Effective labor retention strategies focus on fostering employee satisfaction and creating a positive workplace culture that encourages loyalty and reduces turnover. Investing in professional development, recognizing achievements, and offering competitive benefits can significantly enhance your ability to keep valuable talent. Explore the rest of the article to discover proven techniques that strengthen your workforce and boost productivity.
Table of Comparison
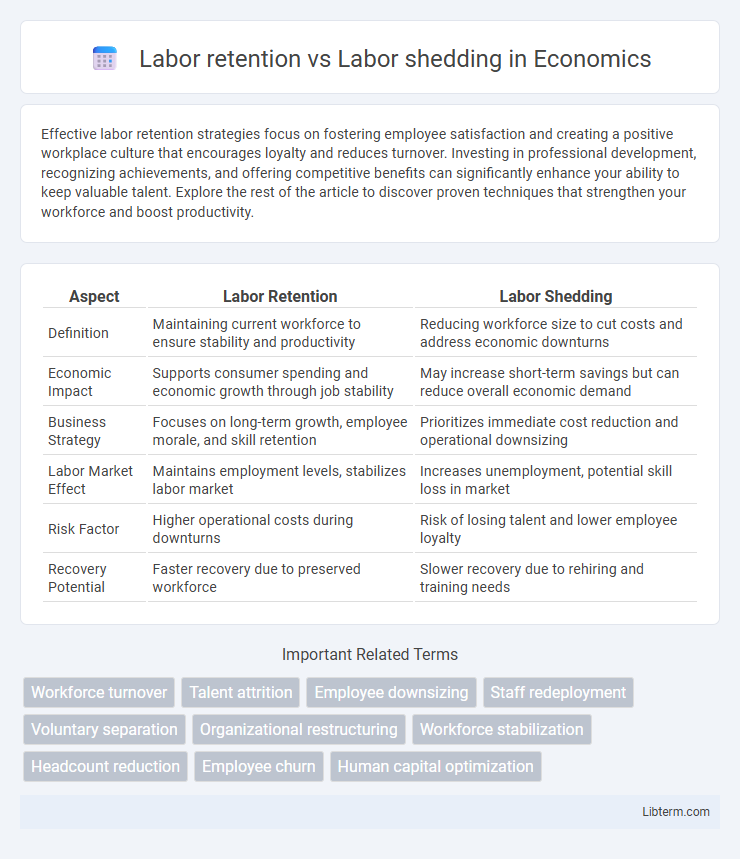
| Aspect | Labor Retention | Labor Shedding |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Maintaining current workforce to ensure stability and productivity | Reducing workforce size to cut costs and address economic downturns |
| Economic Impact | Supports consumer spending and economic growth through job stability | May increase short-term savings but can reduce overall economic demand |
| Business Strategy | Focuses on long-term growth, employee morale, and skill retention | Prioritizes immediate cost reduction and operational downsizing |
| Labor Market Effect | Maintains employment levels, stabilizes labor market | Increases unemployment, potential skill loss in market |
| Risk Factor | Higher operational costs during downturns | Risk of losing talent and lower employee loyalty |
| Recovery Potential | Faster recovery due to preserved workforce | Slower recovery due to rehiring and training needs |
Understanding Labor Retention and Labor Shedding
Labor retention involves strategies and practices aimed at keeping skilled employees engaged and committed to an organization to reduce turnover and maintain productivity. Labor shedding refers to the deliberate reduction of workforce through layoffs, attrition, or other means to cut costs and adapt to changing business conditions. Understanding these concepts is crucial for balancing operational efficiency with employee well-being and organizational stability.
Key Factors Influencing Employee Retention
Employee retention hinges on key factors such as competitive compensation, positive workplace culture, and opportunities for professional growth, which collectively enhance job satisfaction and loyalty. Effective communication and recognition programs strengthen employee engagement and reduce turnover rates. In contrast, labor shedding often results from economic pressures or organizational restructuring, highlighting the strategic importance of maintaining talent to sustain productivity and corporate stability.
Causes and Consequences of Labor Shedding
Labor shedding, often triggered by economic downturns, technological automation, or organizational restructuring, leads to significant workforce reductions aimed at cost-cutting and improving efficiency. Causes include reduced demand, financial instability, or shifts in business strategy, which result in job losses and decreased employee morale. Consequences involve increased unemployment rates, loss of institutional knowledge, reduced consumer spending, and potential declines in company productivity and brand reputation.
Impact on Organizational Productivity
Labor retention enhances organizational productivity by maintaining institutional knowledge, fostering employee engagement, and reducing turnover costs, thereby ensuring consistent operational performance. Labor shedding, while potentially lowering immediate labor expenses, often disrupts workflow continuity, diminishes morale, and leads to knowledge gaps that can degrade overall productivity. Balancing workforce stability with strategic downsizing is critical for sustaining long-term organizational efficiency and competitive advantage.
Financial Implications for Businesses
Labor retention helps businesses avoid significant costs associated with hiring and training new employees, reducing turnover-related expenses such as recruitment fees averaging 20% of an employee's annual salary. Labor shedding may provide short-term payroll relief but often leads to decreased productivity, increased workload on remaining staff, and potential reputational damage impacting revenue. Firms that invest in labor retention strategies typically experience improved financial stability through sustained employee engagement and reduced operational disruptions.
Employee Morale and Workplace Culture
Labor retention strategies boost employee morale by fostering job security and professional growth, which enhances workplace culture through increased engagement and collaboration. In contrast, labor shedding often leads to decreased morale, creating uncertainty and fear that can erode trust and reduce overall productivity. Organizations prioritizing retention cultivate a positive environment that supports long-term success and employee satisfaction.
Strategies to Enhance Labor Retention
Effective strategies to enhance labor retention include implementing competitive compensation packages, fostering a positive work environment, and providing professional development opportunities. Employee engagement initiatives and clear career progression paths significantly reduce turnover by increasing job satisfaction and loyalty. Utilizing data-driven insights to address workforce needs enables organizations to tailor retention efforts and improve overall employee retention rates.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Labor retention emphasizes compliance with employment laws and ethical standards by maintaining fair wages, safe working conditions, and dispute resolution mechanisms to protect workers' rights. Labor shedding involves legal risks such as wrongful termination claims and potential violations of labor contracts, requiring careful adherence to regulations like the Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification (WARN) Act. Ethical considerations in both practices revolve around transparency, respect for employee dignity, and long-term organizational reputation management.
Case Studies: Successes and Failures
Case studies reveal labor retention strategies often lead to higher employee morale and long-term productivity gains, as seen in companies like Google and Toyota, which emphasize skill development and job security. Conversely, labor shedding during economic downturns, exemplified by firms such as General Motors during the 2008 crisis, can result in short-term financial relief but may cause loss of institutional knowledge and reduced innovation capacity. Analyzing these outcomes highlights the critical balance between workforce stability and flexibility in maintaining competitive advantage.
Future Trends in Workforce Management
Labor retention strategies emphasize enhancing employee engagement, skill development, and workplace flexibility to meet evolving workforce expectations. In contrast, labor shedding relies on automation and outsourcing to reduce labor costs and increase operational efficiency. Future trends in workforce management are shifting toward hybrid models combining retention-focused talent nurturing with strategic labor shedding powered by artificial intelligence and data analytics.
Labor retention Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com