KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) measure critical business goals, while metrics track general performance data. Understanding the difference helps you focus on what's most important to drive success. Explore this article to learn how to effectively use KPIs and metrics for your business growth.
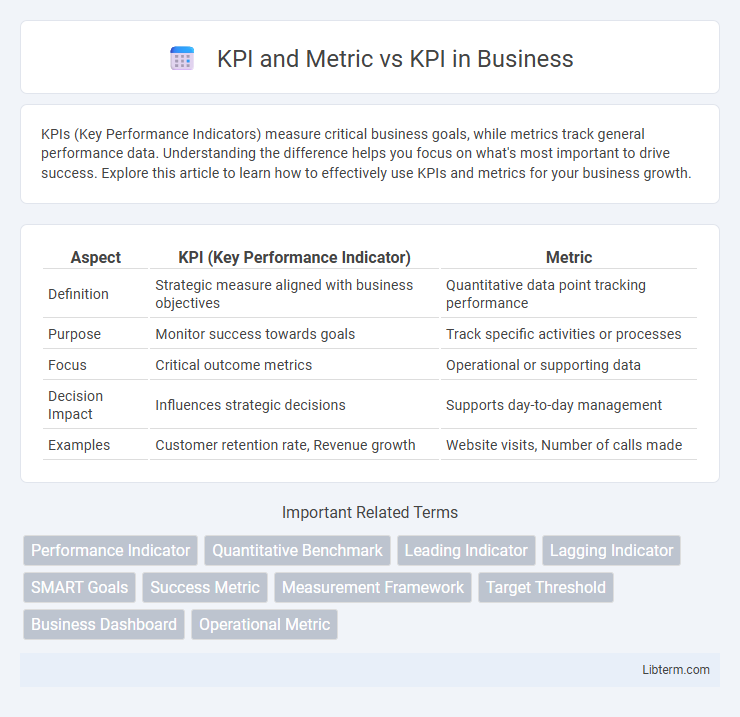
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | KPI (Key Performance Indicator) | Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategic measure aligned with business objectives | Quantitative data point tracking performance |
| Purpose | Monitor success towards goals | Track specific activities or processes |
| Focus | Critical outcome metrics | Operational or supporting data |
| Decision Impact | Influences strategic decisions | Supports day-to-day management |
| Examples | Customer retention rate, Revenue growth | Website visits, Number of calls made |
Understanding KPI: Definition and Importance
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable values that demonstrate how effectively an individual, team, or organization is achieving critical business objectives. Unlike general metrics that track any data point, KPIs are strategically aligned with specific goals and provide actionable insights to drive performance improvements. Understanding the definition and importance of KPIs enables organizations to focus efforts, make data-driven decisions, and track progress toward achieving targeted outcomes.
What is a Metric? Key Differences from KPI
A metric is a quantifiable measure used to track and assess the status of a specific business process, providing raw data that can indicate performance levels. Unlike a Key Performance Indicator (KPI), which is a strategic metric tied directly to business objectives and critical success factors, a metric may not necessarily reflect overall performance priorities. The key difference lies in the purpose and impact: KPIs focus on actionable insights to drive decision-making, whereas metrics serve as general performance data points without inherent strategic weight.
KPI vs Metric: Comparative Overview
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are strategic metrics directly aligned with business objectives, measuring critical success factors to evaluate progress. Metrics represent broader data points or measurements that track specific processes but may not directly impact overall goals. Understanding the distinction between KPIs and metrics is essential for effective performance management, as KPIs provide targeted insights while metrics offer detailed but less goal-oriented information.
The Relationship Between Metrics and KPIs
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are strategic metrics specifically tied to achieving business objectives, whereas metrics encompass all quantifiable measures within an organization. Every KPI is a metric, but not all metrics qualify as KPIs, as KPIs must directly reflect critical success factors. Understanding the relationship between metrics and KPIs helps businesses focus on meaningful data that drives performance and decision-making.
Why Choose KPIs Over Simple Metrics?
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) provide strategic value by directly aligning with business goals, unlike simple metrics that may track data without contextual relevance. KPIs focus on measuring progress toward critical objectives, enabling data-driven decision-making that drives growth and efficiency. Choosing KPIs over basic metrics ensures that performance measurement supports long-term success and prioritizes the most impactful actions.
Establishing Effective KPIs
Establishing effective KPIs requires differentiating between metrics and key performance indicators, where KPIs are strategic measures aligned with business goals while metrics track general performance data. Identifying KPIs involves selecting quantifiable indicators that directly impact organizational objectives, such as customer acquisition cost or revenue growth rate. Clear definition, regular monitoring, and actionable insights derived from KPIs drive focused decision-making and operational improvement.
Common Examples of Metrics and KPIs
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) measure strategic objectives, while metrics track everyday business activities. Common KPIs include Customer Lifetime Value (CLV), Net Promoter Score (NPS), and Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR), reflecting long-term goals, whereas metrics like website traffic, email open rates, and average handling time monitor operational efficiency. Differentiating KPIs from metrics helps organizations align performance measurement with strategic priorities and improve decision-making.
Setting Relevant KPIs for Business Success
Setting relevant KPIs is crucial for measuring business success and aligning team objectives with strategic goals. While metrics provide raw data and track performance, KPIs focus on critical indicators that directly impact core business outcomes. Identifying KPIs requires understanding specific business objectives, ensuring they are measurable, actionable, and time-bound to drive meaningful improvements and decision-making.
Pitfalls to Avoid: Metrics Misused as KPIs
Confusing metrics with Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) often leads to poor decision-making and misaligned business strategies. Metrics track data points like website visits or email open rates, while KPIs focus on critical outcomes such as customer acquisition cost or revenue growth, directly influencing strategic goals. Avoid selecting vanity metrics as KPIs by ensuring every KPI is actionable, measurable, and aligned with core business objectives to drive meaningful performance improvements.
Optimizing Performance: Leveraging KPIs and Metrics
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are strategic metrics directly tied to business objectives, enabling precise performance measurement and goal tracking. Metrics provide broader data points that support analysis but may not directly influence strategic decisions like KPIs do. Leveraging KPIs alongside complementary metrics optimizes performance by aligning operational activities with measurable targets, enhancing decision-making and driving continuous improvement.
KPI and Metric Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com