Trade secrets protect valuable business information by keeping formulas, practices, processes, designs, or compilations confidential to maintain a competitive advantage. Unlike patents, trade secrets do not require public disclosure, enabling companies to safeguard innovations indefinitely as long as secrecy is maintained. Discover how understanding trade secret laws can help you secure your business's most critical assets by reading the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
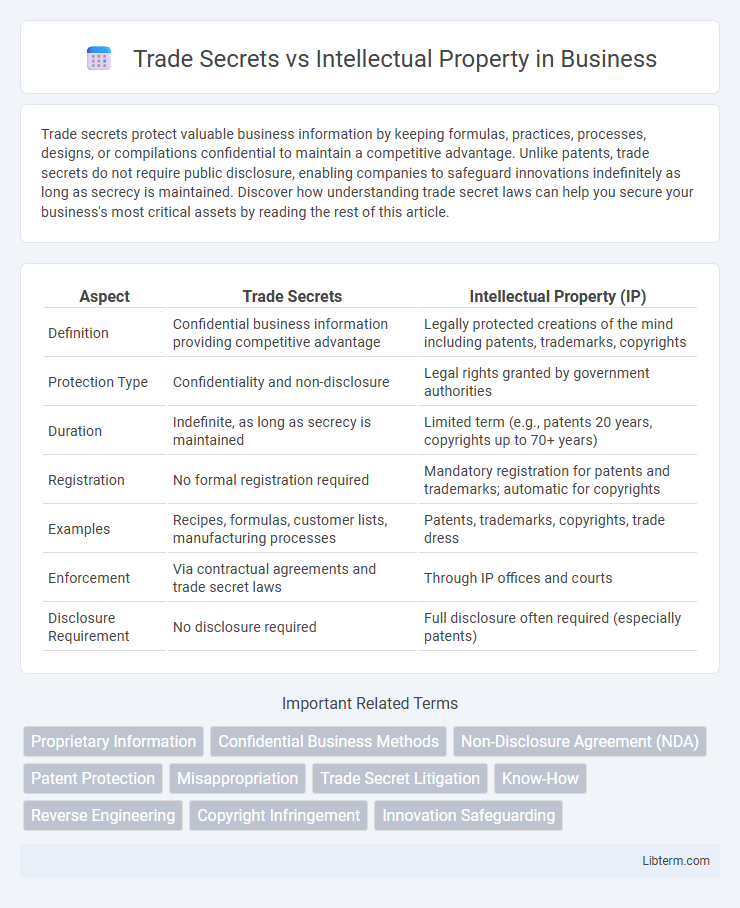
| Aspect | Trade Secrets | Intellectual Property (IP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Confidential business information providing competitive advantage | Legally protected creations of the mind including patents, trademarks, copyrights |
| Protection Type | Confidentiality and non-disclosure | Legal rights granted by government authorities |
| Duration | Indefinite, as long as secrecy is maintained | Limited term (e.g., patents 20 years, copyrights up to 70+ years) |
| Registration | No formal registration required | Mandatory registration for patents and trademarks; automatic for copyrights |
| Examples | Recipes, formulas, customer lists, manufacturing processes | Patents, trademarks, copyrights, trade dress |
| Enforcement | Via contractual agreements and trade secret laws | Through IP offices and courts |
| Disclosure Requirement | No disclosure required | Full disclosure often required (especially patents) |
Introduction to Trade Secrets and Intellectual Property
Trade secrets comprise confidential business information that provides a competitive edge, protected without registration as long as secrecy is maintained. Intellectual Property (IP) encompasses legally recognized creations of the mind, including patents, copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets, each offering distinct protections. Unlike patents and copyrights that require public disclosure, trade secrets rely on internal safeguards to prevent unauthorized access and use.
Defining Trade Secrets: Key Features
Trade secrets are a type of intellectual property characterized by confidential business information that provides a competitive advantage, including formulas, practices, processes, designs, or compilations of information. Unlike patents or copyrights, trade secrets do not require registration but rely on reasonable efforts to maintain secrecy, such as non-disclosure agreements and security measures. The key legal protection for trade secrets is preventing unauthorized use or disclosure, enabling businesses to safeguard valuable knowledge indefinitely as long as secrecy is preserved.
