Dynamic efficiency focuses on the optimal allocation of resources over time to maximize long-term economic growth and innovation. It balances current consumption with investment in research, development, and technology improvements that drive future productivity. Explore the rest of the article to understand how dynamic efficiency can impact Your economic strategies and decisions.
Table of Comparison
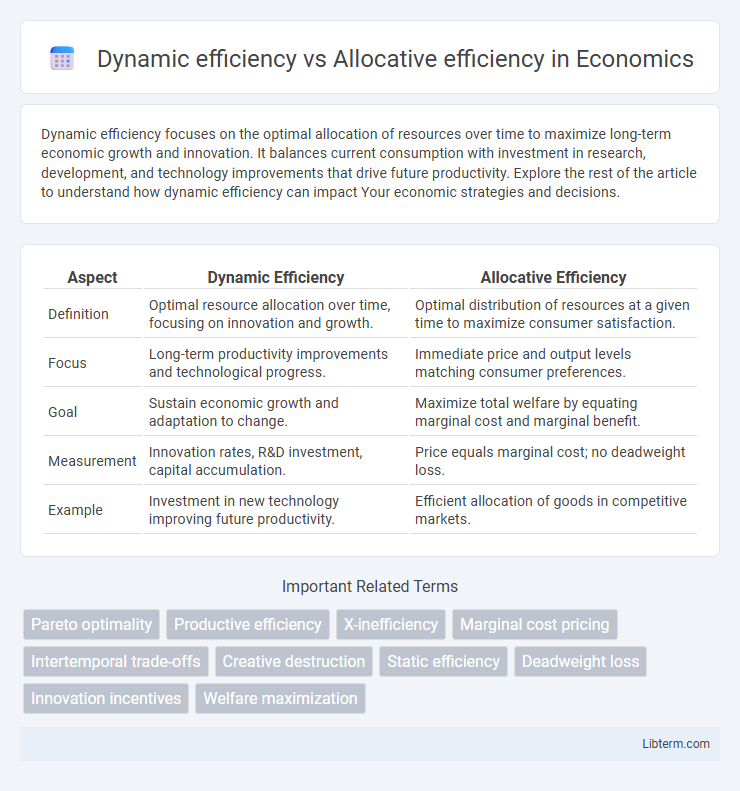
| Aspect | Dynamic Efficiency | Allocative Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Optimal resource allocation over time, focusing on innovation and growth. | Optimal distribution of resources at a given time to maximize consumer satisfaction. |
| Focus | Long-term productivity improvements and technological progress. | Immediate price and output levels matching consumer preferences. |
| Goal | Sustain economic growth and adaptation to change. | Maximize total welfare by equating marginal cost and marginal benefit. |
| Measurement | Innovation rates, R&D investment, capital accumulation. | Price equals marginal cost; no deadweight loss. |
| Example | Investment in new technology improving future productivity. | Efficient allocation of goods in competitive markets. |
Introduction to Economic Efficiencies
Dynamic efficiency measures an economy's ability to improve production processes and innovate over time, driving long-term growth and technological progress. Allocative efficiency occurs when resources are distributed in a way that maximizes consumer satisfaction and reflects consumer preferences accurately. Both types of efficiency are crucial in economic theory, with dynamic efficiency emphasizing innovation and change, while allocative efficiency prioritizes optimal resource allocation for current welfare.
Defining Dynamic Efficiency
Dynamic efficiency refers to the optimal allocation of resources over time, emphasizing innovation, technological progress, and long-term growth. It contrasts with allocative efficiency, which focuses on the optimal distribution of resources at a specific point in time to maximize current welfare. Achieving dynamic efficiency often involves investments in research and development, improving productivity, and adapting to changing market conditions.
Understanding Allocative Efficiency
Allocative efficiency occurs when resources are distributed in a way that maximizes consumer satisfaction and ensures that goods and services reflect consumer preferences at equilibrium prices. It requires that the marginal benefit of a product equals its marginal cost, leading to an optimal allocation where no individual can be made better off without making someone else worse off. This concept contrasts with dynamic efficiency, which emphasizes innovation and improvements over time rather than the immediate optimal distribution of resources.
Key Differences Between Dynamic and Allocative Efficiency
Dynamic efficiency emphasizes the optimal allocation of resources over time, focusing on innovation, technological progress, and long-term growth potential. Allocative efficiency occurs when resources are distributed to maximize immediate consumer satisfaction and production value, ensuring goods and services match consumer preferences at given prices. Key differences lie in their temporal focus--dynamic efficiency prioritizes future gains through investment and innovation, while allocative efficiency optimizes current resource use for maximum output and utility.
Real-World Examples of Dynamic Efficiency
Dynamic efficiency refers to an economy's ability to improve products and processes over time through innovation, investment in research and development, and technological progress, contrasting with allocative efficiency which focuses on optimal resource distribution at a given moment. Tesla exemplifies dynamic efficiency by continuously advancing electric vehicle technology and battery performance, significantly altering the automotive industry landscape. Pharmaceutical companies like Pfizer also demonstrate dynamic efficiency by investing heavily in R&D to develop new drugs, improving health outcomes and market competitiveness over time.
Real-World Applications of Allocative Efficiency
Allocative efficiency occurs when resources are distributed to produce the mix of goods and services most desired by society, maximizing overall welfare. Real-world applications include public goods provision, where governments allocate resources to healthcare and education to meet societal needs unmet by markets. Market failures, such as externalities and monopolies, often justify interventions aiming to achieve allocative efficiency by correcting resource misallocation and promoting equitable outcomes.
Factors Influencing Dynamic Efficiency
Dynamic efficiency is influenced by factors such as technological innovation, investment in research and development, and the adaptive capacity of firms to changing market conditions. The ability to reallocate resources over time, including human capital and capital assets, enhances long-term productivity growth and innovation potential. Market structures that support competition and protect intellectual property rights play a critical role in fostering dynamic efficiency.
Determinants of Allocative Efficiency
Allocative efficiency is primarily determined by the accurate price signals reflecting consumers' preferences and the optimal distribution of resources to produce goods and services that maximize societal welfare. Factors influencing allocative efficiency include market structure, consumer demand elasticity, resource mobility, and government interventions such as taxes or subsidies. In contrast, dynamic efficiency emphasizes innovation and technological progress over time, which may not directly influence immediate resource allocation.
Importance of Balancing Both Efficiencies
Balancing dynamic efficiency and allocative efficiency is crucial for sustainable economic growth and optimal resource utilization. Dynamic efficiency drives innovation and technological progress, enhancing long-term productivity, while allocative efficiency ensures that resources are distributed to produce the goods and services most valued by society. Achieving a balance between these efficiencies maximizes both short-term consumer satisfaction and long-term economic development.
Conclusion: Impacts on Economic Growth and Welfare
Dynamic efficiency drives long-term economic growth through innovation and investment in new technologies, enhancing productivity over time. Allocative efficiency ensures resources are distributed to their most valued uses, maximizing immediate welfare and consumer satisfaction. Balancing both efficiencies is essential for sustainable economic development, as dynamic efficiency fuels future growth while allocative efficiency optimizes current resource utilization.
Dynamic efficiency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com