Bootstrapped companies rely on personal savings and reinvested profits to fund their growth without external investors, ensuring complete control over business decisions. This approach fosters financial discipline, encourages innovation, and minimizes risk exposure. Discover how bootstrapping can shape your startup's future by exploring the advantages and challenges detailed in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
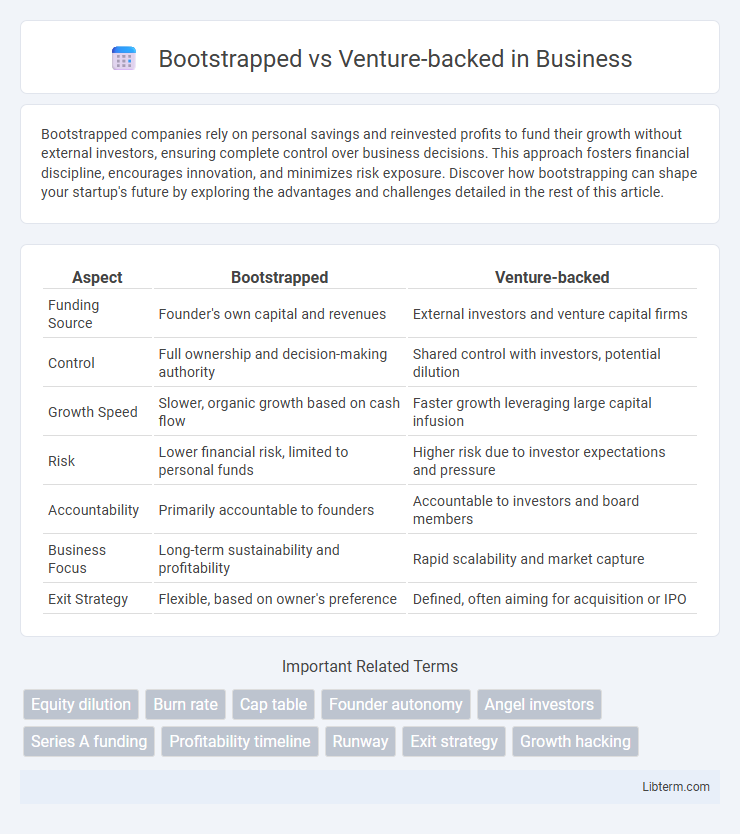
| Aspect | Bootstrapped | Venture-backed |
|---|---|---|
| Funding Source | Founder's own capital and revenues | External investors and venture capital firms |
| Control | Full ownership and decision-making authority | Shared control with investors, potential dilution |
| Growth Speed | Slower, organic growth based on cash flow | Faster growth leveraging large capital infusion |
| Risk | Lower financial risk, limited to personal funds | Higher risk due to investor expectations and pressure |
| Accountability | Primarily accountable to founders | Accountable to investors and board members |
| Business Focus | Long-term sustainability and profitability | Rapid scalability and market capture |
| Exit Strategy | Flexible, based on owner's preference | Defined, often aiming for acquisition or IPO |
Understanding Bootstrapped and Venture-backed Startups
Bootstrapped startups rely on personal savings and internal cash flow to grow, emphasizing financial independence and steady scalability without external influence. Venture-backed startups obtain funding from venture capitalists or angel investors, enabling rapid growth through significant capital infusion but often requiring equity dilution and strategic alignment with investor expectations. Understanding these differences helps entrepreneurs choose between control retention and accelerated expansion based on their business goals and risk tolerance.
Key Differences Between Bootstrapping and Venture Funding
Bootstrapped startups rely on personal savings and revenue to grow, maintaining full control and equity, while venture-backed companies raise external capital, often resulting in shared ownership and investor influence. Bootstrapping emphasizes sustainable growth and financial discipline without immediate pressure for rapid scaling, whereas venture funding enables fast expansion and access to resources but demands high growth targets and exit strategies. Key differences include source of funding, control over business decisions, growth pace, and financial risk tolerance.
Pros and Cons of Bootstrapping Your Business
Bootstrapping your business allows complete control over decision-making and maintains full ownership, reducing reliance on external investors and avoiding equity dilution. However, limited financial resources can constrain growth opportunities and increase personal financial risk, potentially slowing product development and market expansion. Bootstrapped companies often benefit from lean operations and disciplined budgeting but may struggle to scale as rapidly compared to venture-backed startups with access to substantial capital and resources.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Venture Capital
Venture capital provides substantial funding that accelerates growth and market expansion, enabling startups to scale quickly and access expert mentorship and strategic networks. However, it often requires relinquishing significant equity and control, leading to pressure for rapid returns and potential shifts in company vision. The high expectations and rigorous due diligence process can create stress and may limit the entrepreneur's decision-making freedom.
Financial Control and Ownership in Both Models
Bootstrapped companies maintain full financial control and ownership, relying solely on founder resources and generated revenue, which limits dilution but can restrict growth capital. Venture-backed startups trade partial ownership for significant external funding, leading to shared decision-making and potential loss of control but accelerated scaling opportunities. Founders must weigh the trade-off between preserving equity and accessing resources essential for rapid expansion.
Growth Trajectories: Scaling with Bootstrapping vs. VC
Bootstrapped companies often experience slower, steadier growth driven by organic revenue and careful reinvestment, preserving equity and maintaining control. Venture-backed startups typically pursue rapid scaling fueled by significant capital injections, enabling aggressive market expansion and accelerated product development. The choice between bootstrapping and VC influences growth trajectories, balancing sustainable scaling with faster market penetration.
Risk Management: Bootstrapped vs Venture-Backed Startups
Bootstrapped startups assume higher personal financial risk as founders use their own savings and revenues to grow, which limits external debt and investor pressures. Venture-backed startups transfer financial risk to investors, allowing for aggressive scaling but increasing dependency on meeting investor expectations and milestones. Risk management for bootstrapped firms centers on sustainable cash flow and lean operations, while venture-backed startups emphasize strategic growth metrics and investor relations to mitigate valuation and dilution risks.
Impact on Company Culture and Vision
Bootstrapped companies often maintain a culture of independence and resourcefulness, prioritizing long-term vision aligned with founder values due to limited external influence. Venture-backed startups experience accelerated growth pressures driven by investor expectations, shaping a culture that emphasizes scalability, rapid innovation, and frequent performance metrics. The contrasting impact on company culture and vision arises from differing priorities: bootstrapped firms foster sustainability and control, while venture-backed ones focus on market disruption and aggressive expansion.
Real-World Examples: Successful Bootstrapped and VC Startups
Mailchimp exemplifies a successful bootstrapped startup, achieving over $700 million in annual revenue without external funding, leveraging organic growth and customer retention. In contrast, Uber, a venture-backed company, rapidly scaled globally by securing over $25 billion in venture capital, enabling extensive market expansion and technological innovation. Both models demonstrate that strategic capital deployment aligns with growth objectives and market dynamics in the startup ecosystem.
Choosing the Right Funding Path for Your Startup
Bootstrapped startups maintain full control by using personal savings or revenue to fund growth, ensuring autonomy and sustainable scaling without external pressure. Venture-backed ventures access significant capital from investors, enabling rapid expansion and resource acquisition but often at the cost of equity dilution and external guidance. Selecting the right funding path hinges on your startup's growth objectives, risk tolerance, and desire for control versus accelerated development.
Bootstrapped Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com