Understanding Types of Intellectual Property
Intellectual Property (IP) comprises various types including patents, copyrights, trademarks, and trade secrets, each providing distinct legal protections for creative and commercial assets. Trade secrets protect confidential business information that provides a competitive edge, such as formulas, practices, or processes, without public disclosure. Patents safeguard inventions by granting exclusive rights, while copyrights and trademarks protect creative works and brand identity, respectively, highlighting the diverse scope of IP rights.
Legal Protections: Trade Secrets vs IP Rights
Trade secrets offer legal protection by preventing unauthorized use or disclosure of confidential business information without registration, relying on secrecy measures and non-disclosure agreements. Intellectual property rights, such as patents, copyrights, and trademarks, provide formal legal protection through government registration, granting exclusive rights for a specific period. Trade secrets can last indefinitely as long as secrecy is maintained, whereas IP rights have fixed terms and require public disclosure.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Trade Secrets
Trade secrets offer the advantage of indefinite protection without registration costs, allowing businesses to safeguard proprietary formulas, processes, or methods as long as secrecy is maintained. However, the disadvantage lies in the risk of loss through reverse engineering, employee disclosure, or independent development, which can result in the irrevocable loss of competitive advantage. Unlike patents, trade secrets do not provide exclusive rights enforceable through formal legal mechanisms, making monitoring and enforcing protection more challenging.
Benefits and Challenges of Intellectual Property
Intellectual property (IP) provides legal protection for inventions, trademarks, copyrights, and patents, enabling businesses to monetize innovation and establish market exclusivity, which enhances brand value and competitive advantage. However, challenges of IP include high costs of registration and enforcement, potential public disclosure requirements, and the complexity of international protection due to varying legal frameworks. Effective management of IP helps secure long-term revenue streams but demands continuous monitoring and strategic defense against infringement risks.
Key Differences Between Trade Secrets and Intellectual Property
Trade secrets protect confidential business information that provides a competitive advantage, such as formulas, processes, or methods, without public disclosure, and remain protected as long as secrecy is maintained. Intellectual property (IP) includes legally registered rights like patents, copyrights, and trademarks that provide exclusive control over inventions, works, or brands for a limited period. Key differences include the requirement of registration for most IP types, enforceable time limits, and public disclosure obligations, whereas trade secrets rely on non-disclosure and breach of confidentiality for protection.
Strategies for Protecting Business Information
Effective strategies for protecting trade secrets involve implementing strict confidentiality agreements, limiting information access to essential personnel, and conducting regular employee training on data security protocols. Intellectual property protection relies on legal mechanisms such as patents, copyrights, and trademarks to safeguard inventions, creative works, and brand identifiers, each requiring formal registration processes and monitoring for infringement. Combining robust internal controls for trade secrets with proactive legal protection of intellectual property assets enhances overall business security and competitive advantage.
Real-World Examples: Trade Secrets vs IP Cases
The Coca-Cola formula exemplifies a trade secret, protected by confidentiality rather than patent law to maintain its competitive edge indefinitely. Apple's design patents on the iPhone showcase intellectual property rights that safeguard innovation through public disclosure while granting exclusivity for a limited time. The landmark case of Waymo vs. Uber highlighted the critical differences between trade secrets and patents, where theft of self-driving technology trade secrets led to significant legal consequences.
Choosing the Right Protection for Your Assets
Trade secrets protect confidential business information that provides a competitive edge and can remain protected indefinitely without public disclosure, unlike patents that require public filing and have limited terms. Intellectual property, including patents, trademarks, and copyrights, offers formal legal protection but involves registration processes and specific durations of protection. Selecting the right protection depends on factors like the nature of the asset, the importance of confidentiality, enforcement capabilities, and long-term business strategy.
Trade Secrets Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com