Free trade promotes the unrestricted exchange of goods and services across borders, enhancing global economic growth and consumer choice. Lower tariffs and minimal trade barriers allow businesses to access larger markets, increase efficiency, and reduce costs. Discover how free trade impacts your economy and what it means for your opportunities in the global marketplace by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
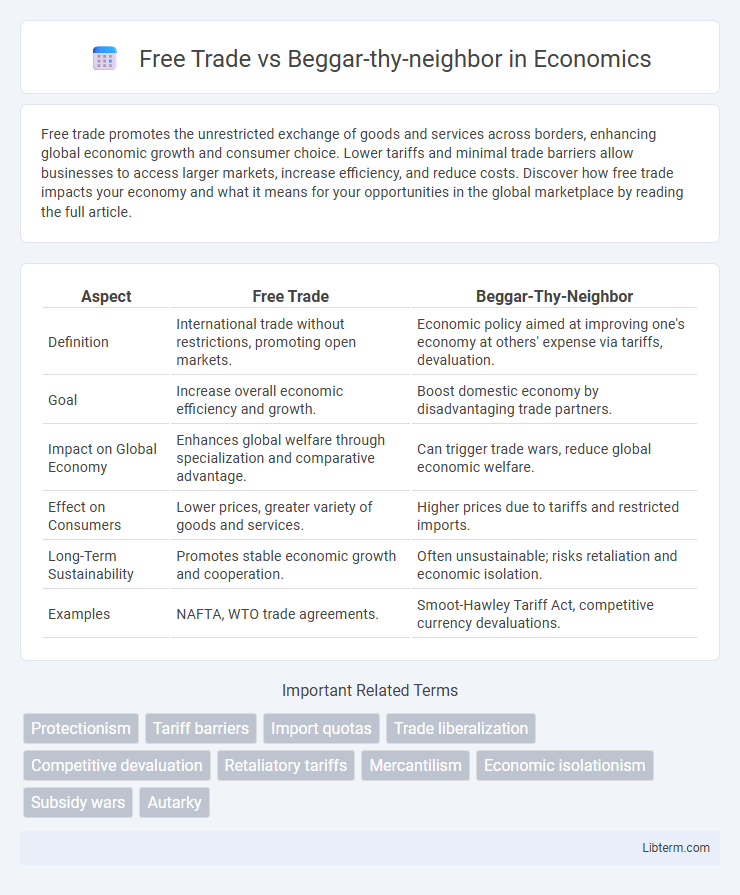
| Aspect | Free Trade | Beggar-Thy-Neighbor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | International trade without restrictions, promoting open markets. | Economic policy aimed at improving one's economy at others' expense via tariffs, devaluation. |
| Goal | Increase overall economic efficiency and growth. | Boost domestic economy by disadvantaging trade partners. |
| Impact on Global Economy | Enhances global welfare through specialization and comparative advantage. | Can trigger trade wars, reduce global economic welfare. |
| Effect on Consumers | Lower prices, greater variety of goods and services. | Higher prices due to tariffs and restricted imports. |
| Long-Term Sustainability | Promotes stable economic growth and cooperation. | Often unsustainable; risks retaliation and economic isolation. |
| Examples | NAFTA, WTO trade agreements. | Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, competitive currency devaluations. |
Understanding Free Trade: Definition and Principles
Free trade is an economic policy that allows goods and services to move across international borders with minimal government restrictions, promoting efficiency and consumer choice. It operates on principles like comparative advantage, where countries specialize in producing goods they can make most efficiently, leading to increased global wealth. Unlike beggar-thy-neighbor policies that impose tariffs or quotas to protect domestic industries at the expense of trade partners, free trade encourages cooperation and mutual economic growth.
The Concept of Beggar-thy-neighbor Policies
Beggar-thy-neighbor policies involve a country implementing economic measures such as tariffs, quotas, or currency devaluation to improve its own economic position at the expense of other nations, often leading to retaliatory actions and trade wars. These protectionist tactics undermine global free trade by disrupting market efficiency and reducing overall economic welfare through distorted competitive advantages. In contrast, free trade promotes mutual economic growth by removing barriers and enabling countries to specialize based on comparative advantage, fostering cooperative international economic relations.
