necessitates careful risk management agreements to protect personal assets. Franchising limits liability primarily to the franchisee, as the franchisor typically retains brand control but not direct financial responsibility; franchisees must manage operational risks while adhering to franchise standards. Effective risk management in franchising includes compliance with franchise contracts and local regulations, whereas partnerships require clear legal frameworks to address potential disputes and liability exposure.
Branding and Marketing Support
Partnerships often provide shared branding strategies where both parties benefit from combined market presence, but individual brand identities remain distinct. Franchising offers a unified branding system with strict guidelines, ensuring consistency and strong brand recognition across all locations. Marketing support in franchising typically includes centralized campaigns, promotional materials, and training, whereas partnerships rely more on collaborative efforts and joint marketing initiatives.
Profit-Sharing Models
Profit-sharing models in partnerships involve direct allocation of earnings based on agreed-upon ownership percentages, allowing for transparent distribution aligned with each partner's contribution. Franchising profit-sharing typically centers around royalties and fees paid by franchisees to franchisors, often calculated as a percentage of gross sales rather than net profits. This distinction influences financial risk and reward distribution, where partnerships share profits and losses collectively, while franchisees operate independently with profit remittance obligations to franchisors.
Expansion and Growth Potential
Partnerships offer flexible expansion opportunities by allowing businesses to share resources, expertise, and risks, enabling rapid adaptation to market changes. Franchising provides scalable growth through a proven business model, leveraging franchisees' investments to accelerate market penetration while maintaining brand consistency. The choice between partnership and franchising impacts control, capital requirements, and speed of expansion, influencing long-term growth potential.
Choosing the Right Model for Your Business
Choosing the right business model between partnership and franchising depends on control preferences, capital investment, and growth objectives. Partnerships offer shared decision-making and resource pooling, ideal for collaborative business ventures with flexible structure. Franchising provides a proven brand and operational support, suitable for rapid expansion using a standardized model with franchisee autonomy.
Partnership Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com