Quality Assurance ensures that products and services meet consistent standards, enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing errors throughout the production process. Implementing robust QA practices helps identify defects early, saves costs, and maintains regulatory compliance. Discover how effective Quality Assurance can transform Your operations by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
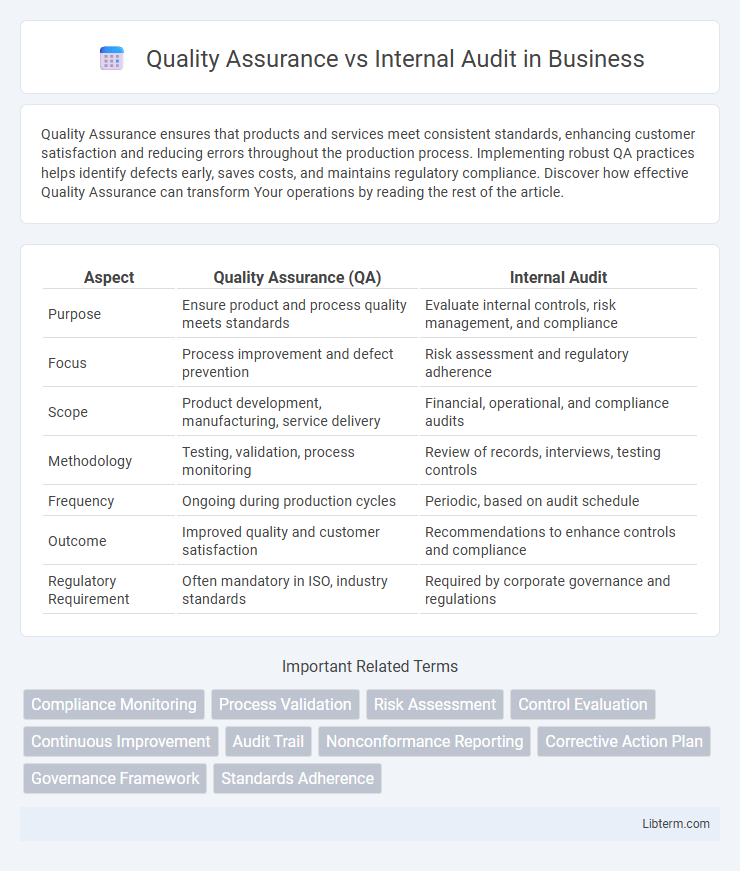
| Aspect | Quality Assurance (QA) | Internal Audit |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Ensure product and process quality meets standards | Evaluate internal controls, risk management, and compliance |
| Focus | Process improvement and defect prevention | Risk assessment and regulatory adherence |
| Scope | Product development, manufacturing, service delivery | Financial, operational, and compliance audits |
| Methodology | Testing, validation, process monitoring | Review of records, interviews, testing controls |
| Frequency | Ongoing during production cycles | Periodic, based on audit schedule |
| Outcome | Improved quality and customer satisfaction | Recommendations to enhance controls and compliance |
| Regulatory Requirement | Often mandatory in ISO, industry standards | Required by corporate governance and regulations |
Understanding Quality Assurance: Definition and Purpose
Quality Assurance (QA) is a systematic process designed to ensure products or services meet specified requirements and standards through planned and documented activities. It focuses on preventing defects by improving development processes and enhancing overall product quality. QA aims to provide confidence to stakeholders that quality objectives are consistently met throughout the production lifecycle.
Defining Internal Audit: Objectives and Scope
Internal Audit primarily focuses on evaluating an organization's governance, risk management, and internal controls to ensure compliance and operational efficiency. Its objectives include identifying weaknesses, recommending improvements, and providing assurance to stakeholders regarding the reliability of financial reporting and adherence to policies. The scope of Internal Audit encompasses financial, operational, IT systems, and compliance audits tailored to assess risk exposure and promote accountability within the organization.
Key Responsibilities of Quality Assurance Teams
Quality Assurance teams are primarily responsible for developing and implementing systematic processes that ensure products and services meet specified quality standards and regulatory requirements. They conduct regular inspections, testing, and process audits to identify defects and areas for improvement, thereby preventing non-conformities and enhancing customer satisfaction. By analyzing quality data and collaborating with cross-functional teams, QA professionals implement corrective actions and continuous improvement initiatives to maintain compliance and optimize operational efficiency.
Core Functions of Internal Audit Departments
Internal Audit departments primarily focus on evaluating and improving the effectiveness of risk management, control, and governance processes within an organization. They conduct systematic assessments of financial and operational activities to ensure compliance with policies, identify control weaknesses, and recommend corrective actions. Unlike Quality Assurance, which centers on product or service quality standards, Internal Audit's core function emphasizes organizational integrity and accountability through independent assurance and advisory services.
Differences in Approach: Preventive vs. Detective Controls
Quality Assurance emphasizes preventive controls by designing processes and standards aimed at avoiding defects during production, ensuring compliance and consistent quality from the outset. Internal Audit relies on detective controls by systematically reviewing and assessing completed processes and transactions to identify discrepancies, non-compliance, or areas for improvement. The distinct approaches highlight Quality Assurance's forward-looking process optimization contrasted with Internal Audit's retrospective evaluation and verification.
Skills and Competencies Required for QA and Internal Audit
Quality Assurance professionals require strong analytical skills, attention to detail, and expertise in process improvement methodologies such as Six Sigma or Lean to identify defects and ensure product or service quality. Internal Auditors need in-depth knowledge of risk assessment, compliance standards, financial auditing principles, and proficiency in data analysis tools to evaluate organizational controls and governance. Both roles demand excellent communication skills and ethical judgment to report findings effectively and recommend corrective actions.
Reporting Lines and Organizational Structure
Quality Assurance typically reports to upper management or the Quality Manager, ensuring unbiased oversight of product or service standards within operational units. Internal Audit functions independently, often reporting directly to the audit committee or board of directors to maintain objective assessment of risk management and internal controls. Organizational structures separate these roles to prevent conflicts of interest, with Quality Assurance embedded in process improvement teams and Internal Audit positioned as a second or third line of defense in corporate governance.
Impact on Business Performance and Risk Management
Quality Assurance enhances business performance by ensuring consistent product and service standards, reducing defects, and improving customer satisfaction, which leads to increased operational efficiency and profitability. Internal Audit strengthens risk management by providing independent evaluations of internal controls, identifying compliance gaps, and recommending corrective actions to mitigate financial, operational, and regulatory risks. Both functions are critical, with Quality Assurance driving process improvement and product reliability, while Internal Audit safeguards organizational integrity and supports strategic risk oversight.
Collaboration and Overlap between QA and Internal Audit
Quality Assurance (QA) and Internal Audit collaborate by aligning processes to enhance organizational compliance and performance metrics. Both functions share overlapping objectives in risk management, control evaluation, and continuous improvement, leveraging data analysis and process validation for operational excellence. Integrated efforts between QA and Internal Audit increase efficiency, reduce redundancies, and strengthen governance frameworks through coordinated assessments and reporting.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors to Consider
Choosing between Quality Assurance and Internal Audit depends on the organization's primary objective, with Quality Assurance focusing on process improvement and Internal Audit emphasizing compliance and risk management. Factors to consider include the scope of review, frequency of assessments, regulatory requirements, and desired outcomes such as enhancing product quality or ensuring adherence to internal policies. Evaluating resource availability, expertise, and integration with existing management systems further guides the selection of the most effective approach.
Quality Assurance Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com