Effective operations management streamlines processes to enhance productivity and reduce costs, directly impacting your organization's profitability and efficiency. By leveraging strategic planning, resource allocation, and continuous improvement practices, businesses can better meet customer demands and stay competitive in dynamic markets. Explore this article to discover key strategies and tools that can optimize your operations management for sustained success.
Table of Comparison
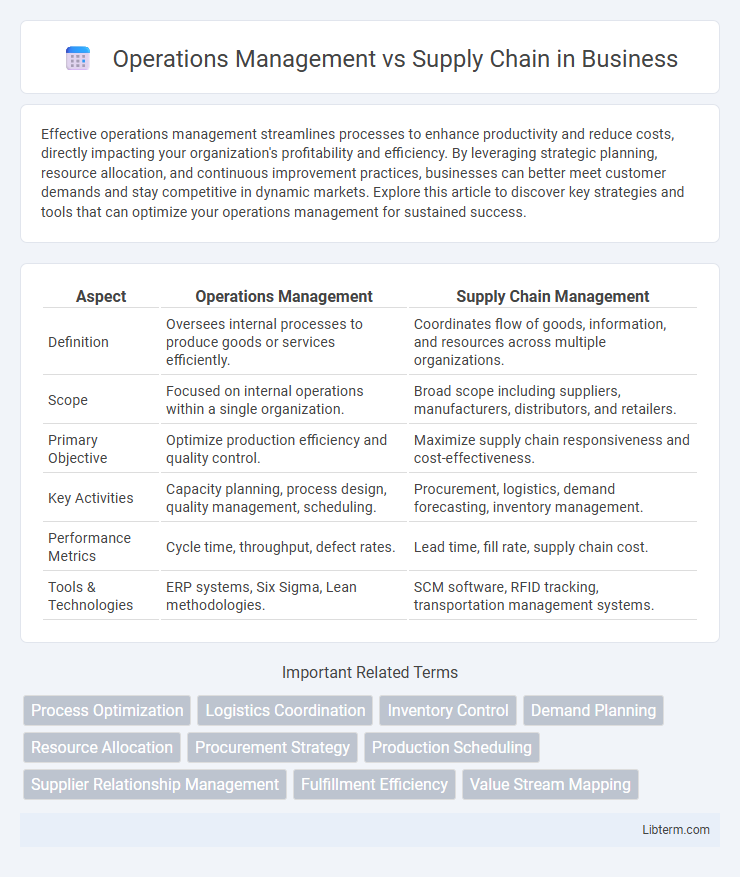
| Aspect | Operations Management | Supply Chain Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Oversees internal processes to produce goods or services efficiently. | Coordinates flow of goods, information, and resources across multiple organizations. |
| Scope | Focused on internal operations within a single organization. | Broad scope including suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. |
| Primary Objective | Optimize production efficiency and quality control. | Maximize supply chain responsiveness and cost-effectiveness. |
| Key Activities | Capacity planning, process design, quality management, scheduling. | Procurement, logistics, demand forecasting, inventory management. |
| Performance Metrics | Cycle time, throughput, defect rates. | Lead time, fill rate, supply chain cost. |
| Tools & Technologies | ERP systems, Six Sigma, Lean methodologies. | SCM software, RFID tracking, transportation management systems. |
Introduction to Operations Management and Supply Chain
Operations Management involves overseeing the production process to ensure efficient resource use, quality control, and timely delivery of goods and services. Supply Chain Management coordinates the flow of materials, information, and finances from suppliers to end customers, optimizing the entire product lifecycle. Integrating both disciplines enhances organizational performance by aligning internal processes with external logistics and demand management.
Defining Operations Management
Operations Management involves planning, organizing, and supervising production processes to efficiently convert inputs into finished goods or services, emphasizing resource optimization and quality control. It encompasses activities such as capacity planning, inventory management, and process improvement to enhance operational efficiency. In contrast, Supply Chain Management extends beyond internal operations, focusing on the coordination of materials, information, and finances across multiple organizations to deliver products to the end customer effectively.
Defining Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management (SCM) involves coordinating and integrating key business processes from raw material sourcing to final product delivery, ensuring efficient flow of goods, information, and finances across the entire supply network. Unlike Operations Management, which concentrates on optimizing internal processes within a single organization, SCM extends beyond organizational boundaries by managing relationships and collaboration among suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and retailers. Effective SCM enhances customer value, reduces costs, and improves competitive advantage through strategic planning, demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics optimization.
Key Differences Between Operations and Supply Chain
Operations management concentrates on efficiently producing goods and services within a company, emphasizing process optimization, quality control, and resource allocation. Supply chain management involves coordinating and integrating the flow of materials, information, and finances across multiple organizations from suppliers to end customers. Key differences include the scope--operations focus on internal processes while supply chain covers external relationships--and primary objectives, where operations aim at production efficiency and supply chain focuses on overall network optimization.
Core Functions of Operations Management
Operations Management focuses on core functions such as process design, capacity planning, quality control, and inventory management to ensure efficient production and service delivery. These functions optimize resource utilization, streamline workflows, and maintain product or service standards. Supply Chain Management, in contrast, extends beyond internal operations by coordinating procurement, logistics, and distribution across multiple organizations to fulfill customer demand.
Core Functions of Supply Chain Management
Core functions of Supply Chain Management (SCM) include procurement, production planning, inventory management, logistics, and distribution, which collectively ensure the smooth flow of goods and information from suppliers to customers. Operations Management focuses on optimizing internal processes, such as manufacturing efficiency and quality control, while SCM extends beyond the organization to coordinate external partners and manage relationships across the entire supply network. Effective SCM integrates demand forecasting, supplier collaboration, and order fulfillment to enhance responsiveness and reduce overall costs.
Overlapping Areas and Interdependencies
Operations management and supply chain management share overlapping areas such as inventory control, demand forecasting, and production scheduling, where efficient coordination enhances overall business performance. Both disciplines rely on data-driven decision-making processes and technology integration like ERP systems to optimize resource allocation and streamline workflow. Interdependencies manifest in logistics planning, supplier relationship management, and quality assurance, where synchronization ensures timely product delivery and customer satisfaction.
Impact on Business Efficiency
Operations management optimizes internal processes such as production scheduling, quality control, and capacity planning to enhance business efficiency by reducing waste and improving productivity. Supply chain management coordinates external activities including sourcing, logistics, and supplier relationships to ensure timely delivery and cost-effective procurement, directly impacting profitability and customer satisfaction. Integrating operations and supply chain strategies boosts overall operational agility, minimizes disruptions, and drives competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Organization
Operations management focuses on optimizing internal processes such as production, quality control, and inventory management to enhance efficiency within an organization. Supply chain management extends beyond internal operations, coordinating the flow of goods, information, and resources across multiple partners from suppliers to customers. Choosing the right approach involves evaluating your company's strategic goals, customer demands, and integration needs to balance operational efficiency with seamless supply chain collaboration.
Future Trends in Operations and Supply Chain Management
Future trends in operations and supply chain management emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to enhance demand forecasting, inventory optimization, and real-time supply chain visibility. The adoption of blockchain technology is increasing for improved transparency, traceability, and security in supply networks. Sustainability initiatives and circular economy principles are transforming operational processes to reduce waste and carbon footprints while promoting ethical sourcing and resource efficiency.
Operations Management Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com