Path dependence describes how historical decisions and events shape current and future outcomes by limiting available choices and reinforcing established patterns. This concept is crucial in economics, technology, and social sciences for understanding why certain processes persist despite alternative options. Explore the rest of the article to discover how path dependence influences your decisions and shapes complex systems.
Table of Comparison
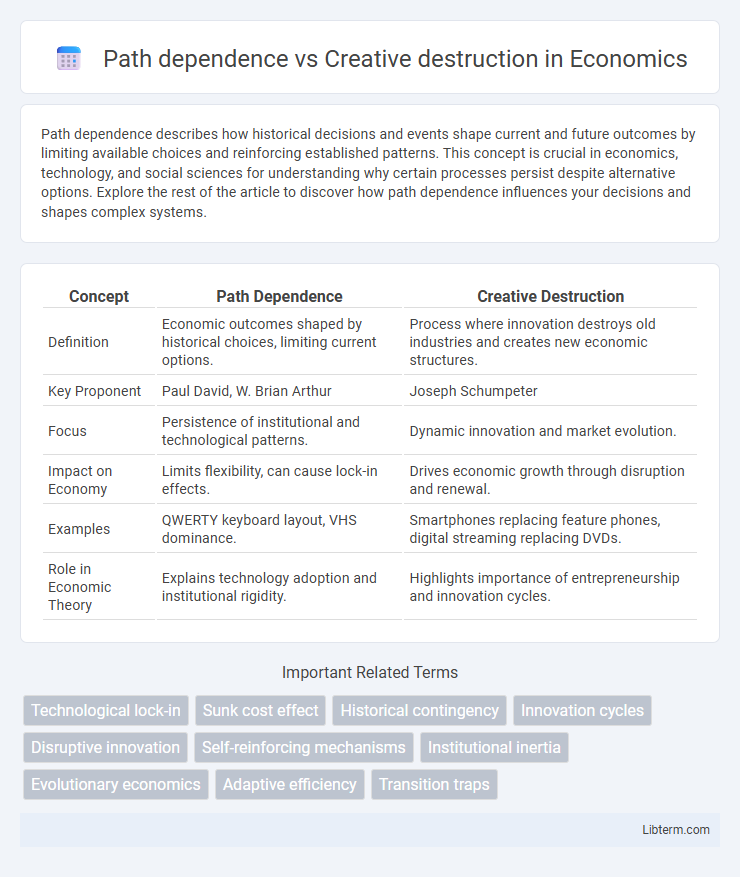
| Concept | Path Dependence | Creative Destruction |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Economic outcomes shaped by historical choices, limiting current options. | Process where innovation destroys old industries and creates new economic structures. |
| Key Proponent | Paul David, W. Brian Arthur | Joseph Schumpeter |
| Focus | Persistence of institutional and technological patterns. | Dynamic innovation and market evolution. |
| Impact on Economy | Limits flexibility, can cause lock-in effects. | Drives economic growth through disruption and renewal. |
| Examples | QWERTY keyboard layout, VHS dominance. | Smartphones replacing feature phones, digital streaming replacing DVDs. |
| Role in Economic Theory | Explains technology adoption and institutional rigidity. | Highlights importance of entrepreneurship and innovation cycles. |
Introduction to Path Dependence and Creative Destruction
Path dependence describes how initial decisions or historical events set a trajectory that shapes future developments, often creating lock-in effects that limit innovation and adaptability. Creative destruction, a concept introduced by economist Joseph Schumpeter, refers to the process where new innovations disrupt and replace outdated technologies, industries, or economic structures, driving economic growth and transformation. Understanding the interplay between path dependence and creative destruction is crucial for analyzing how economies evolve and how innovation overcomes entrenched systems.