Historical Background: Free Trade and Protectionism
Free trade dates back to the 18th century with Adam Smith's advocacy for open markets to enhance economic efficiency, contrasting sharply with protectionist policies seen in mercantilism aimed at maximizing national wealth through tariffs and quotas. The Great Depression of the 1930s intensified beggar-thy-neighbor policies, where countries imposed high trade barriers to protect domestic industries, deepening global economic decline. Post-World War II, institutions like the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) emerged to promote free trade and reduce protectionist measures, fostering international economic cooperation.
Economic Impacts of Free Trade Agreements
Free trade agreements (FTAs) stimulate economic growth by reducing tariffs and trade barriers, enabling countries to specialize based on comparative advantage and boosting market efficiency. Conversely, beggar-thy-neighbor policies, such as competitive devaluations or protectionist measures, can provoke retaliatory actions that disrupt global supply chains and hinder international trade flows. Empirical studies show that FTAs enhance employment, increase consumer welfare through lower prices, and foster innovation by expanding access to diverse inputs and technologies.
Examples of Beggar-thy-neighbor Strategies in History
Beggar-thy-neighbor strategies include protectionist tariffs, competitive devaluations, and export subsidies aimed at improving domestic economic conditions at the expense of trading partners. Notable historical examples include the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act of 1930, which exacerbated the Great Depression by triggering retaliatory tariffs worldwide, and the competitive currency devaluations during the Great Depression era that worsened global economic instability. Post-World War II, the Plaza Accord of 1985 illustrates coordinated efforts to correct imbalances, contrasting prior unilateral beggar-thy-neighbor policies that heightened international tensions.
Free Trade vs Protectionism: Core Differences
Free trade promotes the unrestricted exchange of goods and services across borders, enhancing global efficiency and consumer choice by leveraging comparative advantages. Protectionism enforces barriers like tariffs and quotas to shield domestic industries from foreign competition, often leading to trade tensions and reduced economic welfare. The core difference lies in free trade's emphasis on mutual gains and market openness, while protectionism prioritizes national interests and economic self-sufficiency at the potential cost of global cooperation.
Social and Political Consequences of Trade Policies
Free trade policies promote global cooperation, economic growth, and improved living standards by removing barriers to international markets, fostering social stability and political alliances. In contrast, beggar-thy-neighbor policies, such as protectionism and competitive devaluations, often lead to retaliatory measures, increased unemployment, and social unrest by isolating domestic economies. These adversarial trade strategies undermine diplomatic relations and exacerbate geopolitical tensions, threatening both national security and global economic stability.
Modern Case Studies: Global Trade Disputes
Modern global trade disputes highlight the contrasting impacts of free trade policies and beggar-thy-neighbor strategies, with cases such as the US-China trade war demonstrating the consequences of tariffs and protectionism on supply chains and global market stability. The World Trade Organization's enforcement mechanisms and dispute resolution processes reveal the tensions between promoting open markets and protecting domestic industries through retaliatory tariffs and subsidies. These conflicts underscore the economic ripple effects on international relations, corporate investments, and consumer prices in an increasingly interconnected global economy.
Evaluating the Long-term Effects on Developing Economies
Free trade promotes sustained economic growth in developing economies by enhancing market access, encouraging foreign direct investment, and fostering innovation through competitive pressures. In contrast, beggar-thy-neighbor policies, such as tariffs and export restrictions, often lead to retaliatory measures, market distortions, and reduced global cooperation, stunting growth prospects. Long-term impacts of free trade typically include diversified economies and poverty reduction, while protectionist approaches risk isolation and diminished economic resilience.
The Future of Global Trade: Cooperation or Competition?
Free trade promotes economic growth by reducing tariffs and fostering cooperation among nations, enhancing global market efficiency and innovation. Beggar-thy-neighbor policies, by contrast, prioritize national gain through protectionism, risking retaliatory measures and trade wars that harm global stability. The future of global trade hinges on the balance between collaborative agreements and competitive nationalism, with institutions like the World Trade Organization playing a crucial role in mediating disputes and encouraging fair practices.
Free Trade Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com