Defining Path Dependence: Origins and Implications
Path dependence refers to the concept that historical choices and established processes heavily influence the trajectory of technological, economic, or institutional developments, often limiting future options due to past commitments. Originating from studies in economics and social sciences, path dependence explains why certain inefficient or suboptimal technologies persist despite the availability of better alternatives. Implications include challenges for innovation and policy-making, as entrenched systems can resist transformative change, contrasting sharply with the disruptive, cyclical renewal emphasized in the theory of creative destruction.
Understanding Creative Destruction: Schumpeter’s Legacy
Creative destruction, a concept introduced by Joseph Schumpeter, describes the relentless process where innovation dismantles outdated economic structures, driving long-term growth and industrial transformation. This process contrasts with path dependence, which emphasizes the constraints imposed by historical decisions on future options, potentially limiting innovation and economic evolution. Schumpeter's legacy lies in highlighting how entrepreneurial innovation disrupts existing market equilibria, fostering dynamic competition and technological progress.
Historical Examples of Path Dependence in Industry
The automotive industry exemplifies path dependence through its prolonged reliance on internal combustion engines, stemming from early 20th-century investments and infrastructure favoring gasoline vehicles. The QWERTY keyboard layout illustrates path dependence as it persists despite more efficient alternatives, due to entrenched user familiarity and manufacturing standards. Historical railway gauge standards in the UK demonstrate path dependence by constraining interoperability, influencing network design and limiting technological shifts long after initial adoption.
Case Studies Illustrating Creative Destruction
Case studies illustrating creative destruction include the rise of Netflix and the decline of Blockbuster, exemplifying how digital streaming disrupted traditional video rentals. The transition from horse-drawn carriages to automobiles demonstrates technological innovation dismantling established industries due to path dependence on outdated transportation methods. Similarly, the emergence of smartphones decimated standalone GPS and camera companies, showcasing creative destruction by integrating multiple technologies into a single device.
Factors Driving Path Dependence in Organizations
Factors driving path dependence in organizations include historical decisions, established routines, and accumulated capabilities that create self-reinforcing mechanisms resistant to change. Organizational inertia, lock-in effects from previous investments, and cognitive biases such as confirmation bias further entrench existing practices. These elements collectively restrict adaptive flexibility, contrasting with the disruptive innovation dynamics seen in creative destruction.
Mechanisms and Triggers of Creative Destruction
Creative destruction operates through mechanisms such as innovation, technological breakthroughs, and market competition, which dismantle outdated industries and enable new economic structures to emerge. Triggers include disruptive inventions, regulatory changes, shifts in consumer preferences, and entrepreneurial ventures that challenge incumbent firms and obsolete practices. These dynamic forces contrast with path dependence, where historical decisions and established routines constrain change and maintain the status quo.
Economic and Social Impacts: Comparing Both Concepts
Path dependence emphasizes the economic and social impact of historical choices that constrain future innovation, leading to market lock-ins, reduced competition, and social inequalities. Creative destruction drives economic growth and social transformation by dismantling outdated industries, fostering technological advances, and promoting dynamic labor market shifts that can cause short-term displacement but long-term prosperity. Both concepts highlight different mechanisms of economic evolution, with path dependence underscoring persistence and inertia, while creative destruction emphasizes continuous renewal and disruption.
Strategies for Navigating Path Dependence and Embracing Creative Destruction
Strategies for navigating path dependence involve identifying entrenched routines and leveraging incremental innovation to break free from historical constraints. Embracing creative destruction requires fostering a culture of experimentation and rapid adaptation, encouraging disruptive technologies and business models that challenge existing paradigms. Organizations that balance path-dependent stability with creative destruction's transformative potential can sustain competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
Conclusion: Balancing Stability and Innovation
Path dependence emphasizes the importance of historical decisions in shaping current technological landscapes, ensuring stability and incremental improvement. Creative destruction drives radical innovation by replacing outdated systems with novel solutions, fostering dynamic economic growth. Balancing these forces enables organizations to maintain core competencies while embracing transformative change for long-term success.
Path dependence Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com